Abstract
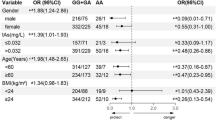
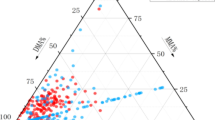
Arsenic (As) exposure in drinking water has become a serious public health issue. AS3MT gene is involved in the metabolism of arsenic, so a single nucleotide polymorphism in this gene may lead to the development of type 2 diabetes in arsenic-exposed areas. This study aimed to evaluate the association of the AS3MT gene with the development of type 2 diabetes in highly arsenic-exposed areas of Punjab, Pakistan. Total 200 samples equal in number from high arsenic exposed-areas of Lahore (Nishtar) and Kasur (Mustafa Abad) were collected. rs11191439 was utilized as an influential variable to evaluate the association between arsenic metabolism and diabetes status to find a single nucleotide polymorphism in the AS3MT gene. We observed the arsenic level in drinking water of the arsenic-exposed selected areas 115.54 ± 1.23 µg/L and 96.88 ± 0.48 µg/L, respectively. The As level in the urine of diabetics (98.54 ± 2.63 µg/L and 56.38 ± 12.66 µg/L) was higher as compared to non-diabetics (77.58 ± 1.8 µg/L and 46.9 ± 8.95 µg/L) of both affected areas, respectively. Correspondingly, the As level in the blood of diabetics (6.48 ± 0.08 µg/L and 5.49 ± 1.43 µg/L) and non-diabetics (6.22 ± 0.12 µg/L and 5.26 ± 0.24 µg/L) in the affected areas. Genoty** showed significant differences in the frequencies of alleles among cases and controls. Nevertheless, notable disparities in genotype distribution were observed in SNPs rs11191439 (T/C) (P < 0.05) and when comparing T2D patients and non-diabetic control subjects. The AS3MT gene and clinical parameters show a significant association with the affected people with diabetes living in arsenic-exposed areas.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hendryx M, Luo J, Chojenta C, Byles JE (2021) Exposure to heavy metals from point pollution sources and risk of incident type 2 diabetes among women: a prospective cohort analysis. Int J Environ Health Res 31(4):453–464
Shaji E, Santosh M, Sarath KV, Prakash P, Deepchand V, Divya BV (2021) Arsenic contamination of groundwater: a global synopsis with focus on the Indian Peninsula. Geosci Front 12(3):101079
Niazi NK, Bibi I, Shahid M, Ok YS, Burton ED, Wang H, ... Lüttge A (2018) Arsenic removal by perilla leaf biochar in aqueous solutions and groundwater: an integrated spectroscopic and microscopic examination. Environ Pollut 232:31–41
Huq ME, Fahad S, Shao Z, Sarven MS, Khan IA, Alam M, ... Khan WU (2020) Arsenic in a groundwater environment in Bangladesh: occurrence and mobilization. J Environ Manag 262:110318
Shen H, Niu Q, Xu M, Rui D, Xu S, Feng G, ... **g M (2016) Factors affecting arsenic methylation in arsenic-exposed humans: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health 13(2):205
Rangel-Moreno K, Gamboa-Loira B, López-Carrillo L, Cebrián ME (2022) Prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus in relation to arsenic exposure and metabolism in Mexican women. Environ Res 210:112948
Signes-Pastor AJ, Gutiérrez-González E, Garcia-Villarino M, Rodríguez-Cabrera FD, López-Moreno JJ, Varea-Jiménez E, ... Karagas MR (2021) Toenails as a biomarker of exposure to arsenic: a review. Environ Res 195:110286
Abdul KSM, Jayasinghe SS, Chandana EP, Jayasumana C, De Silva PMC (2015) Arsenic and human health effects: a review. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 40(3):828–846
Ji JH, ** MH, Kang JH, Lee SI, Lee S, Kim SH, Oh SY (2021) Relationship between heavy metal exposure and type 2 diabetes: a large-scale retrospective cohort study using occupational health examinations. BMJ Open 11(3):e039541
Misra BB, Misra A (2020) The chemical exposome of type 2 diabetes mellitus: opportunities and challenges in the omics era. Diabetes Metab Syndr 14(1):23–38
