Abstract
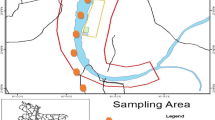
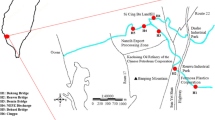
Among environmental contaminants, the rising level of cadmium in freshwater ecosystems is one of the most significant global concerns. The study addresses the current pollution status of cadmium in the middle stretch of River Ganga and explores the potential hazard associated with the consumption of 15 commercially important fish species by the inhabitants. Together 72 water and sediment samples were analyzed from the four representative sampling sites of River Ganga after the surveillance of major anthropogenic stressors. The concentration of cadmium ranges from 0.003 to 0.011 mg/l and 0.2 to 3.48 mg/kg in water and sediment respectively in 2022. The average concentration of cadmium was recorded to be the highest in Channa punctatus (1.35 mg/kg), followed by Rita rita = Johnius coitor (1.15 mg/kg), and the lowest in Labeo bata (0.2 mg/kg). The finding highlights greater exposure duration and feeding preferences of fish species have played a significant role in the bioaccumulation of the metal in the riverine system. Notably, the domestic effluents, agricultural runoffs, and pollutants brought along by the tributaries of River Ganga are identified as the main anthropogenic stressors for the moderate to considerably polluted status of the River Ganga. The target hazard quotient (THQ) and target carcinogenic risk (TCR) have revealed a higher susceptibility to cadmium contamination in children followed by females, and males. In addition, hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) has noted intake of Rita rita, Channa punctata, Puntius sophore, and Johnius coitor could be more detrimental to children’s health than adults.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Hayat MT, Nauman M, Nazir N, Ali S, Bangash N (2019) Environmental hazards of cadmium: past, present, and future. In: Cadmium toxicity and tolerance in plants. Academic Press, pp 163–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-814864-8.00007-3
UNEP (2008) Interim review of scientific information on cadmium. United Nations Environment Program, Geneva
Zafar MM, Kumari A (2024) Spatio-temporal evaluation of the impact of anthropogenic stressors on physico-chemical characteristics and water quality of the river Ganga using GIS-based approach in the middle Gangetic Plains at Patna, Bihar, India. Water Sci Technol 89(5):1382–1400. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2024.053
**e N, Kang C, Ren D, Zhang L (2022) Assessment of the variation of heavy metal pollutants in soil and crop plants through field and laboratory tests. Sci Total Environ 811:152343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152343
Patel UN, Patel UD, Khadayata AV, Vaja RK, Patel HB, Modi CM (2021) Assessment of neurotoxicity following single and co-exposure of cadmium and mercury in adult zebrafish: behavior alterations, oxidative stress, gene expression, and histological impairment in brain. Water Air Soil Pollut 232(8):340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05274-1
Cai Y, Zhu K, Shen L, Ma J, Bao L, Chen D, Wei L, Wei N, Liu B, Wu Y, Chen S (2022) Evolved biosensor with high sensitivity and specificity for measuring cadmium in actual environmental samples. Environ Sci Technol 28;56:(14):10062–71
Haider FU, Coulter JA, Cheema SA, Farooq M, Wu J, Zhang R, Shuaijie G, Liqun C (2021) Co-application of biochar and microorganisms improves soybean performance and remediate cadmium-contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 1(214):112112
Sulaiman MA, Zafar MM, Divya AS, Kumari A (2024) Investigating the 96h LC50 of mercury and cadmium on Channa punctatus (Bloch): a comparative acute toxicity bioassay. J Ecophysiol Occup Health 24(1):89–98. https://doi.org/10.18311/jeoh/2024/36093
Abbas MM, El-Sharkawy SM, Mohamed HR, Elaraby BE, Shaban WM, Metwally MG, Farrag DM (2023) Heavy metals assessment and health risk to consumers of two commercial fish species from polyculture fishponds in El-Sharkia and Kafr El-Sheikh, Egypt: Physiological and Biochemical Study. Biol Trace Elem Res 22:1–6
