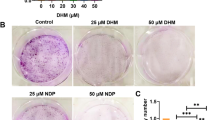
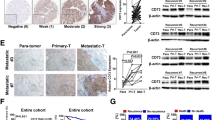
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the second lethal cancer. Short overall survival, low five-year survival rate, and unimproved treatment efficacy urge the need to improve HCC prognosis. Adiponectin is key protector against cancer and hepatic abnormalities. Hypoadiponectinemia occurs in and promotes carcinogenesis and hepatic diseases. Adiponectin reactivation by different methods showed impressive effect against cancer and hepatic diseases. Recently, AdipoRon, an adiponectin receptor agonist, can interact with both Adiponectin receptors. AdipoRon showed promising anti-cancer effect in some cancers, but no study on HCC yet. The in vitro effect of AdipoRon on HCC was investigated by cell viability, migration, invasion, colony formation and apoptosis assays. The signalling alteration was determined by RT-qPCR and Western blot. The effect of treatment was interpreted by comparison between treatments and control. The difference between two cell lines was relatively compared. Our results showed significant in vitro anti-cancer effect of AdipoRon via AMPK- and dose-dependent manner. Huh7 cells showed a lower level of AdipoR1/2 and a superior proliferation and aggressiveness, compared to Hep3B. In addition, Huh7 cells were more sensitive to AdipoRon treatment (lower IC50, less cell growth, migration, invasion and colonies upon AdipoRon treatment) than Hep3B cells. In conclusion, AdipoRon effectively inhibited HCC growth and invasiveness in vitro. The deficient expression of adiponectin receptors affects efficacy of AdipoRon and aggressiveness of HCC cells.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available due to the management policy but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Sung, H., Ferlay, J., Siegel, R. L., Laversanne, M., Soerjomataram, I., Jemal, A. & Bray, F. (2021). Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 71, 209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660.
Ferlay, J., Soerjomataram, I., Dikshit, R., Eser, S., Mathers, C., Rebelo, M., Parkin, D. M., Forman, D. & Bray, F. (2015). Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. International Journal of Cancer, 136, E359–E386. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.29210.
Bray, F., Ferlay, J., Soerjomataram, I., Siegel, R. L., Torre, L. A. & Jemal, A. (2018). Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countrie.CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 68, 394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492.
Torre, L. A., Bray, F., Siegel, R. L., Ferlay, J., Lortet-Tieulent, J. & Jemal, A. (2015). Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 65, 87–108. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21262.
Villanueva, A.(2019). Hepatocellular carcinoma. New England Journal of Medicine, 380, 1450–1462. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1713263.
Kim, D. W., Talati, C. & Kim, R. (2017). Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): beyond sorafenib-chemotherapy. Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology, 8, 256–265. https://doi.org/10.21037/jgo.2016.09.07.
Giannini, E. G., Farinati, F., Ciccarese, F., Pecorelli, A., Rapaccini, G. L., Di Marco, M., Benvegnù, L., Caturelli, E., Zoli, M., Borzio, F., Chiaramonte, M., & Trevisani, F. (2015). Prognosis of untreated hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology, 61, 184–190. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.27443.
Fu, S., Xu, H., Gu, M., Liu, C., Wan, X., Chen, Y., Chen, Q., Zhou, J., & Wang, Z. (2017). Lack of adiponectin and adiponectin receptor 1 contributes to benign prostatic hyperplasia. Oncotarget, 8, 88537–88551. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.19877.
Nehme, R., Diab-Assaf, M., Decombat, C., Delort, L., & Caldefie-Chezet, F. (2022). Targeting adiponectin in breast cancer. Biomedicines 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10112958.
Yamauchi, T., Kamon, J., Ito, Y., Tsuchida, A., Yokomizo, T., Kita, S., Sugiyama, T., Miyagishi, M., Hara, K., Tsunoda, M., Murakami, K., Ohteki, T., Uchida, S., Takekawa, S., Waki, H., Tsuno, N. H., Shibata, Y., Terauchi, Y., Froguel, P., Tobe, K., Koyasu, S., Taira, K., Kitamura, T., Shimizu, T., Nagai, R., & Kadowaki, T. (2003). Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects. Nature, 423, 762–769. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01705.
Dalamaga, M., Diakopoulos, K. N., & Mantzoros, C. S. (2012). The role of adiponectin in cancer: a review of current evidence. Endocrine Reviews, 33, 547–594. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2011-1015.
Kamada, Y., Matsumoto, H., Tamura, S., Fukushima, J., Kiso, S., Fukui, K., Igura, T., Maeda, N., Kihara, S., Funahashi, T., Matsuzawa, Y., Shimomura, I. & Hayashi, N. (2007). Hypoadiponectinemia accelerates hepatic tumor formation in a nonalcoholic steatohepatitis mouse model. Journal of Hepatology, 47, 556–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2007.03.020.
