Abstract
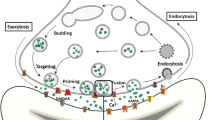
Lithium is a mood stabilizer broadly used to prevent and treat symptoms of mania and depression in people with bipolar disorder (BD). Little is known, however, about its mode of action. Here, we analyzed the impact of lithium on synaptic vesicle (SV) cycling at presynaptic terminals releasing glutamate, a neurotransmitter previously implicated in BD and other neuropsychiatric conditions. We used the pHluorin-based synaptic tracer vGpH and a fully automated image processing pipeline to quantify the effect of lithium on both SV exocytosis and endocytosis in hippocampal neurons. We found that lithium selectively reduces SV exocytic rates during electrical stimulation, and markedly slows down SV recycling post-stimulation. Analysis of single-bouton responses revealed the existence of functionally distinct excitatory synapses with varying sensitivity to lithium—some terminals show responses similar to untreated cells, while others are markedly impaired in their ability to recycle SVs. While the cause of this heterogeneity is unclear, these data indicate that lithium interacts with the SV machinery and influences glutamate release in a large fraction of excitatory synapses. Together, our findings show that lithium down modulates SV cycling, an effect consistent with clinical reports indicating hyperactivation of glutamate neurotransmission in BD.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agam, G., Shamir, A., Shaltiel, G., & Greenberg, M. L. (2002). Myo-inositol-1-phosphate (MIP) synthase: A possible new target for antibipolar drugs. Bipolar Disorders, 4(Suppl 1), 15–20. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1399-5618.4.s1.2.x
Ariel, P., Hoppa, M. B., & Ryan, T. A. (2012). Intrinsic variability in Pv, RRP size, Ca(2+) channel repertoire, and presynaptic potentiation in individual synaptic boutons. Frontier in Synaptic Neuroscience, 4, 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsyn.2012.00009
Armbruster, M., Messa, M., Ferguson, S. M., De Camilli, P., & Ryan, T. A. (2013). Dynamin phosphorylation controls optimization of endocytosis for brief action potential bursts. eLife, 2, e00845. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.00845
Balaji, J., Armbruster, M., & Ryan, T. A. (2008). Calcium control of endocytic capacity at a CNS synapse. Journal of Neuroscience, 28(26), 6742–6749. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1082-08.2008
Balaji, J., & Ryan, T. A. (2007). Single-vesicle imaging reveals that synaptic vesicle exocytosis and endocytosis are coupled by a single stochastic mode. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science USA, 104(51), 20576–20581. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0707574105
Brittain, J. M., Piekarz, A. D., Wang, Y., Kondo, T., Cummins, T. R., & Khanna, R. (2009). An atypical role for collapsin response mediator protein 2 (CRMP-2) in neurotransmitter release via interaction with presynaptic voltage-gated calcium channels. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 284(45), 31375–31390. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.009951
Burrone, J., Li, Z., & Murthy, V. N. (2006). Studying vesicle cycling in presynaptic terminals using the genetically encoded probe synaptopHluorin. Nature Protocols, 1(6), 2970–2978. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.449
Cade, J. F. (1949). Lithium salts in the treatment of psychotic excitement. Medical Journal of Australia, 2(10), 349–352. https://doi.org/10.1080/j.1440-1614.1999.06241.x
Chanaday, N. L., & Kavalali, E. T. (2018). Optical detection of three modes of endocytosis at hippocampal synapses. eLife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.36097
Chitty, K. M., Lagopoulos, J., Lee, R. S., Hickie, I. B., & Hermens, D. F. (2013). A systematic review and meta-analysis of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy and mismatch negativity in bipolar disorder. European Neuropsychopharmacology, 23(11), 1348–1363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroneuro.2013.07.007
Cipriani, A., Pretty, H., Hawton, K., & Geddes, J. R. (2005). Lithium in the prevention of suicidal behavior and all-cause mortality in patients with mood disorders: A systematic review of randomized trials. American Journal of Psychiatry, 162(10), 1805–1819. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.162.10.1805
Clayton, E. L., Evans, G. J., & Cousin, M. A. (2008). Bulk synaptic vesicle endocytosis is rapidly triggered during strong stimulation. Journal of Neuroscience, 28(26), 6627–6632. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1445-08.2008