Afifi MA, Radwan M, Abbas MM, Hwihy HM, Alabssawy AN, Khalaf-Allah HM (2024) Threat of heavy metal pollutants and parasites to freshwater fish with special reference to their risk of cancer to humans in Egypt. Aquaculture 16:740833
Jali P, Pradhan C, Das AB (2016) Effects of cadmium toxicity in plants: a review article. Sch Acad J Biosci 4(12):1074–1081
Bautista OV, Fischer G, Cárdenas JF (2013) Cadmium and chromium effects on seed germination and root elongation in lettuce, spinach and Swiss chard. Agronomía colombiana 31(1):48–57
Liu L, Shang YK, Li L, Chen YH, Qin ZZ, Zhou LJ, Liao JQ (2018) Impact of cadmium stress on seedling growth, cadmium accumulation, and photosynthesis in Dongying wild soybean. Photosynthetica 56:1346–1352
Zhang C, Chen Y, Xu W, Chi S, Li T, Li Y, Feng D (2019) Resistance of alfalfa and Indian mustard to cadmium and the correlation of plant cadmium uptake with soil cadmium form. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:13804–13811
Kumari A, Sinha SK, Rani N, Sinha RK (2021) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in water, sediment, and fish of the river Ganga at Varanasi. India Arab J Geosci 14(22):2346
Hossain MB, Tan** F, Rahman MS, Yu J, Akhter S, Noman MA, Sun J (2022) Metals bioaccumulation in 15 commonly consumed fishes from the lower Meghna river and adjacent areas of Bangladesh and associated human health hazards. Toxics 10(3):139
Lech T, Sadlik JK (2017) Cadmium concentration in human autopsy tissues. Biol Trace Elem Res 179:172–177
Hayashi C, Koizumi N, Nishio H, Koizumi N, Ikeda M (2012) Cadmium and other metals in autopsy samples from a cadmium-polluted area and non-polluted control areas in Japan. Biol Trace Elem Res 145:10–22
Beneš B, Jakubiec K, Šmid J, Spĕváčková V (2000) Determination of thirty-two elements in human autopsy tissues. Biol Trace Elem Res 75:195–203
Bocio A, Nadal M, Garcia F, Domingo JL (2005) Monitoring metals in the population living in the vicinity of a hazardous waste incinerator. Biol Trace Elem Res 106:41–50
Mari M, Nadal M, Schumacher M, Domingo JL (2014) Human exposure to metals: levels in autopsy tissues of individuals living near a hazardous waste incinerator. Biol Trace Elem Res 159:15–21
García A, Ortega J, Domingo JL, Corbella J (2001) Accumulation of metals in autopsy tissues of subjects living in Tarragona county. Spain J Environ Sci Health A 36:1767–1786
Thompson J, Bannigan J (2008) Cadmium: toxic effects on the reproductive system and the embryo. Reprod Toxicol 25:304–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2008.02.001
Fatima G, Raza AM, Hadi N, Nigam N, Mahd AA (2019) Cadmium in human diseases: it’s more than just a mere metal. Indian J Clin Biochem 34:371–378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-019-00839-8
Kumar S, Sharma A (2019) Cadmium toxicity: effects on human reproduction and fertility. Rev Environ Health 34:327–338. https://doi.org/10.1515/reveh-2019-0016
Geng HX, Wang L (2019) Cadmium: toxic effects on placental and embryonic development. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 67:102–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2019.02.006
Bernard A (2008) Cadmium & its adverse effects on human health. Indian J Med Res 128(4):557–564
Orieux N, Cambier S, Gonzalez P, Morin B, Adam C, Garnier-Laplace J, Bourdineaud JP (2011) Genotoxic damages in zebrafish submitted to a polymetallic gradient displayed by the Lot River (France). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:974–983
Genchi G, Sinicropi MS, Lauria G, Carocci A, Catalano A (2020) The effects of cadmium toxicity. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:3782
Reyes-Hinojosa D, Lozada-Pérez CA, Zamudio Cuevas Y, López-Reyes A, Martínez-Nava G, Fernández-Torres J, Olivos-Meza A, Landa-Solis C, Gutiérrez-Ruiz MC, Rojas del Castillo E et al (2019) Toxicity of cadmium in musculoskeletal diseases. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 72:103219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2019.103219
Noman A, Feng W, Zhu G, Hossain MB, Chen Y, Zhang H, Sun J (2022) Bioaccumulation and human health risks of metals in commercially important fish and shellfish from Hangzhou Bay. China Sci Rep 12(1):4634