Grau-Perez M, Kuo CC, Gribble MO, Balakrishnan P, Jones Spratlen M, Vaidya D, ... Navas-Acien A (2017. Association of low-moderate arsenic exposure and arsenic metabolism with incident diabetes and insulin resistance in the Strong Heart Family Study. Environ Health Perspect 125(12):127004
Mendez MA, González-Horta C, Sánchez-Ramírez B, Ballinas-Casarrubias L, Cerón RH, Morales DV, ... Stýblo M (2016) Chronic exposure to arsenic and markers of cardiometabolic risk: a cross-sectional study in Chihuahua, Mexico. Environ Health Perspect 124(1):104–111
Bommarito PA, Beck R, Douillet C, Del Razo LM, Garcia-Vargas GG, Valenzuela OL, ... Fry RC (2019) Evaluation of plasma arsenicals as potential biomarkers of exposure to inorganic arsenic. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 29(5):718–729
Drobna Z, Naranmandura H, Kubachka KM, Edwards BC, Herbin-Davis K, Styblo M, ... Le XC (2009) Disruption of the arsenic (+3 oxidation state) methyltransferase gene in the mouse alters the phenotype for methylation of arsenic and affects distribution and retention of orally administered arsenate. Chem Res Toxicol 22(10):1713–1720
Maull EA, Ahsan H, Edwards J, Longnecker MP, Navas-Acien A, Pi J, ... Thayer KA (2012). Evaluation of the association between arsenic and diabetes: a National Toxicology Program workshop review. Environ Health Perspect 120(12):1658–1670
Tseng CH (2004) The potential biological mechanisms of arsenic-induced diabetes mellitus. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 197(2):67–83
Agusa T, Fujihara J, Takeshita H, Iwata H (2011) Individual variations in inorganic arsenic metabolism associated with AS3MT genetic polymorphisms. Int J Mol Sci 12(4):2351–2382
Nuvolone D, Stoppa G, Petri D, Voller F (2023) Long-term exposure to low-level arsenic in drinking water is associated with cause-specific mortality and hospitalization in the Mt. Amiata area (Tuscany, Italy). BMC Public Health 23(1):71
Amir M, Asghar S, Ahsin M, Hussain S, Ismail A, Riaz M, Naz S (2021) Arsenic exposure through drinking groundwater and consuming wastewater-irrigated vegetables in Multan, Pakistan. Environ Geochem Health 43(12):5025–5035
González-Martínez F, Sánchez-Rodas D, Varela NM, Sandoval CA, Quiñones LA, Johnson-Restrepo B (2020) As3MT and GST polymorphisms influencing arsenic metabolism in human exposure to drinking groundwater. Int J Mol Sci 21(14):4832
Sambrook J, Fritsch ER, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Xu Y, Wang A, Lin X, Xu J, Shan Y, Pan X, Shan PF (2021) Global burden and gender disparity of vision loss associated with diabetes retinopathy. Acta Ophthalmol 99(4):431–440
Simayi A, Mohemaiti P (2019) Risk and protective factors of co-morbid depression in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a metaanalysis. Endocr J 66(9):793–805
Zhang Y, Tong M, Wang B, Shi Z, Wang P, Li L, ... Lu T (2021) Geographic, gender, and seasonal variation of diabetes: a nationwide study with 1.4 million participants. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol 106(12):e4981–e4992
Nayak BS, Sobrian A, Latiff K, Pope D, Rampersad A, Lourenço K, Samuel N (2014) The association of age, gender, ethnicity, family history, obesity and hypertension with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Trinidad. Diabetes Metab Syndr 8(2):91–95
Gao C, Sun X, Lu L, Liu F, Yuan J (2019) Prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus in mainland China: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Diabetes Investig 10(1):154–162
Ren X, Chen ZA, Zheng S, Han T, Li Y, Liu W, Hu Y (2016) Association between triglyceride to HDL-C ratio (TG/HDL-C) and insulin resistance in Chinese patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus. PLoS One 11(4):e0154345
Ezema GO, Omeh NY, Egbachukwu S, Agbo EC, Ikeyi AP, Obeagu EI (2023) Evaluation of biochemical parameters of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus based on age and gender in Umuahia. Asian J Dent Health Sci 3(2):32–36