Clayton, E. L., Sue, N., Smillie, K. J., O’Leary, T., Bache, N., Cheung, G., Cole, A. R., Wyllie, D. J., Sutherland, C., Robinson, P. J., & Cousin, M. A. (2010). Dynamin I phosphorylation by GSK3 controls activity-dependent bulk endocytosis of synaptic vesicles. Nature Neuroscience, 13(7), 845–851. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2571
Crabtree, G. W., Sun, Z., Kvajo, M., Broek, J. A., Fenelon, K., McKellar, H., **ao, L., Xu, B., Bahn, S., O’Donnell, J. M., & Gogos, J. A. (2017). Alteration of neuronal excitability and short-term synaptic plasticity in the prefrontal cortex of a mouse model of mental illness. Journal of Neuroscience, 37(15), 4158–4180. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4345-15.2017
Dandekar, M. P., Valvassori, S. S., Dal-Pont, G. C., & Quevedo, J. (2018). Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta as a putative therapeutic target for bipolar disorder. Current Drug Metabolism, 19(8), 663–673. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389200219666171227203737
Fernandez-Alfonso, T., & Ryan, T. A. (2004). The kinetics of synaptic vesicle pool depletion at CNS synaptic terminals. Neuron, 41(6), 943–953. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(04)00113-8
Geddes, J. R., Burgess, S., Hawton, K., Jamison, K., & Goodwin, G. M. (2004). Long-term lithium therapy for bipolar disorder: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. American Journal of Psychiatry, 161(2), 217–222. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.161.2.217
Gideons, E. S., Lin, P. Y., Mahgoub, M., Kavalali, E. T., & Monteggia, L. M. (2017). Chronic lithium treatment elicits its antimanic effects via BDNF-TrkB dependent synaptic downscaling. eLife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.25480
Granseth, B., Odermatt, B., Royle, S. J., & Lagnado, L. (2006). Clathrin-mediated endocytosis is the dominant mechanism of vesicle retrieval at hippocampal synapses. Neuron, 51(6), 773–786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2006.08.029
Kaech, S., & Banker, G. (2006). Culturing hippocampal neurons. Nature Protocols, 1(5), 2406–2415. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.356
Khayachi, A., Ase, A., Liao, C., Kamesh, A., Kuhlmann, N., Schorova, L., Chaumette, B., Dion, P., Alda, M., Seguela, P., Rouleau, G., & Milnerwood, A. (2021). Chronic lithium treatment alters the excitatory/ inhibitory balance of synaptic networks and reduces mGluR5-PKC signalling in mouse cortical neurons. Journal of Psychiatry and Neuroscience, 46(3), E402–E414. https://doi.org/10.1503/jpn.200185
Lan, M. J., McLoughlin, G. A., Griffin, J. L., Tsang, T. M., Huang, J. T., Yuan, P., Manji, H., Holmes, E., & Bahn, S. (2009). Metabonomic analysis identifies molecular changes associated with the pathophysiology and drug treatment of bipolar disorder. Molecular Psychiatry, 14(3), 269–279. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4002130
Leitz, J., & Kavalali, E. T. (2011). Ca(2)(+) influx slows single synaptic vesicle endocytosis. Journal of Neuroscience, 31(45), 16318–16326. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3358-11.2011
Lueke, K., Kaiser, T., Svetlitchny, A., Welzel, O., Wenzel, E. M., Tyagarajan, S., Kornhuber, J., & Groemer, T. W. (2014). Basic presynaptic functions in hippocampal neurons are not affected by acute or chronic lithium treatment. Journal of Neural Transmission (vienna), 121(2), 211–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-013-1087-9
Luo, J. K., Melland, H., Nithianantharajah, J., & Gordon, S. L. (2021). Postsynaptic neuroligin-1 mediates presynaptic endocytosis during neuronal activity. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience, 14, 744845. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2021.744845
Merikangas, K. R., **, R., He, J. P., Kessler, R. C., Lee, S., Sampson, N. A., Viana, M. C., Andrade, L. H., Hu, C., Karam, E. G., Ladea, M., Medina-Mora, M. E., Ono, Y., Posada-Villa, J., Sagar, R., Wells, J. E., & Zarkov, Z. (2011). Prevalence and correlates of bipolar spectrum disorder in the world mental health survey initiative. Archives of General Psychiatry, 68(3), 241–251. https://doi.org/10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.12
Mertens, J., Wang, Q. W., Kim, Y., Yu, D. X., Pham, S., Yang, B., Zheng, Y., Diffenderfer, K. E., Zhang, J., Soltani, S., Eames, T., Schafer, S. T., Boyer, L., Marchetto, M. C., Nurnberger, J. I., Calabrese, J. R., Odegaard, K. J., McCarthy, M. J., Zandi, P. P., … Yao, J. (2015). Differential responses to lithium in hyperexcitable neurons from patients with bipolar disorder. Nature, 527(7576), 95–99. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature15526
