Abstract
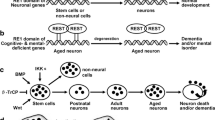
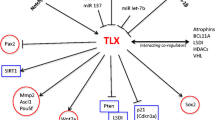
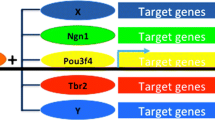
The neuron-restrictive silencer factor (NRSF) a transcriptional regulator that function as a hub that coordinately regulates multiple aspects of neurogenesis, orchestrates neural differentiation, and preserves the unique neural phenotype. NRSF also acts as an oncogene in neural tumorigenesis, although its effect differs depending on the cell type and tissues. Intriguingly, far more than above functions, potential roles for NRSF and its target genes have also been implicated in the pathogenesis and therapeutic mechanism of neurodegenerative diseases. NRSF acts as a flexible and complicated regulator in nervous system, from transcriptional repressor to activator or modulator, and plays a part in neuronal survival or neuronal death. Here, we present the mechanisms proposed to account for the multiple roles of NRSF in neurogenesis and neurological diseases and discuss the therapeutic perspective of recent advances. The mechanisms underlying this duality of NRSF are helpful to understanding the physiological and pathological conditions of neurons and provide new therapeutic approaches to neurological disorders and diseases.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anastas JN, Moon RT (2013) WNT signalling pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 13:11–26
Andres ME, Burger C, Peral-Rubio MJ et al (1999) CoREST: a functional corepressor required for regulation of neural-specific gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:9873–9878
Aoki H, Hara A, Era T et al (2012) Genetic ablation of Rest leads to in vitro-specific derepression of neuronal genes during neurogenesis. Development 139:667–677
Bahn S, Mimmack M, Ryan M et al (2002) Neuronal target genes of the neuron-restrictive silencer factor in neurospheres derived from fetuses with Down’s syndrome: a gene expression study. Lancet 359:310–315
Ballas N, Mandel G (2005) The many faces of REST oversee epigenetic programming of neuronal genes. Curr Opin Neurobiol 15:500–506
Ballas N, Grunseich C, Lu DD et al (2005) REST and its corepressors mediate plasticity of neuronal gene chromatin throughout neurogenesis. Cell 121:645–657
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Baryawno N, Sveinbjornsson B, Eksborg S et al (2010) Small-molecule inhibitors of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling inhibit Wnt/beta-catenin pathway cross-talk and suppress medulloblastoma growth. Cancer Res 70:266–276
Belyaev ND, Wood IC, Bruce AW et al (2004) Distinct RE-1 silencing transcription factor-containing complexes interact with different target genes. J Biol Chem 279:556–561
Berendsen S, Broekman M, Seute T et al (2012) Valproic acid for the treatment of malignant gliomas: Review of the preclinical rationale and published clinical results. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 21:1391–1415
Bonev B, Stanley P, Papalopulu N (2012) MicroRNA-9 Modulates Hes1 ultradian oscillations by forming a double-negative feedback loop. Cell Rep 2:10–18
Bruce AW, Donaldson IJ, Wood IC et al (2004) Genome-wide analysis of repressor element 1 silencing transcription factor/neuron-restrictive silencing factor (REST/NRSF) target genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:10458–10463
Bruce AW, Krejci A, Ooi L et al (2006) The transcriptional repressor REST is a critical regulator of the neurosecretory phenotype. J Neurochem 98:1828–1840
Buckley NJ, Johnson R, Sun YM et al (2009) Is REST a regulator of pluripotency? Nature 457:E5–E6, E7
Cai L, Bian M, Liu M et al (2011) Ethanol-induced neurodegeneration in NRSF/REST neuronal conditional knockout mice. Neuroscience 181:196–205
Calderone A, Jover T, Noh KM et al (2003) Ischemic insults derepress the gene silencer REST in neurons destined to die. J Neurosci 23:2112–2121
Chen ZF, Paquette AJ, Anderson DJ (1998) NRSF/REST is required in vivo for repression of multiple neuronal target genes during embryogenesis. Nat Genet 20:136–142
Chong JA, Tapia-Ramirez J, Kim S et al (1995) REST: a mammalian silencer protein that restricts sodium channel gene expression to neurons. Cell 80:949–957
