Abstract
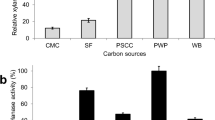
Brewer spent grains (BSGs) are one of the most abundant by-products in brewing industry. Due to microbiological instability and high perishability, the efficient degradation of BSGs is of environmental and economic importance. Streptomyces sp. F-3 could grow in the medium with BSGs as the only carbon and nitrogen source. Proteome mass spectrometry revealed that a GH10 xylanase SsXyn10A could be secreted in large quantities. SsXyn10A showed optimum activity at pH 7.0 and 60 °C. SsXyn10A exhibited excellent thermostability which retained approximately 100% and 58% after incubation for 5 h at 50 and 60 °C. SsXyn10A displayed high activity to beechwood xylan (BX) and wheat arabinoxylan (WAX). SsXyn10A is active against xylotetracose (X4), xylopentose (X5), and xylohexose (X6) to produce main products xylobiose (X2) and xylotriose (X3). Ssxyn10A showed synergistic effects with commercial cellulase on BSGs hydrolyzing into soluble sugar. In addition, the steam explosion pretreatment of BSGs as the substrate produced twice as much reducing sugar as the degradation of the original substrate. This study will contribute to efficient utilization of BSGs and provide a thermostable GH10 xylanase which has potential application in biomass hydrolysis.






Similar content being viewed by others

Data availability
The data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files. Further datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Puligundla, P., & Mok, C. (2021). Food Science and Biotechnology, 30, 341–353.
Bianco, A., Budroni, M., Zara, S., Mannazzu, I., Fancello, F., et al. (2020). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 104, 8661–8678.
Akermann, A., Weiermuller, J., Christmann, J., Guirande, L., Glaser, G., et al. (2020). Engineering in Life Sciences, 20, 168–180.
Gbenebor, O. P., Olanrewaju, O. A., Usman, M. A., & Adeosun, S. O. (2023). Polymers (Basel), 15.
Rahman, M. J., Malunga, L. N., Eskin, M., Eck, P., Thandapilly, S. J., et al. (2021). Frontiers in Nutrition, 8, 634519.
Merten, D., Erman, L., Marabelli, G. P., Leners, B., Ney, Y., et al. (2022). Food & Function, 13, 5327–5342.
Ikram, S., Huang, L., Zhang, H., Wang, J., & Yin, M. (2017). Journal of Food Science, 82, 2232–2242.
Leite, P., Silva, C., Salgado, J. M., & Belo, I. (2019). Industrial Crops and Products, 137, 315–322.
Hassan, S. S., Ravindran, R., Jaiswal, S., Tiwari, B. K., Williams, G. A., et al. (2020). Waste Management, 105, 240–247.
Pathania, S., Sharma, S., & Kumari, K. (2018). Indian Journal of Natural Products and Resources, 9, 70–74.
Lao, E. J., Dimoso, N., Raymond, J., & Mbega, E. R. (2020). Tropical Animal Health and Production, 52, 461–472.
Sajib, M., Falck, P., Sardari, R. R. R., et al. (2018). Journal of Biotechnology, 268, 61–70.
Amorim, C., Silverio, S. C., Silva, S. P., Coelho, E., Coimbra, M. A., et al. (2018). Carbohydrate Polymers, 199, 546–554.
Amorim, C., Silverio, S. C., Prather, K. L. J., & Rodrigues, L. R. (2019). Biotechnology Advances, 37, 107397.
Berger, K., Burleigh, S., Lindahl, M., Bhattacharya, A., Patil, P., et al. (2021). Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 69, 3617–3625.
Gong, W., Zhang, H., Tian, L., Liu, S., Wu, X., et al. (2016). Electrophoresis, 37, 1640–1650.
Paes, G., Berrin, J. G., & Beaugrand, J. (2012). Biotechnology Advances, 30, 564–592.
Yang, Y., Yang, J. S., Wang, R. N., Liu, J. W., Zhang, Y., et al. (2019). Microbial Cell Factories, 18, 159.
Wu, X., Shi, Z., Tian, W., Liu, M., Huang, S., et al. (2022). Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 10, 939550.
Corchado-Lopo, C., Martínez-Avila, O., Marti, E., Llimós, J., Busquets, A. M., et al. (2021). New Biotechnology, 62, 60–67.
