Abstract
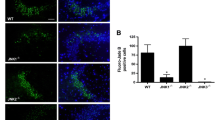
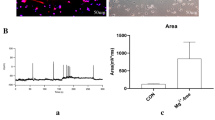
Studies have shown that the protective effect of carbamazepine (CBZ) on seizure-induced neuronal injury. However, its precise mechanisms remain unknown. Here, to investigate the neuroprotective mechanism of CBZ against seizure-induced neuronal cell death, we identified the change of gene expressions by CBZ in the hippocampus of kainic acid (KA)-treated mice using microarray method, and studied the involvement of candidate gene in neuroprotective action of CBZ. KA (15 mg/kg) and/or CBZ (30 mg/kg, 0.5 h after KA exposure) were injected intraperitoneally into mice. Through microarray analysis, we found that signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (Stat3) gene expression was upregulated in the hippocampal CA3 region, 24 h after KA injection (15 mg/kg), and that CBZ further elevated Stat3 expression in KA-treated mice. KA also increased the protein level and phosphorylation of Stat3, and CBZ further increased the Stat3 phosphorylation, without changing Stat3 protein level in KA-treated mice. In particular, phospho-Stat3 immunoreactivity (IR) by KA was shown in astrocytes rather than in neurons; whereas phospho-Stat3 IR by CBZ in KA-treated mice was observed predominantly in neurons, and also in neuroprotective protein Bcl-xL-expression cells. These results indicate that Stat3 may play an important role in neuroprotective action of CBZ on seizure-induced neuronal injury.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almgren M, Nyengaard JR, Persson B, Lavebratt C (2008) Carbamazepine protects against neuronal hyperplasia and abnormal gene expression in the megencephaly mouse. Neurobiol Dis 32:364–376
Bambrick L, Kristian T, Fiskum G (2004) Astrocyte mitochondrial mechanisms of ischemic brain injury and neuroprotection. Neurochem Res 29:601–608
Benoit ME, Tenner AJ (2011) Complement protein C1q-mediated neuroprotection is correlated with regulation of neuronal gene and miRNA expression. J Neurosci 31:3459–3269
Bernier M, Paul RK, Martin-Montalvo A et al (2011) Negative regulation of STAT3 protein-mediated cellular respiration by SIRT1 protein. J Biol Chem 286:19270–19279
Bolte S, Cordelières FP (2006) A guided tour into subcellular colocalization analysis in light microscopy. J Microsc 224:213–232
Chang YC, Rapoport SI, Rao JS (2009) Chronic administration of mood stabilizers upregulates BDNF and bcl-2 expression levels in rat frontal cortex. Neurochem Res 34:536–541
Choi JS, Kim SY, Cha JH et al (2003) Upregulation of gp130 and STAT3 activation in the rat hippocampus following transient forebrain ischemia. Glia 41:237–246
Costa C, Belcastro V, Tozzi A et al (2008) Electrophysiology and pharmacology of striatal neuronal dysfunction induced by mitochondrial complex I inhibition. J Neurosci 28:8040–8052
Coyle JT (1987) Kainic acid: insights into excitatory mechanisms causing selective neuronal degeneration. Ciba Found Symp 126:186–203
Dziennis S, Alkayed NJ (2008) Role of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in neuronal survival and regeneration. Rev Neurosci 19:341–361
Dziennis S, Jia T, Rønnekleiv OK, Hum PD, Alkayed NJ (2007) Role of signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 in estradiol-mediated neuroprotection. J Neurosci 27:7268–7274
Farkas I, Takahashi M, Fukuda A et al (2003) Complement C5a receptor-mediated signaling may be involved in neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease. J Immunol 170:5764–5771
Fearnley IM, Carroll J, Shannon RJ, Runswick MJ, Walker JE, Hirst J (2001) GRIM-19, a cell death regulatory gene product, is a subunit of bovine mitochondrial NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (complex I). J Biol Chem 276:38345–38348
Gardner J, Ghorpade A (2003) Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP)-1: the TIMPed balance of matrix metalloproteinases in the central nervous system. J Neurosci Res 74:801–806
Gouder N, Fritschy JM, Boison D (2003) Seizure suppression by adenosine A1 receptor activation in a mouse model of pharmacoresistant epilepsy. Epilepsia 44:877–885
Grabenstatter HL, Clark S, Dudet FE (2007) Anticonvulsant effects of carbamazepine on spontaneous seizures in rats with kainate-induced epilepsy: comparison of intraperitoneal injections with drug-in-food protocols. Epilepsia 48:2287–2295
Grad JM, Zeng XR, Boise LH (2000) Regulation of Bcl-xL: a little bit of this and a little bit of STAT. Curr Opin Oncol 12:543–549
Greenamyre JT, Sherer TB, Betarbet R, Panov AV (2001) Complex I and Parkinson's disease. I U B M B Life 52:135–141
Hattori R, Maulik N, Otani H et al (2001) Role of STAT3 in ischemic preconditioning. J Mol Cell Cardiol 33:1929–1936
Jaworski DM (2000) Differential regulation of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase mRNA expression in response to intracranial injury. Glia 30:199–208
Kalakonda S, Nallar SC, Lindner DJ, Hu J, Reddy SP, Kalvakolanu DV (2007) Tumor-suppressive activity of the cell death activator GRIM-19 on a constitutively active signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. Cancer Res 67:6212–6220
Kitano Y, Komiyama C, Makino M et al (2005) Anticonvulsant and neuroprotective effects of the novel nootropic agent nefiracetam on kainic acid-induced seizures in rats. Brain Res 1057:168–176