Conaco C, Otto S, Han JJ et al (2006) Reciprocal actions of REST and a microRNA promote neuronal identity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:2422–2427
Conforti P, Zuccato C, Gaudenzi G et al (2013) Binding of the repressor complex REST-mSIN3b by small molecules restores neuronal gene transcription in Huntington’s disease models. J Neurochem 127:22–35
Conti L, Crisafulli L, Caldera V et al (2012) REST controls self-renewal and tumorigenic competence of human glioblastoma cells. PLoS One 7:e38486
Coulson JM, Edgson JL, Woll PJ et al (2000) A splice variant of the neuron-restrictive silencer factor repressor is expressed in small cell lung cancer: a potential role in derepression of neuroendocrine genes and a useful clinical marker. Cancer Res 60:1840–1844
Covey MV, Streb JW, Spektor R et al (2012) REST regulates the pool size of the different neural lineages by restricting the generation of neurons and oligodendrocytes from neural stem/progenitor cells. Development 139:2878–2890
Cruciat CM, Dolde C, de Groot RE et al (2013) RNA helicase DDX3 is a regulatory subunit of casein kinase 1 in Wnt-beta-catenin signaling. Science 339:1436–1441
D’Adda DFF, Reaper PM, Clay-Farrace L et al (2003) A DNA damage checkpoint response in telomere-initiated senescence. Nature 426:194–198
D’Alessandro R, Klajn A, Stucchi L et al (2008) Expression of the neurosecretory process in PC12 cells is governed by REST. J Neurochem 105:1369–1383
Das CM, Taylor P, Gireud M et al (2013) The deubiquitylase USP37 links REST to the control of p27 stability and cell proliferation. Oncogene 32:1691–1701
Dietrich N, Lerdrup M, Landt E et al (2012) REST-mediated recruitment of polycomb repressor complexes in mammalian cells. PLoS Genet 8:e1002494
Donev RM, Gray LC, Sivasankar B et al (2008) Modulation of CD59 expression by restrictive silencer factor-derived peptides in cancer immunotherapy for neuroblastoma. Cancer Res 68:5979–5987
Ekici M, Hohl M, Schuit F et al (2008) Transcription of genes encoding synaptic vesicle proteins in human neural stem cells: chromatin accessibility, histone methylation pattern, and the essential role of rest. J Biol Chem 283:9257–9268
Fasano CA, Phoenix TN, Kokovay E et al (2009) Bmi-1 cooperates with Foxg1 to maintain neural stem cell self-renewal in the forebrain. Genes Dev 23:561–574
Fowler A, Thomson D, Giles K et al (2011) miR-124a is frequently down-regulated in glioblastoma and is involved in migration and invasion. Eur J Cancer 47:953–963
Fuller GN, Su X, Price RE et al (2005) Many human medulloblastoma tumors overexpress repressor element-1 silencing transcription (REST)/neuron-restrictive silencer factor, which can be functionally countered by REST-VP16. Mol Cancer Ther 4:343–349
Gao Z, Ure K, Ding P et al (2011) The master negative regulator REST/NRSF controls adult neurogenesis by restraining the neurogenic program in quiescent stem cells. J Neurosci 31:9772–9786
Garriga-Canut M, Schoenike B, Qazi R et al (2006) 2-Deoxy-D-glucose reduces epilepsy progression by NRSF-CtBP-dependent metabolic regulation of chromatin structure. Nat Neurosci 9:1382–1387
Gates KP, Mentzer L, Karlstrom RO et al (2010) The transcriptional repressor REST/NRSF modulates hedgehog signaling. Dev Biol 340:293–305
Greenway DJ, Street M, Jeffries A et al (2007) RE1 Silencing transcription factor maintains a repressive chromatin environment in embryonic hippocampal neural stem cells. Stem Cells 25:354–363
Grimes JA, Nielsen SJ and Battaglioli E, et al. (2000) The co-repressor mSin3A is a functional component of the REST-CoREST repressor complex. Journal Of Biological Chemistry 275: 9461-9467
Guardavaccaro D, Frescas D, Dorrello NV et al (2008) Control of chromosome stability by the beta-TrCP-REST-Mad2 axis. Nature 452:365–369
Hanashima C, Li SC, Shen L et al (2004) Foxg1 suppresses early cortical cell fate. Science 303:56–59
Hatano Y, Yamada Y, Hata K et al (2011) Genetic ablation of a candidate tumor suppressor gene, rest, does not promote mouse colon carcinogenesis. Cancer Sci 102:1659–1664
He L, Hannon GJ (2004) MicroRNAs: Small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet 5:522–531