Fujisawa, T., Endo, H., Tomimoto, A., Sugiyama, M., Takahashi, H., Saito, S., Inamori, M., Nakajima, N., Watanabe, M., Kubota, N., Yamauchi, T., Kadowaki, T., Wada, K., Nakagama, H., & Nakajima, A. (2008). Adiponectin suppresses colorectal carcinogenesis under the high-fat diet condition. Gut, 57, 1531–1538. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2008.159293.
Nigro, E., Scudiero, O., Sarnataro, D., Mazzarella, G., Sofia, M., Bianco, A. & Daniele, A. (2013). Adiponectin affects lung epithelial A549 cell viability counteracting TNFalpha and IL-1ss toxicity through AdipoR1. International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 45, 1145–1153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2013.03.003.
Gamberi, T., Magherini, F., Modesti, A. & Fiaschi, T. (2018) Adiponectin signaling pathways in liver diseases. Biomedicines 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines6020052.
Yokota, T., Oritani, K., Takahashi, I., Ishikawa, J., Matsuyama, A., Ouchi, N., Kihara, S., Funahashi, T., Tenner, A. J., Tomiyama, Y., & Matsuzawa, Y. (2000). Adiponectin, a new member of the family of soluble defense collagens, negatively regulates the growth of myelomonocytic progenitors and the functions of macrophages. Blood, 96, 1723–1732. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.V96.5.1723.
Kelesidis, I., Kelesidis, T. & Mantzoros, C. S. (2006). Adiponectin and cancer: a systematic review. British Journal of Cancer, 94, 1221–1225. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6603051.
Ouchi, N., Shibata, R. & Walsh, K. (2005). AMP-activated protein kinase signaling stimulates VEGF expression and angiogenesis in skeletal muscle. Circulation Research, 96, 838–846. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.0000163633.10240.3b.
Saxena, N. K., Fu, P. P., Nagalingam, A., Wang, J., Handy, J., Cohen, C., Tighiouart, M., Sharma, D., & Anania, F. A. (2010). Adiponectin modulates C-jun N-terminal kinase and mammalian target of rapamycin and inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology, 139, 1762–1773. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2010.07.001.
Okada-Iwabu, M., Yamauchi, T., Iwabu, M., Honma, T., Hamagami, K., Matsuda, K., Yamaguchi, M., Tanabe, H., Kimura-Someya, T., Shirouzu, M., Ogata, H., Tokuyama, K., Ueki, K., Nagano, T., Tanaka, A., Yokoyama, S., & Kadowaki, T. (2013). A small-molecule AdipoR agonist for type 2 diabetes and short life in obesity. Nature, 503, 493–499. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12656.
Akimoto, M., Maruyama, R., Kawabata, Y., Tajima, Y., & Takenaga, K. (2018). Antidiabetic adiponectin receptor agonist AdipoRon suppresses tumour growth of pancreatic cancer by inducing RIPK1/ERK-dependent necroptosis. Cell Death & Disease, 9, 804 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0851-z.
Ragone, A., Salzillo, A., Spina, A., Naviglio, S. & Sapio, L. (2022). Integrating gemcitabine-based therapy with adiporon enhances growth inhibition in human PDAC cell lines. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 13, 837503. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.837503.
Zhang, Z., Du, J., Xu, Q., **ng, C., Li, Y., Zhou, S., Zhao, Z., Mu, Y., Zhao, Z. A., Cao, S., & Li, F. (2022) Adiponectin suppresses metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through blocking the activation of NF-kappaB and STAT3 signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232112729.
Zhang, Z., Du, J., Shi, H., Wang, S., Yan, Y., Xu, Q., Zhou, S., Zhao, Z., Mu, Y., Qian, C., Zhao, A. Z., Cao, S. & Li, F. (2022). Adiponectin suppresses tumor growth of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through activating AMPK signaling pathway. Journal of Translational Medicine, 20, 89. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-022-03283-0.
Sapio, L., Nigro, E., Ragone, A., Salzillo, A., Illiano, M., Spina, A., Polito, R., Daniele, A., & Naviglio, S. (2020). AdipoRon affects cell cycle progression and inhibits proliferation in human osteosarcoma cells. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2020, 7262479 https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/7262479.
Wang, S. J., Wang, C., Wang, W. Q., Hao, Q. Q., & Liu, Y. F. (2020). [Adiponectin receptor agonist adiporon inhibits the proliferation of myeloma cells via the AMPK/Autophagy pathway]. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi, 28, 171–176. https://doi.org/10.19746/j.cnki.issn.1009-2137.2020.01.029.
Ramzan, A. A., Bitler, B. G., Hicks, D., Barner, K., Qamar, L., Behbakht, K., Powell, T., Jansson, T., & Wilson, H. (2019). Adiponectin receptor agonist AdipoRon induces apoptotic cell death and suppresses proliferation in human ovarian cancer cells. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 461, 37–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-019-03586-9.
Garcia-Areas, R., Libreros, S., Amat, S., Keating, P., Carrio, R., Robinson, P., Blieden, C., & Iragavarapu-Charyulu, V. (2014). Semaphorin7A promotes tumor growth and exerts a pro-angiogenic effect in macrophages of mammary tumor-bearing mice. Frontiers in Physiology, 5, 17 https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2014.00017.