Kavalopoulos, M., Stoumpou, V., Christofi, A., Mai, S., Barampouti, E. M., et al. (2021). Environmental Pollution, 270, 116069.
Parchami, M., Ferreira, J. A., & Taherzadeh, M. J. (2021). Bioresource Technology, 337, 125409.
Weiermuller, J., Akermann, A., Laudensack, W., Chodorski, J., Blank, L. M., et al. (2021). Bioresource Technology, 336, 125262.
Ravindran, R., Jaiswal, S., Abu-Ghannam, N., & Jaiswal, A. K. (2018). Bioresource Technology, 248, 272–279.
Ikram, S., Zhang, H., Ahmed, M. S., & Wang, J. (2020). Journal of Food Science, 85, 1045–1059.
Montipó, S., Ballesteros, I., Fontana, R. C., Liu, S., Martins, A. F., et al. (2018). Bioresource Technology, 249, 1017–1024.
Ma, Q., Gao, X., Bi, X., **a, M., & Wang, M. (2021). Biomass and Bioenergy, 145, 105967.
Carvalho, A. F. A., Marcondes, W. F., de Oliva Neto, P., et al. (2018). Bioresource Technology, 250, 221–229.
Teng, C., Yan, Q., Jiang, Z., Fan, G., & Shi, B. (2010). Bioresource Technology, 101(19), 7679–7682.
You, S., Li, J., Zhang, F., Bai, Z. Y., Shittu, S., et al. (2021). Bioresource Technology, 342, 125962.
Sun, X., Li, Y., Tian, Z., Qian, Y., Zhang, H., et al. (2019). Biotechnology for Biofuels, 12, 136.
Sun, X., Meng, J., Liu, S., Zhang, H., & Wang, L. (2016). Genome Announcements, 4, e00780–e00716.
Shi, Z., Gong, W., Zhang, L., Dai, L., Chen, G., et al. (2019). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 187, 1515–1538.
Zhou, J. Y., Schepmoes, A. A., Zhang, X., Moore, R. J., Monroe, M. E., et al. (2010). Journal of Proteome Research, 9, 5698–5704.
Hu, G., Heitmann, J. A., Jr., & Rojas, O. J. (2009). Analytical Chemistry, 81, 1872–1880.
Kim, D. Y., Lee, S. H., Lee, M. J., Cho, H. Y., Lee, J. S., et al. (2018). International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 106, 620–628.
Alokika, & Singh, B. (2019). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 103, 8763–8784.
Wang, K., Cao, R., Wang, M., Lin, Q., Zhan, R., et al. (2019). Biotechnology for Biofuels, 12, 48.
Xue, X., Wang, R., Tu, T., Shi, P., Ma, R., et al. (2015). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 81, 3823–3833.
Wu, X., Tian, Z., Jiang, X., Zhang, Q., & Wang, L. (2018). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 102, 249–260.
Sepulchro, A. G. V., Pellegrini, V. O. A., Briganti, L., de Araujo, E. A., de Araujo, S. S., et al. (2020). Carbohydrate Polymers, 247, 116714.
Vacilotto, M. M., Pellegrini, V. O. A., Sepulchro, A. G. V., Capetti, C. C. M., Curvelo, A. A. S., et al. (2022). Carbohydrate Polymers, 275, 118684.
Wang, X., Huang, H., **e, X., Ma, R., Bai, Y., et al. (2016). Bioresource Technology, 222, 277–284.
Song, H. T., Gao, Y., Yang, Y. M., **ao, W. J., Liu, S. H., et al. (2016). Bioresource Technology, 219, 710–715.
Funding
This work was funded by the Open Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Biological Fermentation Engineering of Beer (K202005), The National Natural Science Foundation of China (32100022), and the Key Research and Develop Program of Shandong Province (2020CXGC010601).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ML performed the experiments and analyzed the data. SH and PY analyzed the data. HY and JY modified the article. XW conceived the study design and wrote the manuscript. LW edited the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of authors.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 2520 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Huang, S., Yan, P. et al. Effective Degradation of Brewer Spent Grains by a Novel Thermostable GH10 Xylanase. Appl Biochem Biotechnol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04779-1
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04779-1