Rahman MS, Molla AH, Saha N, Rahman A (2012) Heavy metal levels and risk assessment in edible fishes from the Bangshi River, Savar, Dhaka. Bangladesh Food Chem 134(4):1847–1854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.03.071
Jiang H, Qin D, Chen Z, Tang S, Bai S, Mou Z (2016) Fish heavy metal levels and health risk assessment in the Heilongjiang River. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 97:536–542. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1894-4
Ali H, Khan E (2018) Bioaccumulation of non-essential hazardous heavy metals and metalloids in freshwater fish: risks to human health. Environ Chem Lett 16(3):903–917. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-0734-7
Ahmad J, Ali AA, Baig MA, Iqbal M, Haq I, Qureshi MI (2019) Role of phytochelatins in plant cadmium stress tolerance. Cadmium Toxicity Tolerance Plants 185–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/B9780128148648000085
Arisekar U, Shakila RJ, Shalini R, Jeyasekaran G (2020) Human health risk assessment of heavy metals in aquatic sediments and freshwater fish from the Thamirabarani River, Western Ghats of South Tamil Nadu. Mar Pollut Bull 159:111496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111496
Shah AA, Khan WU, Yasin NA, Akram W, Ahmad A, Abbas M, Ali A, Safdar MN (2020) Butanolide mitigates cadmium stress by enhancing plant growth, photosynthetic parameters, and antioxidant defense in Brassica oleracea. Chemosphere 261:127728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127728
Gupta A, Rai DK, Pandey RS, Sharma B (2009) Analysis of heavy metals in riverine water, sediments, and fish from the River Ganges at Allahabad. Environ Monit Assess 157:449–458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0547-4
Leena S, Choudhary SK, Singh PK (2012) Assessment of heavy metal concentrations in water and sediment of the River Ganga at selected sites in the Middle Ganga Plain. Int J Res Chem Environ 2(4):236–243
Jaiswal D, Pandey J (2018) Impact of heavy metals on microbial enzyme activity in riverbed sediments: Ecotoxicological implications in the Ganga River (India). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 150:104–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.12.015
Siddiqui E, Verma K, Pandey U, Pandey J (2019) Metal contamination in seven tributaries of the Ganga River and assessment of health risks from fish consumption. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 77:263–278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-019-00638-5
Kumar A, Garg V (2019) Heavy metal and physico-chemical characteristics of the River Ganga from Rishikesh to Brijghat. India J Environ Biosci 33(2):243–250
Maurya PK, Malik DS, Yadav KK, Kumar A, Kumar S, Kamyab H (2019) Bioaccumulation and potential sources of heavy metal contamination in fish species in the River Ganga basin: evaluation of possible human health risks. Toxicol Rep 6:472–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2019.06.005
Sulaiman MA, Zafar MM, Prabhakar R, Kumar R, Sinha RK, Kumari A (2023) Multivariate statistical approach to assess the hydro-geochemistry of groundwater quality in the middle Ganga river basin, Patna, India. Acta Geophys 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-023-01071-y
Zafar MM, Sulaiman MA, Prabhakar R, Kumari A (2022) Suitability evaluation of groundwater for irrigation using irrigation water quality indices and geographical information systems (GIS) at Patna (Bihar), India. Int J Energy Water Resour 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42108-022-00193-1
Census (2011) https://www.census2011.co.in/census/district/82-patna.html. Accessed 19 Mar 2024
Bihar State Ganga River Conservation and Program Management Society, Bihar State Pollution Control Board (2017). Action plan for conservation of River Ganga in Bihar. https://bspcb.bihar.gov.in/Conservation%20%20River%20Ganga.pdf. Accessed 19 March 2024
Khalili Tilami S, Sampels S (2018) Nutritional value of fish: lipids, proteins, vitamins, and minerals. Rev Fish Sci Aquac 26(2):243–253. https://doi.org/10.1080/23308249.2017.1399104
Bosch AC, O’Neill B, Sigge GO, Kerwath SE, Hoffman LC (2016) Heavy metals in marine fish meat and consumer health: a review. J Sci Food Agric 96(1):32–48. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.7360
