Abstract
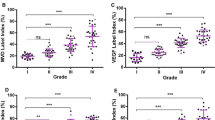
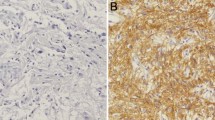
The purpose of this study is to determine whether the expressions of MMP-7 and MMP-14 are associated with the ERK 1/2 signaling pathway in human brain gliomas of different pathological grades. Immunohistochemistry and western blot methods were used to determine the expressions of MMP-7, MMP-14 and the phosphorylation status of ERK1/2 in 73 cases of human brain glioma specimens and two cases of normal brain tissues. Results indicated that the protein expression levels of MMP-7, MMP-14 and ERK1/2 phosphorylation level were all elevated with the increasing pathological grades in brain glioma tissues, and correlation assay indicated that the level of ERK1/2 phosphorylation was positively correlated with protein expression levels of MMP-7 and MMP-14 in gliomas of different pathological grades respectively. Moreover, the impact of ERK1/2 inhibitor U0126 on the expressions of MMP-7 and MMP-14 was examined in human U87 glioma cells by western blot analysis. The expressions of MMP-7 and MMP-14 were significantly decreased in human U87 glioma cells after treatment with ERK1/2 inhibitor U0126. The above results suggest that the expressions of MMP-7 and MMP-14 may be associated with activation of ERK1/2 signaling pathway in human brain gliomas of different pathological grades.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rao JS. Molecular mechanisms of glioma invasiveness: the role of proteases. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:489–501.
Stamenkovic I. Matrix metalloproteinases in tumor invasion and metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 2000;10:415–33.
VanMeter TE, et al. The role of matrix metalloproteinase genes in glioma invasion: co-dependent and interactive proteolysis. J Neurooncol. 2001;53:213–35.
Ma Z, Qin H, Benveniste EN. Transcriptional suppression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene expression by IFN-gamma and IFN-beta: critical role of STAT-1alpha. J Immunol. 2001;167:5150–9.
Curran S, Murray GI. Matrix metalloproteinases in tumour invasion and metastasis. J Pathol. 1999;189:300–8.
Stetler-Stevenson WG, Hewitt R, Corcoran M. Matrixmetalloproteinases and tumor invasion: from correlation and causality to the clinic. Semin Cancer Biol. 1996;7:147–54.
Misugi F, et al. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase in uterine endometrial carcinoma and a correlation between expression of matrix metalloproteinase-7 and prognosis. Int J Mol Med. 2005;16:541–6.
Ichikawa Y, et al. Function of MMP-7 in colorectal cancer. Nippon Rinsho. 2003;61:209–14.
Lee KH, et al. Relationship between E-cadherin, matrix metalloproteinase-7 gene expression and clinicopathological features in gastric carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2006;16:823–30.
Liu D, et al. Overexpression of matrix metalloproteinase-7 (MMP-7) correlates with tumor proliferation, and a poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2007;58:384–91.
Ii M, Yamamoto H, Adachi Y, Maruyama Y, Shinomura Y. Role of matrix metalloproteinase-7 (matrilysin) in human cancer invasion, apoptosis, growth, and angiogenesis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2006;231:20–7.
Maquoi E, et al. Membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase-associated degradation of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2 in human tumor cell lines. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:11368–78.
Shim KN, Jung SA, Joo YH, Yoo K. Clinical significance of tissue levels of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol. 2007;42:120–8.
Ellenrieder V, et al. Role of MT-MMPs and MMP-2 in pancreatic cancer progression. Int J Cancer. 2000;85:14–20.
Adley BP, Gleason KJ, Yang XJ, Stack MS. Expression of membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-14) in epithelial ovarian cancer: high level expression in clear cell carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. 2009;112:319–24.
de Vicente JC, Leguerica-Fernández P, Santamaría J, Fresno MF. Expression of MMP-7 and MT1-MMP in oral squamous cell carcinoma as predictive indicator for tumor invasion and prognosis. J Oral Pathol Med. 2007;36:415–24.
Reddy KB, Nabha SM, Atanaskova N. Role of MAP kinase in tumor progression and invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003;22:395–403.
Kunapuli P, Kasyapa CS, Hawthorn L, Cowell JK. LGI1, a putative tumor metastasis suppressor gene, controls in vitro invasiveness and expression of matrix metalloproteinases in glioma cells through the ERK1/2 pathway. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:23151–7.
Kim JH, Choi C, Benveniste EN, Kwon D. TRAIL induces MMP-9 expression via ERK activation in human astrocytoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;377:195–9.
Rome C, Arsaut J, Taris C, Couillaud F, Loiseau H. MMP-7 (Matrilysin) expression in human brain tumors. Mol Carcinog. 2007;46:446–52.
Nakada M, et al. Expression and tissue localization of membrane-type 1, 2, and 3 matrix metalloproteinases in human astrocytic tumors. Am J Pathol. 1999;154:417–28.
Guo P, et al. Up-regulation of angiopoietin-2, matrix metalloprotease-2, membrane Type 1 metalloprotease, and laminin 5 gamma 2 correlates with the invasiveness of human glioma. Am J Pathol. 2005;166:877–90.
Inamoto T, et al. Invasive ability of human renal cell carcinoma cell line Caki-2 is accelerated by gamma-aminobutyric acid, via sustained activation of ERK1/2 inducible matrix metalloproteinases. Cancer Invest. 2007;25:574–83.
Jelinek T, Dent P, Sturgill TW, Weber MJ. Ras-induced activation of Raf-1 is dependent on tyrosine phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1996;16:1027–34.
Kaomongkolgit R, Cheeosunthorn P, Pavasant P, Sanchavanakit N. Iron increase MMP-9 expression through activation of AP-1 via ERK/Akt pathway in human head and neck squamous carcinoma cells. Oral Oncol. 2008;44:587–94.
Lee SJ, et al. Activation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 by TNF-α in human urinary bladder cancer HT1376 cells: The role of MAP kinase signaling pathways. Oncol Rep. 2008;19:1007–13.
Tan CT, et al. CXCL12/CXCR4 promotes laryngeal and hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma metastasis through MMP-13-dependent invasion via the ERK1/2/AP-1 pathway. Carcinogenesis. 2008;29:1519–27.
Lopez-Gines C, et al. The activation of ERK1/2 MAP kinases in glioblastoma pathobiology and its relationship with EGFR amplification. Neuropathology. 2008;28:507–15.
Bhaskara VK, Panigrahi M, Challa S, Babu PP. Comparative status of activated ERK1/2 and PARP cleavage in human gliomas. Neuropathology. 2005;25:48–53.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China, under contract numbers 30800451, 30872656, 30700861, 30670723, and 30973079; Scientific and Technological Research Projects in Colleges and Universities of Liaoning Province, number 2008850; the special fund for Scientific Research of Doctor-degree Subjects in Colleges and Universities, number 20092104110015; and Scientific and Technological Planning Projects of Shenyang, numbers 1072033-1-00 and 1081266-9-00.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Hui **e, Yi-xue Xue contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
**e, H., Xue, Yx., Liu, Lb. et al. Expressions of matrix metalloproteinase-7 and matrix metalloproteinase-14 associated with the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase1/2 in human brain gliomas of different pathological grades. Med Oncol 28 (Suppl 1), 433–438 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-010-9660-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-010-9660-7