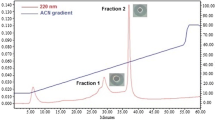
Abstract
Staphylococcus aureus is a common Gram-positive pathogen that causes food poisoning and foodborne illnesses. In this study, a peptide-designated NGJ1D (GAPNDLTARFIAKK) was found among 8 peptides in the fermentation broth of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei. NGJ1D had a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 62.5 μg/mL against Staphylococcus aureus and could kill the bacteria within 3 h. In a mimicked bacterial cell membrane environment, NGJ1D could change its secondary structure from a random coil to an α-helix to increase its membrane permeability and subsequent interaction with bacteria genomic DNA. Further analysis using SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS), and molecular docking revealed that NGJ1D affects the DNA-binding protein HU of S. aureus to interfere with DNA synthesis. These results indicate that novel peptides with antimicrobial potential, such as NGJ1D, could be identified in fermentation broths and can be used for application in food preservation and the prevention and treatment of infections caused by S. aureus.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Anunthawan, T., de la Fuente-Nunez, C., Hancock, R. E., & Klaynongsruang, S. (2015). Cationic amphipathic peptides KT2 and RT2 are taken up into bacterial cells and kill planktonic and biofilm bacteria. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta, 1848(6), 1352–1358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.02.021
Belguesmia, Y., Hazime, N., Kempf, I., Boukherroub, R., & Drider, D. (2020). New bacteriocins from Lacticaseibacillus paracasei CNCM I-5369 adsorbed on alginate nanoparticles are very active against Escherichia coli. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(22), 8654. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228654
Boman, H. G., Agerberth, B., & Boman, A. (1993). Mechanisms of action on Escherichia coli of cecropin P1 and PR-39, two antibacterial peptides from pig intestine. Infection and Immunity, 61(7), 2978–2984. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.61.7.2978-2984.1993
Boparai, J. K., & Sharma, P. K. (2020). Mini review on antimicrobial peptides, sources, mechanism and recent applications. Protein & Peptide Letters, 27(1), 4–16. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929866526666190822165812
Caldwell, C. C., & Spies, M. (2020). Dynamic elements of replication protein A at the crossroads of DNA replication, recombination, and repair. Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 55(5), 482–507. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409238.2020.1813070
Chan, K. T., Song, X., Shen, L., Liu, N., Zhou, X., Cheng, L., & Chen, J. (2023). Nisin and its application in oral diseases. Journal of Functional Foods, 105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2023.105559
Cutrona, K. J., Kaufman, B. A., Figueroa, D. M., & Elmore, D. E. (2015). Role of arginine and lysine in the antimicrobial mechanism of histone-derived antimicrobial peptides. FEBS Letters, 589(24), 3915–3920. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2015.11.002
de Oliveira, A. M., de Abreu Filho, B. A., de Jesus Bassetti, F., Bergamasco, R., & Gomes, R. G. (2020). Natural extract of Moringa oleifera leaves promoting control of Staphylococcus aureus strains biofilm on PVC surface. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 13(10), 1817–1832. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-020-02521-x
Fensterseifer, I. C. M., Felicio, M. R., Alves, E. S. F., Cardoso, M. H., Torres, M. D. T., Matos, C. O., Silva, O. N., Lu, T. K., Freire, M. V., Neves, N. C., Goncalves, S., Liao, L. M., Santos, N. C., Porto, W. F., de la Fuente-Nunez, C., & Franco, O. L. (2019). Selective antibacterial activity of the cationic peptide PaDBS1R6 against Gram-negative bacteria. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes, 1861(7), 1375–1387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2019.03.016
Graf, M., Mardirossian, M., Nguyen, F., Seefeldt, A. C., Guichard, G., Scocchi, M., Innis, C. A., & Wilson, D. N. (2017). Proline-rich antimicrobial peptides targeting protein synthesis. Natural Product Reports, 34(7), 702–711. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NP00020K
Han, X., Kou, Z., Jiang, F., Sun, X., & Shang, D. (2021). Interactions of designed Trp-containing antimicrobial peptides with DNA of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. DNA and Cell Biology, 40(2), 414–424. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2019.4874
Hartmann, M., Berditsch, M., Hawecker, J., Ardakani, M. F., Gerthsen, D., & Ulrich, A. S. (2010). Damage of the bacterial cell envelope by antimicrobial peptides gramicidin S and PGLa as revealed by transmission and scanning electron microscopy. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 54(8), 3132–3142. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.00124-10
Helmy, Y. A., Taha-Abdelaziz, K., Hawwas, H. A. E., Ghosh, S., AlKafaas, S. S., Moawad, M. M. M., Saied, E. M., Kassem, I. I., & Mawad, A. M. M. (2023). Antimicrobial resistance and recent alternatives to antibiotics for the control of bacterial pathogens with an emphasis on foodborne pathogens. Antibiotics, 12(2), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020274
Hernández-Carranza, P., Fierro-Corona, G., Tapia-Maruri, D., Ruiz-Martínez, I., Ávila-Reyes, S. V., Ruiz-López, I. I., & Ochoa-Velasco, C. E. (2023). Bioactive edible films based on LAB-fermented whey solution and potato starch: Characterization and storage behavior. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 16, 3045–3056. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03115-z
Hu, J., Rao, L., Zhu, Y. H., Zhang, G. J., & Yu, D. J. (2021). TargetDBP+: Enhancing the performance of identifying DNA-binding proteins via weighted convolutional features. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 61(1), 505–515. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.0c00735