Hu XL, Cheng X, Cai L et al (2011) Conditional deletion of NRSF in forebrain neurons accelerates epileptogenesis in the kindling model. Cereb Cortex 21:2158–2165
Huang Z, Bao S (2012) Ubiquitination and deubiquitination of REST and its roles in cancers. Febs Lett 586:1602–1605
Huang YZ, McNamara JO (2006) Inhibiting glycolysis to reduce seizures: how it might work. Nat Neurosci 9:1351–1352
Huang X, Summers MK, Pham V et al (2011a) Deubiquitinase USP37 is activated by CDK2 to antagonize APC(CDH1) and promote S phase entry. Mol Cell 42:511–523
Huang Z, Wu Q, Guryanova OA et al (2011b) Deubiquitylase HAUSP stabilizes REST and promotes maintenance of neural progenitor cells. Nat Cell Biol 13:142–152
Hummel R, Maurer J, Haier J (2011) MicroRNAs in brain tumors: a new diagnostic and therapeutic perspective? Mol Neurobiol 44:223–234
Hwang JY, Kaneko N, Noh KM et al (2014) The gene silencing transcription factor REST represses miR-132 expression in hippocampal neurons destined to die. J Mol Biol 426:3454–3466
Jiang L, Yao M, Shi J et al (2008) Yin yang 1 directly regulates the transcription of RE-1 silencing transcription factor. J Neurosci Res 86:1209–1216
Johnson DS, Mortazavi A, Myers RM et al (2007) Genome-wide map** of in vivo protein-DNA interactions. Science 316:1497–1502
Jorgensen HF, Chen ZF et al (2009a) Is REST required for ESC pluripotency? Nature 457:E4–E5, E7
Jorgensen HF, Terry A et al (2009b) REST selectively represses a subset of RE1-containing neuronal genes in mouse embryonic stem cells. Development 136:715–721
Kageyama R, Ohtsuka T, Kobayashi T (2008) Roles of Hes genes in neural development. Develop Growth Differ 50(Suppl 1):S97–S103
Kamal MM, Sathyan P, Singh SK et al (2012) REST regulates oncogenic properties of glioblastoma stem cells. Stem Cells 30:405–414
Kaneko N, Hwang JY, Gertner M et al (2014) Casein kinase 1 suppresses activation of REST in insulted hippocampal neurons and halts ischemia-induced neuronal death. J Neurosci 34:6030–6039
Kim CS, Hwang CK, Choi HS et al (2004) Neuron-restrictive silencer factor (NRSF) functions as a repressor in neuronal cells to regulate the mu opioid receptor gene. J Biol Chem 279:46464–46473
Kreisler A, Strissel PL, Strick R et al (2010) Regulation of the NRSF/REST gene by methylation and CREB affects the cellular phenotype of small-cell lung cancer. Oncogene 29:5828–5838
Laneve P, Gioia U, Andriotto A et al (2010) A minicircuitry involving REST and CREB controls miR-9-2 expression during human neuronal differentiation. Nucleic Acids Res 38:6895–6905
Lemonde S, Rogaeva A, Albert PR (2004) Cell type-dependent recruitment of trichostatin A-sensitive repression of the human 5-HT1A receptor gene. J Neurochem 88:857–868
Loe-Mie Y, Lepagnol-Bestel AM, Maussion G et al (2010) SMARCA2 and other genome-wide supported schizophrenia-associated genes: Regulation by REST/NRSF, network organization and primate-specific evolution. Hum Mol Genet 19:2841–2857
Lu T, Aron L, Zullo J et al (2014) REST and stress resistance in ageing and Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 507:448–454
Lunyak VV, Burgess R and Prefontaine GG, et al. (2002) Corepressordependent silencing of chromosomal regions encoding neuronal genes. Science 298: 1747–1752
Lv H, Pan G, Zheng G et al (2010) Expression and functions of the repressor element 1 (RE-1)-silencing transcription factor (REST) in breast cancer. J Cell Biochem 110:968–974
Makeyev EV, Zhang J, Carrasco MA et al (2007) The MicroRNA miR-124 promotes neuronal differentiation by triggering brain-specific alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Mol Cell 27:435–448
Moss AC, Jacobson GM, Walker LE et al (2009) SCG3 transcript in peripheral blood is a prognostic biomarker for REST-deficient small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 15:274–283
Nakagawa Y, Kuwahara K and Harada M, et al. (2006) Class II HDACs mediate CaMK-dependent signaling to NRSF in ventricular myocytes. Journal Of Molecular And Cellular Cardiology 41: 1010–1022
Naruse Y, Aoki T and Kojima T, et al. (1999) Neural restrictive silencer factor recruits mSin3 and histone deacetylase complex to repress neuron-specific target genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96: 13691–13696