Kovacs GG, Gasque P, Ströbel T et al (2004) Complement activation in human prion disease. Neurobiol Dis 15:21–28
Levy DE, Darnell JE Jr (2002) Stats: transcriptional control and biological impact. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:651–662
Li Q, Zhang R, Guo YL, Mei YW (2009) Effect of neuregulin on apoptosis and expressions of STAT3 and GFAP in rats following cerebral ischemic reperfusion. J Mol Neurosci 37:67–73
Löscher W (1998) Pharmacology of glutamate receptor antagonists in the kindling model of epilepsy. Prog Neurobiol 54:721–741
Lund IV, Hu Y, Raol YH et al (2008) BDNF selectively regulates GABAA receptor transcription by activation of the JAK/STAT pathway. Sci Signal 1:1–14
MacDonald RL, Kelly KM (1993) Antiepileptic drug mechanisms of action. Epilepsia 34:S1–S8
Merry DE, Korsmeyer SJ (1997) Bcl-2 gene family in the nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci 20:245–267
Minato H, Kikuta C, Fujitani B, Masuda Y (1997) Protective effect of zonisamide, an antiepileptic drug, against transient focal cerebral ischemia with middle cerebral artery occlusion-reperfusion in rats. Epilepsia 38:975–980
Morrison RS, Wenzel HJ, Kinoshita Y, Robbins CA, Donehower LA, Schwartzkroin PA (1996) Loss of the p53 tumor suppressor gene protects neurons from kainate-induced cell death. J Neurosci 16:1337–1345
Nadler JV (1981) Minireview. Kainic acid as a tool for the study of temporal lobe epilepsy. Life Sci 29:2031–2042
Natale JE, Ahmed F, Cernak I, Stoica B, Faden AI (2003) Gene expression profile changes are commonly modulated across models and species after traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 20:907–927
Nedergaard M, Dirnagl U (2005) Role of glial cells in cerebral ischemia. Glia 50:281–286
Ng YP, Cheung ZH, Ip NY (2006) STAT3 as a downstream mediator of Trk signaling and functions. J Biol Chem 281:15636–15644
Noh HS, Kim YS, Kim YH et al (2006) Ketogenic diet protects the hippocampus from kainic acid toxicity by inhibiting the dissociation of bad from 14-3-3. J Neurosci Res 84:1829–1836
Olayioye MA, Beuvink I, Horsch K, Daly JM, Hynes NE (1999) ErbB receptor-induced activation of stat transcription factors is mediated by Src tyrosine kinases. J Biol Chem 274:17209–17218
Parsadanian AS, Cheng Y, Keller-Peck CR, Holtzman DM, Snider WD (1998) Bcl-xL is an antiapoptotic regulator for postnatal CNS neurons. J Neurosci 18:1009–1019
Pisalyaput K, Tenner AJ (2008) Complement component C1q inhibits beta-amyloid- and serum amyloid Pinduced neurotoxicity via caspase- and calpain-independent mechanisms. J Neurochem 104:696–707
Schirrmacher K, Mayer A, Walden J, Düsing R, Bingmann D (1993) Effects of carbamazepine on action potentials and calcium currents in rat spinal ganglion cells in vitro. Neuropsychobiology 27:176–179
Shulga N and Pastorino JG (2012) GRIM-19 Mediated Translocation of STAT3 to Mitochondria is Necessary for TNF Induced Necroptosis. J. Cell Sci. doi:10.1242/jcs.103093
Sperk G (1994) Kainic acid seizures in the rat. Prog Neurobiol 42:1–32
Stephanou A, Brar BK, Knight RA, Latchman DS (2000) Opposing actions of STAT-1 and STAT-3 on the Bcl-2 and Bcl-x promoters. Cell Death Differ 7:329–330
Stevens B, Allen NJ, Vazquez LE et al (2007) The classical complement cascade mediates CNS synapse elimination. Cell 131:1164–1178
Suzuki S, Tanaka K, Nogawa S, Dembo T, Kosakai A, Fukuuchi Y (2001) Phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (Stat3) after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Exp Neurol 170:63–71
Tejima E, Guo S, Murata Y et al (2009) Neuroprotective effects of overexpressing tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase TIMP-1. J Neurotrauma 26:1935–1941
Thomas MA, Joshi PP, Klaper RD (2012) Gene-class analysis of expression patterns induced by psychoactive pharmaceutical exposure in fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) indicates induction of neuronal systems. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 155:109–120
Vignais ML, Sadowski HB, Watling D, Rogers NC, Gilman M (1996) Platelet-derived growth factor induces phosphorylation of multiple JAK family kinases and STAT proteins. Mol Cell Biol 16:1759–1769
Wang L, Zuo CH, Zhao DY, Wu XR (2000) Brain distribution and efficacy of carbamazepine in kainic acid induced seizure in rats. Brain Dev 22:154–157
Wang T, Yan XB, Zhao JJ et al (2011) Gene associated with retinoid-interferon-induced mortality-19 suppresses growth of lung adenocarcinoma tumor in vitro and in vivo. Lung Cancer 72:287–293
Xuan YT, Guo Y, Han H, Zhu Y, Bolli R (2001) An essential role of the JAK-STAT pathway in ischemic preconditioning. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:9050–9055
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant of the Korea Healthcare technology R&D Project, Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (A100768).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, H.J., Kim, S.K., Chung, JH. et al. Protective Effect of Carbamazepine on Kainic Acid-induced Neuronal Cell Death Through Activation of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription-3. J Mol Neurosci 49, 172–181 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9854-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9854-x