Hao X, Zhu P, Zhang H, Liang Y, Yin H, Liu X, Bai L, Liu H, Jiang H (2019) Mixotrophic acidophiles increase the soluble fraction of cadmium and phytoextraction efficiency from cadmium-contaminated soils. Sci Total Environ 655:347–355
Sinha RK, Kannan K (2014) Ganges River dolphin: overview of biology, ecology, and conservation status in India. Ambio 43:1029–1046
APHA (2017) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 23rd edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, D.C
De Zwart D, and Trivedi RC (1995) Manual on integrated water quality evaluation
Turekian KK, Wedepohl KH (1961) Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth’s crust. Geol Soc Am Bull 72(2):175–192
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14(8):975–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
Karki D, Verma A (2021) Assessment of heavy metal contamination within the sediments in some freshwater lakes of Udaipur. EQA - Int J Environ Qual 46:37–45. https://doi.org/10.6092/issn.2281-4485/13351
WHO (World Health Organization) (2008) Guidance for identifying populations at risk from mercury exposure. Mercury Publications, Geneva https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/guidance-for-identifying-populations-at-risk-frommercury-exposure. Accessed 24 Jan 2024
USEPA (2000) Guidance for assessing chemical contaminant data for use in fish advisories. Volume 1 fish sampling and analysis, 3rd edn. Office of Science and Technology Office of Water U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Washington, DC: Document No. EPA 823-B-00–007. https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2018-11/documents/guidance-assess-chemicalcontaminant-vol1-third-edition.pdf. Accessed 02 Mar 2024
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (1999) Integrated risk information system (IRIS) on cadmium. National Center for Environmental Assessment, Office of Research and Development, Washington, DC. Document No. EPA 823-B-00–007. https://www.epa.gov/risk/regional-screening-levels-rsls-users-guide#toxicity. Accessed 22 Jan 2024
Divya, Sulaiman MA, Zafar MM, Kumari A (2023) Assessing fluoride toxicity and the major contributors to ionic constituents in the groundwater aquifer of the Middle Ganga River Basin, Rohtas, India. Int J Energy Water Resour 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42108-023-00245-0
USEPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency) (1989) Risk assessment guidance for superfund (Volume 1) - Human Health Evaluation Manual Part A Interim Final. EPA/540/1–89/002. Office of Emergency and Remedial Response, Washington, DC, USA
Abdel-Kader HH, Mourad MH (2023) Estimation of cadmium in muscles of five freshwater fish species from Manzalah Lake and possible human risk assessment of fish consumption (Egypt). Biol Trace Elem Res 201(2):937–945. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03188-5
Tomlinson DL, Wilson JG, Harris CR, Jeffrey DW (1980) Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresun 33:566–575
Arnot JA, Gobas FA (2006) A review of bioconcentration factor (BCF) and bioaccumulation factor (BAF) assessments for organic chemicals in aquatic organisms. Environ Rev 14(4):257–297. https://doi.org/10.1139/a06-005
Salam MA, Paul SC, Shaari FI, Rak AE, Ahmad RB, Kadir WR (2019) Geostatistical distribution and contamination status of heavy metals in the sediment of Perak River. Malays Hydrol 6(2):30
US EPA (2000) Handbook for non-cancer health effects evaluation. Washington (DC): U.S. Environ Prot Agency
US EPA (2000) Guidance for Assessing Chemical Contamination Data for Use in Fish Advisories, vol. II. Risk Assessment and Fish Consumption Limits EPA/823-B94- 004. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
CCFAC (Codex Committee on Food Additives and Contaminants) (2001) Comments Submitted on Draft Maximum Levels for Lead and Cadmium, Thirty-third session, Agenda 16c/16d, joint FAO/WHO standards Programme, Hague, The Netherlands
WHO (2011) Joint FAO/ WHO Food Standards Programme Codex Committee on Contaminants in Foods. Fifth Session. The Hague, the Netherlands 90, pp. 21–25.FDA. Total diet study statistics on element results. Washington, DC: US Food and Drug Administration, (2000)
FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization) (1983) Compilation of legal limits for hazardous substances in fish and fishery products. FAO Fisheries Circular No. 764, FAO, Rome, p 102
Jaiswal M, Gupta SK, Chabukdhara M, Nasr M, Nema AK, Hussain J, Malik T (2022) Heavy metal contamination in the complete stretch of Yamuna River: a fuzzy logic approach for comprehensive health risk assessment. PLoS ONE 17(8):e0272562
Kumar S, Saxena A (2021) Evaluation of heavy metals in sediment, water and Macrophyte (Eicchornea crassipes) of Yamuna River at Delhi. IJCS 9(1):3552–3556
Haloi N, Sarma HP (2012) Heavy metal contaminations in the groundwater of Brahmaputra flood plain: an assessment of water quality in Barpeta District, Assam (India). Environ Monit Assess 184:6229–6237
Sachan A, Singh RV, Gupta B, Kulesh R, Gupta V, Khare A (2023) Quantitative analysis of cadmium, chromium, and nickel in different water resources of Jabalpur by ICP-OES. Retrieved Pharma J
Sani, Shehu A (2018) Determination of heavy metal concentrations in selected detergents used in Kano Metropolis Nigeria. Environ Toxicol Stud J 2(1):1–3
Saini S, and Dhania G (2020) Cadmium as an environmental pollutant: ecotoxicological effects, health hazards, and bioremediation approaches for its detoxification from contaminated sites. Bioremediation of Industrial Waste for Environmental Safety: Volume II: Biological Agents and Methods for Industrial Waste Management 357–387
Kaur M, Kumar A, Mehra R, Kaur I (2020) Quantitative assessment of exposure of heavy metals in groundwater and soil on human health in Reasi district, Jammu and Kashmir. Environ Geochem Health 42:77–94
Aonghusa CN, Gray NF (2002) Laundry detergents as a source of heavy metals in Irish domestic wastewater. J Environ Sci Health A 37(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1081/ESE-100108477
Ali S, Hussain S, Khan R, Mumtaz S, Ashraf N, Andleeb S, Shakir HA, Tahir HM, Khan MKA, Ulhaq M (2019) Renal toxicity of cadmium and mercury and their amelioration with ascorbic acid in rabbits. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:3909–3920
Pandey J, Singh R (2017) Urban influences on heavy metals in sediments of the Ganga River: upstream and downstream analysis. Appl Water Sci 7:1669–1678
Das S, Nath M, Laskar AK, DebRoy S, Deb S, Barhai A, Choudhury AP (2021) Lead and cadmium exposure network in children in a periurban area in India: susceptibility and health risk. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:28133–28145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12608-3
Alam MF, Akhter M, Mazumder B, Ferdous A, Hossain MD, Dafader NC, Ahmed FT, Kundu SK, Taheri T, Atique Ullah AKM (2019) Assessment of heavy metals in commonly used cosmetics in Bangladesh and associated human health risks. J Anal Sci Technol 10(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40543-018-0162-0
Saleh FA, Saif RN, Murshed DM, Abdulmageed BA (2020) Determination of Cadmium in some cosmetic products. Preprints
Radwan A, El-Sewify IM, Azzazy HMES (2022) Monitoring of cobalt and cadmium in daily cosmetics using powder and paper optical chemosensors. ACS Omega 7(18):15739–15750
Kumar D, Malik DS, Kumar N, Gupta N, Gupta V (2020) Spatial changes in water and heavy metal contamination in water and sediment of river Ganga in the river belt Haridwar to Kanpur. Environ Geochem Health 42:2059–2079
Singh V, Nagpoore NK, Lehri A (2020) Monitoring and assessment of pollution load in surface water of River Ganga around Kanpur, India: a study for suitability of this water for different uses. Environ Technol Innov 18:100676
Matta G, Kumar A, Nayak A, Kumar P, Pant G (2022) Pollution complexity quantification using NPI and HPI of River Ganga system in Himalayan Region. Proc Indian Natl Sci Acad 88(4):651–663
Boral S, Sen IS, Tripathi A, Sharma B, Dhar S (2020) Tracking dissolved trace and heavy metals in the Ganga River from source to sink: a baseline to judge future changes. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 21(10):e2020GC009203
Zaman S, Gobato R, Pramanick P, Biswas P, Chatterjee U, Mitra S, Mitra A (2018) Water quality of the River Ganga in and around the city of Kolkata during and after Goddess Durga immersion. Parana J Sci Educ 4(9):1–7