Negrini S, Prada I, D’Alessandro R et al (2013) REST: an oncogene or a tumor suppressor? Trends Cell Biol 23:289–295
Nesti E, Corson GM, McCleskey M et al (2014) C-terminal domain small phosphatase 1 and MAP kinase reciprocally control REST stability and neuronal differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:E3929–E3936
Ning H, Li T, Zhao L et al (2006) TRF2 promotes multidrug resistance in gastric cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther 5:950–956
Nishihara S, Tsuda L, Ogura T (2003) The canonical Wnt pathway directly regulates NRSF/REST expression in chick spinal cord. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 311:55–63
Noh KM, Hwang JY, Follenzi A et al (2012) Repressor element-1 silencing transcription factor (REST)-dependent epigenetic remodeling is critical to ischemia-induced neuronal death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:E962–E971
Ohnuki T, Nakamura A, Okuyama S et al (2010) Gene expression profiling in progressively MPTP-lesioned macaques reveals molecular pathways associated with sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res 1346:26–42
Ooi L, Belyaev ND and Miyake K, et al. (2006) BRG1 chromatin remodeling activity is required for efficient chromatin binding by repressor element 1-silencing transcription factor (REST) and facilitates REST-mediated repression. Journal Of Biological Chemistry 281: 38974–38980
Ooi L, Wood IC (2007) Chromatin crosstalk in development and disease: Lessons from REST. Nat Rev Genet 8:544–554
Ovando-Roche P, Yu JS, Testori S et al (2014) TRF2-mediated stabilization of hREST4 is critical for the differentiation and maintenance of neural progenitors. Stem Cells 32:2111–2122
Packer AN, **ng Y, Harper SQ et al (2008) The bifunctional microRNA miR-9/miR-9* regulates REST and CoREST and is downregulated in Huntington’s disease. Journal Of Neuroscience 28:14341–14346
Palm K, Belluardo N, Metsis M et al (1998) Neuronal expression of zinc finger transcription factor REST/NRSF/XBR gene. Journal Of Neuroscience 18:1280–1296
Palm K, Metsis M, Timmusk T (1999) Neuron-specific splicing of zinc finger transcription factor REST/NRSF/XBR is frequent in neuroblastomas and conserved in human, mouse and rat. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 72:30–39
Pozzi D, Lignani G, Ferrea E et al (2013) REST/NRSF-mediated intrinsic homeostasis protects neuronal networks from hyperexcitability. Embo J 32:2994–3007
Quinn JP, Warburton A, Myers P et al (2013) Polymorphic variation as a driver of differential neuropeptide gene expression. Neuropeptides 47:395–400
Qureshi IA, Gokhan S, Mehler MF (2010) REST and CoREST are transcriptional and epigenetic regulators of seminal neural fate decisions. Cell Cycle 9:4477–4486
Raj B, O’Hanlon D, Vessey JP et al (2011) Cross-regulation between an alternative splicing activator and a transcription repressor controls neurogenesis. Mol Cell 43:843–850
Ravache M, Weber C, Merienne K et al (2010) Transcriptional activation of REST by Sp1 in Huntington’s disease models. PLoS One 5:e14311
Ren X, Kerppola TK (2011) REST interacts with Cbx proteins and regulates polycomb repressive complex 1 occupancy at RE1 elements. Mol Cellu Biol 31:2100–2110
Rockowitz S, Lien WH, Pedrosa E et al (2014) Comparison of REST cistromes across human cell types reveals common and context-specific functions. PLoS Comput Biol 10:e1003671
Rodenas-Ruano A, Chavez AE, Cossio MJ et al (2012) REST-dependent epigenetic remodeling promotes the developmental switch in synaptic NMDA receptors. Nat Neurosci 15:1382–1390
Roopra A, Qazi R and Schoenike B, et al. (2004a) Localized domains of G9a-mediated histone methylation are required for silencing of neuronal genes. Molecular Cell 14: 727–738
Roopra A, Qazi R and Schoenike B, et al. (2004b) Localized domains of G9a-mediated histone methylation are required for silencing of neuronal genes. Molecular Cell 14: 727–738
Sanson M, Laigle-Donadey F, Benouaich-Amiel A (2006) Molecular changes in brain tumors: Prognostic and therapeutic impact. Curr Opin Oncol 18:623–630
Schilling G, Becher MW, Sharp AH et al (1999) Intranuclear inclusions and neuritic aggregates in transgenic mice expressing a mutant N-terminal fragment of huntingtin. Hum Mol Genet 8:397–407