Pánico P, Velasco M, Salazar AM, Picones A, Ortiz-Huidobro RI, Guerrero-Palomo G, ... Hiriart M (2022) Is arsenic exposure a risk factor for metabolic syndrome? A review of the potential mechanisms. Front Endocrinol 13:878280
Klisic A, Kavaric N, Vujcic S, Mihajlovic M, Zeljkovic A, Ivanisevic J, ... Vekic J (2020) Inverse association between serum endocan levels and small LDL and HDL particles in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24(15)
Artha IMJR, Bhargah A, Dharmawan NK, Pande UW, Triyana KA, Mahariski PA, ... Rina IK (2019) High level of individual lipid profile and lipid ratio as a predictive marker of poor glycemic control in type-2 diabetes mellitus. Vasc Health Risk Manag 149–157
Pradhan AD, Paynter NP, Everett BM, Glynn RJ, Amarenco P, Elam M, ... Ridker PM (2018) Rationale and design of the pemafibrate to reduce cardiovascular outcomes by reducing triglycerides in patients with diabetes (PROMINENT) study. Am Heart J 206:80–93
Lee EY, Yang HK, Lee J, Kang B, Yang Y, Lee SH, ... Cho JH (2016) Triglyceride glucose index, a marker of insulin resistance, is associated with coronary artery stenosis in asymptomatic subjects with type 2 diabetes. Lipids Health Dis 15(1):1–7
Alqahtani SAM, Awan ZA, Alasmary MY, Al Amoudi SM (2022) Association between serum uric acid with diabetes and other biochemical markers. J Fam Med Prim Care 11(4):1401
Ji P, Zhu J, Feng J, Li H, Yu Q, Qin H, Zhang J (2022) Serum uric acid levels and diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a dose-response meta-analysis. Prim Care Diabetes 16(3):457–465
Suijk DL, van Baar MJ, van Bommel EJ, Iqbal Z, Krebber MM, Vallon V, ... van Raalte DH (2022) SGLT2 inhibition and uric acid excretion in patients with type 2 diabetes and normal kidney function. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 17(5):663–671
Rehman K, Fatima F, Akash MSH (2019) Biochemical investigation of association of arsenic exposure with risk factors of diabetes mellitus in Pakistani population and its validation in animal model. Environ Monit Assess 191:1–15
Lu J, Yu K, Fan S, Liu W, Dong Z, Li J, ... Zhou J (2019) Influence of AS3MT polymorphisms on arsenic metabolism and liver injury in APL patients treated with arsenic trioxide. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 379:114687
Fujihara J, Soejima M, Koda Y, Kunito T, Takeshita H (2008) Asian specific low mutation frequencies of the M287T polymorphism in the human arsenic (+ 3 oxidation state) methyltransferase (AS3MT) gene. Mutat Res/Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 654(2):158–161
Lu J, Hu S, Wang W, Li J, Dong Z, Zhou J, Hai X (2018) AS3MT polymorphisms, arsenic metabolism, and the hematological and biochemical values in APL patients treated with arsenic trioxide. Toxicol Sci 166(1):219–227
Funding
Government College University, Lahore, Pakistan and University of the Punjab, Pakistan provided partial funding; every type of facility which help in completion of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contribute equally. Saima shokat wrote the main manuscript as research scholar, Dr. Riffat Iqbal helps in proof reading the manuscript, Dr. Samreen provide research lab facilities and Dr. Atif guides in genetic analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
No, I declare that the authors have no competing interests as defined by Springer, or other interests that might be perceived to influence the results and/or discussion reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shokat, S., Iqbal, R., Riaz, S. et al. Association Between Arsenic Toxicity, AS3MT Gene Polymorphism and Onset of Type 2 Diabetes. Biol Trace Elem Res 202, 1550–1558 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-023-03919-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-023-03919-2