Dhiman A, Ramanthan AL, Macklin M, Yadav S, Kushwaha S, Mudbhatkal A, Senapathi V (2023) Heavy metal distribution in various environmental matrices and their risk assessment in Ganga River Basin, India. Hum Ecol Risk Assess Int J 29(2):621–650
Khan MYA, Gani KM, Chakrapani GJ (2017) Spatial and temporal variations of physicochemical and heavy metal pollution in Ramganga River—a tributary of River Ganges India. Environ Earth Sci 76:1–13
Ahmad P, Jamaluddin M (2021) Estimation of some heavy metal estimation at sites of Saryug River as lateral tributary of the Ganga in Northern Bihar. Sci Temper 102
Khan R, Saxena A, Shukla S (2020) Evaluation of heavy metal pollution for River Gomti, in parts of Ganga Alluvial Plain. India SN Appl Sci 2(8):1451
Myvizhi P, Devi PA (2020) Heavy metal contamination in water of the River Cauvery-a case study of Erode, Salem and Namakkal districts, Tamil Nadu. J Himalayan Ecol Sustain Dev 15:1–18
Mishra S, Kumar A (2021) Estimation of physicochemical characteristics and associated metal contamination risk in the Narmada River, India. Environ Eng Res 26(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2019.521
Zhang M, Huang F, Wang G, Liu X, Wen J, Zhang X, **a Y (2017) Geographic distribution of cadmium and its interaction with the microbial community in the Longjiang River: risk evaluation after a shocking pollution accident. Sci Rep 7(1):227
Zhao XM, Yao LA, Ma QL, Zhou GJ, Wang L, Fang QL, Xu ZC (2018) Distribution and ecological risk assessment of cadmium in water and sediment in Longjiang River, China: implication on water quality management after pollution accident. Chemosphere 194:107–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.127
Li K, Cui S, Zhang F, Hough R, Fu Q, Zhang Z, An L (2020) Concentrations, possible sources and health risk of heavy metals in multi-media environment of the Songhua River, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(5):1766
He W, Li F, Yu J, Chen M, Deng Y, Li J, Yan Z (2021) Risk assessment and source apportionment of trace elements in multiple compartments in the lower reach of the **sha River. China Sci Rep 11(1):20041
Abdel-Satar AM, Ali MH, Goher ME (2017) Indices of water quality and metal pollution of Nile River Egypt. Egypt J Aquat Res 43(1):21–29
Ghandour MA, Ali AM, Atef HAM (2021) Temporal variation of lead and cadmium in Nile Water, Assiut City Egypt. Assiut Univ J Chem (AUJC) 50:1–12
Muhammad S, Usman QA (2022) Heavy metal contamination in water of Indus River and its tributaries, northern Pakistan: evaluation for potential risk and source apportionment. Toxin Rev 41(2):380–388. https://doi.org/10.1080/15569543.2021.1882499
Ahmad W, Zubair A, Abbasi HN, Nasir MI (2021) Water study of physical, chemical and heavy metals parameters in river Indus and its tributaries, Sindh, Pakistan: heavy metals in the river Indus. Pak J Sci Ind Res Ser A: Phys Sci 64(2):103–109. https://doi.org/10.52763/PJSIR.PHYS.SCI.64.2.2021.103.109
Kabir MH, Islam MS, Tusher TR, Hoq ME, Muliadi M, Mamun SA (2020) Changes of heavy metal concentrations in Shitalakhya river water of Bangladesh with seasons. Indones J Sci Technol 5(3):395–409
Dey M, Akter A, Islam S, Dey SC, Choudhury TR, Fatema KJ, Begum BA (2021) Assessment of contamination level, pollution risk and source apportionment of heavy metals in the Halda River water. Bangladesh Heliyon 7(12):e08314
Jafarzadeh S, Fard RF, Ghorbani E, Saghafipour A, Moradi-Asl E, Ghafuri Y (2020) Potential risk assessment of heavy metals in the Aharchai River in northwestern Iran. Phys Chem Earth Parts A/B/C 115:102812
Hourieh Fallah S, Bakaeian M, Parsian H, Amouei A, Asgharnia H, Ghanbarian M, Miri SA (2022) Potentially harmful heavy metal contamination in Babolrood river: evaluation for risk assessment in the Mazandaran province Iran. Int J Environ Anal Chem 102(18):7209–7223. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1828386
Bureau of Indian Standards Drinking water (BIS)-specification. IS: 10500, New Delhi (2012)
US EPA. Drinking Water Contaminants (2014). https://www.epa.gov/ground-water-and-drinking-water/table-regulated-drinking-water-contaminants. Accessed 4 Feb 2024
Pandey.