Schoenherr CJ, Anderson DJ (1995) The neuron-restrictive silencer factor (NRSF): a coordinate repressor of multiple neuron-specific genes. Science 267:1360–1363
Schoenherr CJ, Paquette AJ, Anderson DJ (1996) Identification of potential target genes for the neuron-restrictive silencer factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:9881–9886
Sedaghat Y, Bui HH, Mazur C et al (2013) Identification of REST-regulated genes and pathways using a REST-targeted antisense approach. Nucleic Acid Ther 23:389–400
Sempere LF, Freemantle S, Pitha-Rowe I et al (2004) Expression profiling of mammalian microRNAs uncovers a subset of brain-expressed microRNAs with possible roles in murine and human neuronal differentiation. Genome Biol 5:R13
Shi Y, Chichung LD, Taupin P et al (2004) Expression and function of orphan nuclear receptor TLX in adult neural stem cells. Nature 427:78–83
Shimojo M (2008) Huntingtin regulates RE1-silencing transcription factor/neuron-restrictive silencer factor (REST/NRSF) nuclear trafficking indirectly through a complex with REST/NRSF-interacting LIM domain protein (RILP) and dynactin p150 Glued. J Biol Chem 283:34880–34886
Shimojo M, Hersh LB (2006) Characterization of the REST/NRSF-interacting LIM domain protein (RILP): Localization and interaction with REST/NRSF. J Neurochem 96:1130–1138
Shimojo M, Paquette AJ, Anderson DJ et al (1999) Protein kinase A regulates cholinergic gene expression in PC12 cells: REST4 silences the silencing activity of neuron-restrictive silencer factor/REST. Mol Cell Biol 19:6788–6795
Singh SK, Kagalwala MN, Parker-Thornburg J et al (2008) REST maintains self-renewal and pluripotency of embryonic stem cells. Nature 453:223–227
Singh A, Rokes C, Gireud M et al (2011) Retinoic acid induces REST degradation and neuronal differentiation by modulating the expression of SCF(beta-TRCP) in neuroblastoma cells. Cancer 117:5189–5202
Singh SK, Veo BL, Kagalwala MN et al (2012) Dynamic status of REST in the mouse ESC pluripotency network. PLoS One 7:e43659
Smith R, Chung H, Rundquist S et al (2006) Cholinergic neuronal defect without cell loss in Huntington’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 15:3119–3131
Soldati C, Bithell A, Conforti P et al (2011) Rescue of gene expression by modified REST decoy oligonucleotides in a cellular model of Huntington’s disease. J Neurochem 116:415–425
Soldati C, Bithell A, Johnston C et al (2012) Repressor element 1 silencing transcription factor couples loss of pluripotency with neural induction and neural differentiation. Stem Cells 30:425–434
Spencer EM, Chandler KE, Haddley K et al (2006) Regulation and role of REST and REST4 variants in modulation of gene expression in in vivo and in vitro in epilepsy models. Neurobiol Dis 24:41–52
Stapels M, Piper C, Yang T et al (2010) Polycomb group proteins as epigenetic mediators of neuroprotection in ischemic tolerance. Sci Signal 3:a15
Tabuchi A, Yamada T, Sasagawa S et al (2002) REST4-mediated modulation of REST/NRSF-silencing function during BDNF gene promoter activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 290:415–420
Tahiliani M, Mei P, Fang R et al (2007) The histone H3K4 demethylase SMCX links REST target genes to X-linked mental retardation. Nature 447:601–605
Taylor P, Fangusaro J, Rajaram V et al (2012) REST is a novel prognostic factor and therapeutic target for medulloblastoma. Mol Cancer Ther 11:1713–1723
Thiel G, Ekici M, Rossler OG (2014) RE-1 silencing transcription factor (REST): a regulator of neuronal development and neuronal/endocrine function. Cell Tissue Res. doi:10.1007/s00441-014-1963-0
Tomasoni R, Negrini S, Fiordaliso S et al (2011) A signaling loop of REST, TSC2 and beta-catenin governs proliferation and function of PC12 neural cells. J Cell Sci 124:3174–3186
Tsai LH, Madabhushi R (2014) Alzheimer’s disease: a protective factor for the ageing brain. Nature 507:439–440
Tsai MC, Manor O, Wan Y et al (2010) Long noncoding RNA as modular scaffold of histone modification complexes. Science 329:689–693
Uchida S, Hara K, Kobayashi A et al (2010) Early life stress enhances behavioral vulnerability to stress through the activation of REST4-mediated gene transcription in the medial prefrontal cortex of rodents. J Neurosci 30:15007–15018