Mehta, V., Suman, P., & Chander, H. (2022). High levels of unfolded protein response component CHAC1 associates with cancer progression signatures in malignant breast cancer tissues. Clinical and Translational Oncology, 24, 2351–2365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-022-02889-6.
**ao, R., Wang, S., Guo, J., Liu, S., Ding, A., Wang, G., Li, W., Zhang, Y., Bian, X., Zhao, S., & Qiu, W. (2022). Ferroptosis-related gene NOX4, CHAC1 and HIF1A are valid biomarkers for stomach adenocarcinoma. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 26, 1183–1193. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.17171.
Kadowaki, T., Yamauchi, T., Kubota, N., Hara, K., Ueki, K., & Tobe, K. (2006). Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in insulin resistance, diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 116, 1784–1792. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI29126.
Kadowaki, T., & Yamauchi, T. (2005). Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors. Endocrine Reviews, 26, 439–451. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2005-0005.
Yamauchi, T., Nio, Y., Maki, T., Kobayashi, M., Takazawa, T., Iwabu, M., Okada-Iwabu, M., Kawamoto, S., Kubota, N., Kubota, T., Ito, Y., Kamon, J., Tsuchida, A., Kumagai, K., Kozono, H., Hada, Y., Ogata, H., Tokuyama, K., Tsunoda, M., Ide, T., Murakami, K., Awazawa, M., Takamoto, I., Froguel, P., Hara, K., Tobe, K., Nagai, R., Ueki, K., & Kadowaki, T. (2007). Targeted disruption of AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 causes abrogation of adiponectin binding and metabolic actions. Nature Medicine, 13, 332–339. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1557.
Parida, S., Siddharth, S., & Sharma, D. (2019) Adiponectin, obesity, and cancer: clash of the bigwigs in health and disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102519.
Nigro, E., Daniele, A., Salzillo, A., Ragone, A., Naviglio, S., & Sapio, L. (2021) AdipoRon and other adiponectin receptor agonists as potential candidates in cancer treatments. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115569.
Pham, D. V., & Park, P. H. (2022). Adiponectin triggers breast cancer cell death via fatty acid metabolic reprogramming. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 41, 9 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-021-02223-y.
Falk Libby, E., Liu, J., Li, Y. I., Lewis, M. J., Demark-Wahnefried, W., & Hurst, D. R. (2016). Globular adiponectin enhances invasion in human breast cancer cells. Oncology Letters, 11, 633–641. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2015.3965.
Gao, Q., & Zheng, J. (2014). Adiponectin-induced antitumor activity on prostatic cancers through inhibiting proliferation. Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics, 70, 461–465. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-9941-4.
Nakayama, S., Miyoshi, Y., Ishihara, H., & Noguchi, S. (2008). Growth-inhibitory effect of adiponectin via adiponectin receptor 1 on human breast cancer cells through inhibition of S-phase entry without inducing apoptosis. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment, 112, 405–410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-007-9874-3.
Abdul-Ghafar, J., Oh, S. S., Park, S. M., Wairagu, P., Lee, S. N., Jeong, Y., Eom, M., Yong, S. J., & Jung, S. H. (2013). Expression of adiponectin receptor 1 is indicative of favorable prognosis in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine, 229, 153–162. https://doi.org/10.1620/tjem.229.153.
Niu, K., Asada, M., Okazaki, T., Yamanda, S., Ebihara, T., Guo, H., Zhang, D., Nagatomi, R., Arai, H., Kohzuki, M., & Ebihara, S. (2012). Adiponectin pathway attenuates malignant mesothelioma cell growth. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology, 46, 515–523. https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2011-0068OC.
Manley, S. J., Olou, A. A., Jack, J. L., Ruckert, M. T., Walsh, R. M., Eades, A. E., Bye, B. A., Ambrose, J., Messaggio, F., Anant, S., & VanSaun, M. N. (2022). Synthetic adiponectin-receptor agonist, AdipoRon, induces glycolytic dependence in pancreatic cancer cells. Cell Death & Disease, 13, 114 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-022-04572-8.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Department of equipment and material supplies, Vietnam Military Medical University for their support.
Funding
Thi Mai Ly Nguyen was funded by Vingroup JSC and supported by the Postdoctoral Scholarship Programme of Vingroup Innovation Foundation (VINIF), Institute of Big Data, code VINIF.2021.STS.25”. This research is funded by Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED) under grant number 108.02-2019.324. The funder had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.C.B., L.T.N. and M.L.T.N. designed the study and acquired the fund. K.C.B., P.B. and M.L.T.N. interpreted data and drafted manuscript. V.T.P. and B.T.T. provide technical and ideal consultant. M.L.T.N., C.P. and P.L.T.N. performed experiments. Q.V.L., X.C.H. and D.T.L. revised data analysis. All authors reviewed and approved the final version of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, M.L.T., Pham, C., Pham, V.T. et al. Adiponectin Receptor Agonist Effectively Suppresses Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth. Cell Biochem Biophys (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-024-01217-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-024-01217-9