Gupta V, Kumar D, Dwivedi A, Umesh Vishwakarma DS, Malik SP, Mohan N, Gupta N (2023) Heavy metal contamination in river water, sediment, groundwater and human blood, from Kanpur, Uttar Pradesh India. Environ Geochem Health 45(5):1807–1818. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01290-0
Debnath A, Singh PK, Sharma YC (2024) Spatial distribution of heavy metals in the sediments of River Ganges, India: occurrence, contamination, source identification, seasonal variations, map**, and ecological risk evaluation. Mar Pollut Bull 198:115910
Radhakrishnan N, Taneja S, Ambastha S, Pipil H, Haritash AK (2023) Heavy metal profile, mobility, and source characterization in size-fractionated bed-sediments of River Ganga. India Mar Pollut Bull 188:114650
Dhamodharan A, Abinandan S, Aravind U, Ganapathy GP, Shanthakumar S (2019) Distribution of metal contamination and risk indices assessment of surface sediments from Cooum River, Chennai, India. Int J Environ Res 13:853–860
Kumari A, Sulaiman MA, Zafar MM (2023) Heavy metals in the sediment of River Ganga: a review. Weathering and Erosion Processes in the Natural Environment 1–25
Mohanta VL, Naz A, Mishra BK (2019) Distribution of heavy metals in the water, sediments, and fishes from Damodar river basin at steel city, India: a probabilistic risk assessment. Hum Ecol Risk Assess: Int J 26(2):406–429. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1511968
Mondal P, Lofrano G, Carotenuto M, Guida M, Trifuoggi M, Libralato G, Sarkar SK (2021) Health risk and geochemical assessment of trace elements in surface sediment along the Hooghly (Ganges) River Estuary (India). Water 13(2):110
Patel P, Raju NJ, Reddy BSR, Suresh U, Sankar DB, Reddy TVK (2018) Heavy metal contamination in river water and sediments of the Swarnamukhi River Basin, India: risk assessment and environmental implications. Environ Geochem Health 40:609–623
Paramasivam K, Ramasamy V, Suresh G (2015) Impact of sediment characteristics on the heavy metal concentration and their ecological risk level of surface sediments of Vaigai river, Tamilnadu, India. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 137:397–407
Neha KD, Shukla P, Kumar S, Bauddh K, Tiwari J, Kumar N (2017) Metal distribution in the sediments, water and naturally occurring macrophytes in the river Gomti, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India. Curr Sci 1578–1585
Patil SS, Kaushik G (2016) Heavy metal assessment in water and sediments at Jaikwadi dam (Godavari river) Maharashtra. India Int J Environ 5(2):75–88
Kumari P, Hansdah P (2023) Sources and toxicological effects of metal and metalloids on human health through fish consumption in mineral-rich city, Ranchi. India Environ Monit Assess 195(9):1032
Singh H, Kushwaha A, Shukla DN (2018) Assessment of eco-environmental geochemistry of heavy metals pollution of the river Gandak, a major tributary of the river Ganga in northern India. AIP Conf Proc 1952(1):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5032000
Suthar S, Nema AK, Chabukdhara M, Gupta SK (2009) Assessment of metals in water and sediments of Hindon River, India: impact of industrial and urban discharges. J Hazard Mater 171(1–3):1088–1095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.06.109
Ali MM, Saima Rahman Md, Saiful Islam Md, Rakib RJ, Shaharior Hossen Md, Rahman Z, Kormoker T, Idris AM, Phoungthong K (2022) Distribution of heavy metals in water and sediment of an urban river in a develo** country: a probabilistic risk assessment. Int J Sediment Res 37(2):173–187
Jewel AS, Haque A, Amin R, Hasan J, Mondal S, Ahmed S (2020) Heavy metal contamination and human health risk associated with sediment of Ganges River (Northwestern Bangladesh). Nat Environ Pollut Technol 19(2):783–790
Islam MS, Kabir MH, Ali MM, Islam MT, Niger A, Kabir H, Ismail Z, Ahmed S, Ibrahim KA, Idris AM (2023) Assessment of ecological risk for heavy metals in surface sediment of an urban river in a develo** country. Int J Sediment Res 38(6):834–846
Ali J, Khan MA, Nazneen S, Muhammad J, Nasir MJ, Shah MT, Khan S (2018) Assessment of heavy metals and physicochemical characteristics of water and sediments, Kurram River (Pakistan). J Himal Earth Sci 51(1):113–126
El-Saadani Z, Mingqi W, He Z, Hamukwaya SL, Abdel Wahed MSM, Abu Khatita A (2022) Environmental geochemistry and fractionation of cadmium metal in surficial bottom sediments and water of the Nile River. Egypt Toxics 10(5):221. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050221
El-Amier YA, Abd El-Gawad AM (2016) Assessing the sediment pollution using heavy metals indices in the Nile River Branches in Egypt. J Environ Sci Pollut Res 2(3):107–112
Karimian S, Chamani A, Shams M (2020) Evaluation of heavy metal pollution in the Zayandeh-Rud River as the only permanent river in the central plateau of Iran. Environ Monit Assess 192:1–13
Liu B, Dong D, Hua X, Dong W, Li M (2021) Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediment of Songhua River, Northeast China. Chin Geogra Sci 31:223–233