Valouev A, Johnson DS, Sundquist A et al (2008) Genome-wide analysis of transcription factor binding sites based on ChIP-Seq data. Nat Methods 5:829–834
Visvanathan J, Lee S, Lee B et al (2007) The microRNA miR-124 antagonizes the anti-neural REST/SCP1 pathway during embryonic CNS development. Genes Dev 21:744–749
Wagoner MP, Roopra A (2012) A REST derived gene signature stratifies glioblastomas into chemotherapy resistant and responsive disease. BMC Genomics 13:686
Wagoner MP, Gunsalus KT, Schoenike B et al (2010) The transcription factor REST is lost in aggressive breast cancer. PLoS Genet 6:e1000979
Warburton A, Breen G, Rujescu D et al (2014) Characterization of a REST-regulated internal promoter in the schizophrenia genome-wide associated gene MIR137. Schizophr Bull. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbu117
Warburton A, Savage AL, Myers P et al (2015) Molecular signatures of mood stabilisers highlight the role of the transcription factor REST/NRSF. J Affect Disord 172:63–73
Westbrook TF, Hu G, Ang XL et al (2008) SCFbeta-TRCP controls oncogenic transformation and neural differentiation through REST degradation. Nature 452:370–374
Wong HK, Veremeyko T, Patel N et al (2013) De-repression of FOXO3a death axis by microRNA-132 and -212 causes neuronal apoptosis in Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 22:3077–3092
**a H, Cheung WK, Ng SS et al (2012) Loss of brain-enriched miR-124 microRNA enhances stem-like traits and invasiveness of glioma cells. J Biol Chem 287:9962–9971
Yamada Y, Aoki H, Kunisada T et al (2010) Rest promotes the early differentiation of mouse ESCs but is not required for their maintenance. Cell Stem Cell 6:10–15
Yoo AS, Staahl BT, Chen L et al (2009) MicroRNA-mediated switching of chromatin-remodelling complexes in neural development. Nature 460:642–646
Yu M, Cai L, Liang M et al (2009) Alteration of NRSF expression exacerbating 1-methyl-4-phenyl-pyridinium ion-induced cell death of SH-SY5Y cells. Neurosci Res 65:236–244
Yu HB, Johnson R, Kunarso G et al (2011) Coassembly of REST and its cofactors at sites of gene repression in embryonic stem cells. Genome Res 21:1284–1293
Yu M, Suo H, Liu M et al (2013) NRSF/REST neuronal deficient mice are more vulnerable to the neurotoxin MPTP. Neurobiol Aging 34:916–927
Zhang P, Pazin MJ, Schwartz CM et al (2008) Nontelomeric TRF2-REST interaction modulates neuronal gene silencing and fate of tumor and stem cells. Curr Biol 18:1489–1494
Zhang P, Lathia JD, Flavahan WA et al (2009) Squelching glioblastoma stem cells by targeting REST for proteasomal degradation. Trends Neurosci 32:559–565
Zhang K, Biswas N, Gayen JR et al (2014) Chromogranin B: Intra- and extra-cellular mechanisms to regulate catecholamine storage and release, in catecholaminergic cells and organisms. J Neurochem 129:48–59
Zheng D, Zhao K, Mehler MF (2009) Profiling RE1/REST-mediated histone modifications in the human genome. Genome Biol 10:R9
Zuccato C, Cattaneo E (2007) Role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in Huntington’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 81:294–330
Zuccato C, Tartari M, Crotti A et al (2003) Huntingtin interacts with REST/NRSF to modulate the transcription of NRSE-controlled neuronal genes. Nat Genet 35:76–83
Zuccato C, Belyaev N, Conforti P et al (2007) Widespread disruption of repressor element-1 silencing transcription factor/neuron-restrictive silencer factor occupancy at its target genes in Huntington’s disease. J Neurosci 27:6972–6983
Zukin RS (2010) Eradicating the mediators of neuronal death with a fine-tooth comb. Sci Signal 3:e20
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 31172293, No. 31272532, and No.31472166), 948 projects (2013-S11; 2014-S9), and the Program for Cheung Kong Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University of China (No. IRT0866).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, Z., Zhao, D., Zhao, H. et al. NRSF: an Angel or a Devil in Neurogenesis and Neurological Diseases. J Mol Neurosci 56, 131–144 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0474-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0474-5