Miesenbock, G., De Angelis, D. A., & Rothman, J. E. (1998). Visualizing secretion and synaptic transmission with pH-sensitive green fluorescent proteins. Nature, 394(6689), 192–195. https://doi.org/10.1038/28190
Newberg, A. R., Catapano, L. A., Zarate, C. A., & Manji, H. K. (2008). Neurobiology of bipolar disorder. Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics, 8(1), 93–110. https://doi.org/10.1586/14737175.8.1.93
Nonaka, S., Hough, C. J., & Chuang, D. M. (1998). Chronic lithium treatment robustly protects neurons in the central nervous system against excitotoxicity by inhibiting N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-mediated calcium influx. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 95(5), 2642–2647. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.5.2642
Pyott, S. J., & Rosenmund, C. (2002). The effects of temperature on vesicular supply and release in autaptic cultures of rat and mouse hippocampal neurons. Journal of Physiology, 539(Pt 2), 523–535. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2001.013277
Sankaranarayanan, S., De Angelis, D., Rothman, J. E., & Ryan, T. A. (2000). The use of pHluorins for optical measurements of presynaptic activity. Biophysical Journal, 79(4), 2199–2208. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(00)76468-X
Sharma, R., & Markar, H. R. (1994). Mortality in affective disorder. Journal of Affective Disorders, 31(2), 91–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0327(94)90112-0
Soykan, T., Kaempf, N., Sakaba, T., Vollweiter, D., Goerdeler, F., Puchkov, D., Kononenko, N. L., & Haucke, V. (2017). Synaptic vesicle endocytosis occurs on multiple timescales and is mediated by formin-dependent actin assembly. Neuron, 93(4), 854–866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.02.011
Srisurapanont, M., Pratoomsri, W., & Maneeton, N. (2000). Evaluation of three simple methods for predicting therapeutic lithium doses. Psychiatry Research, 94(1), 83–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0165-1781(00)00133-5
Tang, W., Thevathasan, J. V., Lin, Q., Lim, K. B., Kuroda, K., Kaibuchi, K., Bilger, M., Soong, T. W., & Fivaz, M. (2016). Stimulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis by the mental disease gene DISC1 is mediated by N-type voltage-gated calcium channels. Frontier in Synaptic Neuroscience, 8, 15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsyn.2016.00015
Tobe, B. T. D., Crain, A. M., Winquist, A. M., Calabrese, B., Makihara, H., Zhao, W. N., Lalonde, J., Nakamura, H., Konopaske, G., Sidor, M., Pernia, C. D., Yamashita, N., Wada, M., Inoue, Y., Nakamura, F., Sheridan, S. D., Logan, R. W., Brandel, M., Wu, D., … Snyder, E. Y. (2017). Probing the lithium-response pathway in hiPSCs implicates the phosphoregulatory set-point for a cytoskeletal modulator in bipolar pathogenesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 114(22), E4462–E4471. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1700111114
Voglmaier, S. M., Kam, K., Yang, H., Fortin, D. L., Hua, Z., Nicoll, R. A., & Edwards, R. H. (2006). Distinct endocytic pathways control the rate and extent of synaptic vesicle protein recycling. Neuron, 51(1), 71–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2006.05.027
Yoshimura, T., Kawano, Y., Arimura, N., Kawabata, S., Kikuchi, A., & Kaibuchi, K. (2005). GSK-3beta regulates phosphorylation of CRMP-2 and neuronal polarity. Cell, 120(1), 137–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2004.11.012
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Drs Simon Richardson, Giulia Getty, Lauren Pecorino, and members of the Fivaz lab for critical reading of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by research grants to K-LL from the Ministry of Education, Singapore under its AcRF Tier 3 (MOE2017-T3-1-002) and research grants to MF from the Leverhulme Trust (RPG-2018-265) and from the Ministry of Education Singapore (MOE2013-T2-1-053).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by WT, BC, and MF under the supervision of K-LL The first draft of the manuscript was written by MF and all authors commented on previous version of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical Approval
All animal procedures were approved by the SingHealth Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) Singapore.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, W., Cory, B., Lim, KL. et al. The Mood Stabilizer Lithium Slows Down Synaptic Vesicle Cycling at Glutamatergic Synapses. Neuromol Med 25, 125–135 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-022-08729-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-022-08729-8