Li R, Tang X, Guo W, Lin L, Zhao L, Hu Y, Liu M (2020) Spatiotemporal distribution dynamics of heavy metals in water, sediment, and zoobenthos in mainstream sections of the middle and lower Changjiang River. Sci Total Environ 714:136779
Chai LY, Li H, Yang ZH, Min XB, Liao Q, Liu Y, Men SH, Xu JX (2017) Heavy metals and metalloids in the surface sediments of the **angjiang River, Hunan, China: distribution, contamination, and ecological risk assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(1):874–885
EPA (2000) Prediction of sediment toxicity using consensus-based freshwaters sediment quality guidelines. https://archive.epa.gov/reg5sfun/ecology/web/pdf/91126.pdf. Accessed 02 Mar 2024
CCME (Conseil canadien des ministres de l’environnement) (1999) Recommandations canadiennes pour la qualité des eaux: protection de la vie aquatique d arsenic. In: Recommandations canadiennes pour la qualité de l’environnement
Singh H, Pandey R, Singh SK, Shukla DN (2017) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in the sediment of the River Ghaghara, a major tributary of the River Ganga in Northern India. Appl Water Sci 7:4133–4149
Park HJ, Kim SU, Jung KY, Lee S, Choi YD, Owens VN, Kumar S, Yun SW, Hong CO (2021) Cadmium phytoavailability from 1976 through 2016: changes in soil amended with phosphate fertilizer and compost. Sci Total Environ 762:143132
Suciu NA, Devivo R, Rizzati N, Capri E (2022) Cd content in phosphate fertilizer: potential risk for the environment and human health? Curr Opin Environ Sci Health 30:100392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coesh.2022.100392
Maqbool A, Ali S, Rizwan M, Arif MS, Yasmeen T, Riaz M, Hussain A, Noreen S, Abdel-Daim MM, Alkahtani S (2020) N-fertilizer (urea) enhances the phytoextraction of cadmium through Solanum nigrum L. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(11):3850
Halcrow W, Mackay DW, Thornton I (1973) The distribution of trace metals and fauna in the Firth of Clyde in relation to the disposal of sewage sludge. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 53(3):721–739. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0025315400058914
Kumari P, Maiti SK (2020) Metal (loid) contamination in water, sediment, epilithic periphyton and fish in three interconnected ecosystems and health risk assessment through intake of fish cooked in Indian style. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(33):41914–41927
Jiang X, Wang J, Pan B, Li D, Wang Y, Liu X (2022) Assessment of heavy metal accumulation in freshwater fish of Dongting Lake, China: effects of feeding habits, habitat preferences and body size. J Environ Sci 112:355–365
Chapman D (1996) Water quality assessments: a guide to the use of biota, sediments and water monitoring report, 2nd edn. Environmental Monitoring, UNESCO, WHO and UNEP, London, UK
Balali-Mood M, Naseri K, Tahergorabi Z, Khazdair MR, Sadeghi M (2021) Toxic mechanisms of five heavy metals: mercury, lead, chromium, cadmium, and arsenic. Front Pharmacol 12:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.643972
Kumar R, Kumar R, Singh A, Sinha RK, Kumari A, Gupta A, Singh J (2019) Distribution of trace metal in Shaune Garang catchment: evidence from particles and nanoparticles. Mater Today: Proc 15:586–594
Abbas MM (2023) Heavy metal levels and cancer risk assessments of the commercial Denis, Sparus aurata collected from Bardawil Lake and private fish farm waters as a cultured source, Egypt. Biol Trace Elem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-023-03880-0
Carroquino MJ, Posada M, Landrigan PJ (2013) Environmental toxicology: children at risk. Environmental Toxicology: Selected Entries from the Encyclopedia of Sustainability Science and Technology 239–291. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-5764-0_11
Jayan (2021) How much fish is eaten in each state in India? The Hindu (Business line). Last Accessed 4 Feb 2024. https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/news/variety/how-much-fish-is-eaten-in-each-state-in-india/article35535769.ece
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to JOINT CSIR-UGC NET JRF fellowship, for providing the financial support needed for this research, and all members of the Environmental Biology Laboratory at Patna University, Patna.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mohammed Aasif Sulaiman [Conceptualization, Investigation, Formal analysis, Data curation, Writing -original draft, software], Anupma Kumari [Conceptualization, Supervision, Resources, Writing -review and editing].
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sulaiman, M.A., Kumari, A. Unveiling the Rising Threat of Cadmium Pollution and Alarming Health Risks Associated with the Consumption of 15 Commercially Important Fish Species in the Middle Stretch of River Ganga, at Patna, India. Biol Trace Elem Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-024-04164-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-024-04164-x