Kaur, B., Gupta, J., Sharma, S., Sharma, D., & Sharma, S. (2021). Focused review on dual inhibition of quorum sensing and efflux pumps: A potential way to combat multi drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 190, 33–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.08.199
Li, J., Li, C., Shi, C., Aliakbarlu, J., Cui, H., & Lin, L. (2022). Antibacterial mechanisms of clove essential oil against Staphylococcus aureus and its application in pork. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 380, 109864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2022.109864
Li, S., Wang, Y., Xue, Z., Jia, Y., Li, R., He, C., & Chen, H. (2021). The structure-mechanism relationship and mode of actions of antimicrobial peptides: A review. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 109, 103–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.01.005
Liang, Y., Zhang, X., Yuan, Y., Bao, Y., & **ong, M. (2020). Role and modulation of the secondary structure of antimicrobial peptides to improve selectivity. Biomaterials Science, 8(24), 6858–6866. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0BM00801J
Liu, T., Kang, J., & Liu, L. (2021a). Thymol as a critical component of Thymus vulgaris L. essential oil combats Pseudomonas aeruginosa by intercalating DNA and inactivating biofilm. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 136(2), 110354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110354
Liu, H., Pei, H., Han, Z., Feng, G., & Li, D. (2015). The antimicrobial effects and synergistic antibacterial mechanism of the combination of ε-Polylysine and nisin against Bacillus subtilis. Food Control, 47, 444–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.07.050
Liu, S., Aweya, J. J., Zheng, L., Zheng, Z., Huang, H., Wang, F., Yao, D., Ou, T., & Zhang, Y. (2022). LvHemB1, a novel cationic antimicrobial peptide derived from the hemocyanin of Litopenaeus vannamei, induces cancer cell death by targeting mitochondrial voltage-dependent anion channel 1. Cell Biology and Toxicology, 38(1), 87–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-021-09588-y
Liu, X., Li, Y., Wang, S., Huangfu, L., Zhang, M., & **ang, Q. (2021b). Synergistic antimicrobial activity of plasma-activated water and propylparaben: Mechanism and applications for fresh produce sanitation. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 146, 111447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111447
Luo, X., Ye, X., Ding, L., Zhu, W., Yi, P., Zhao, Z., Gao, H., Shu, Z., Li, S., Sang, M., Wang, J., Zhong, W., & Chen, Z. (2021). Fine-tuning of alkaline residues on the hydrophilic face provides a non-toxic cationic α-helical antimicrobial peptide against antibiotic-resistant ESKAPE pathogens. Frontiers in Microbiology, 12, 684591. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.684591
Mahlapuu, M., Hakansson, J., Ringstad, L., & Bjorn, C. (2016). Antimicrobial peptides: An emerging category of therapeutic agents. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 6, 194. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2016.00194
Mardirossian, M., Barriere, Q., Timchenko, T., Muller, C., Pacor, S., Mergaert, P., Scocchi, M., & Wilson, D. N. (2018). Fragments of the nonlytic proline-rich antimicrobial peptide Bac5 kill Escherichia coli cells by inhibiting protein synthesis. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 62(8), e00534-e618. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.00534-18
Mardirossian, M., Grzela, R., Giglione, C., Meinnel, T., Gennaro, R., Mergaert, P., & Scocchi, M. (2014). The host antimicrobial peptide Bac71-35 binds to bacterial ribosomal proteins and inhibits protein synthesis. Chemistry & Biology, 21(12), 1639–1647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2014.10.009
Miao, J., Guo, H., Ou, Y., Liu, G., Fang, X., Liao, Z., Ke, C., Chen, Y., Zhao, L., & Cao, Y. (2014). Purification and characterization of bacteriocin F1, a novel bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. tolerans FX-6 from Tibetan kefir, a traditional fermented milk from Tibet. China. Food Control, 42, 48–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.01.041
Nam, J., Yun, H., Rajasekaran, G., Kumar, S. D., Kim, J. I., Min, H. J., Shin, S. Y., & Lee, C. W. (2018). Structural and functional assessment of mBjAMP1, an antimicrobial peptide from Branchiostoma japonicum, revealed a novel α-hairpinin-like scaffold with membrane permeable and DNA binding activity. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 61(24), 11101–11113. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01135
Nicolas, P. (2009). Multifunctional host defense peptides: Intracellular-targeting antimicrobial peptides. FEBS Journal, 276(22), 6483–6496. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07359.x
Ning, Y., Yan, A., Yang, K., Wang, Z., Li, X., & Jia, Y. (2017). Antibacterial activity of phenyllactic acid against Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli by dual mechanisms. Food Chemistry, 228, 533–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.01.112
Sakaguchi, Y., Nakamura, R., Konishi, M., Hatakawa, Y., Toyoda, H., & Akizawa, T. (2019). Effects of Cu2+ on conformational change and aggregation of hPrP180-192 with a V180I mutation of the prion protein. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 514(3), 798–802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.05.009
Santos, J. C., Sousa, R. C., Otoni, C. G., Moraes, A. R., Souza, V. G., Medeiros, E. A., Espitia, P. J., Pires, A. C., Coimbra, J. S., & Soares, N. F. (2018). Nisin and other antimicrobial peptides: Production, mechanisms of action, and application in active food packaging. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 48, 179–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2018.06.008
Shabir, U., Ali, S., Magray, A. R., Ganai, B. A., Firdous, P., Hassan, T., & Nazir, R. (2018). Fish antimicrobial peptides (AMP’s) as essential and promising molecular therapeutic agents: A review. Microbial Pathogenesis, 114, 50–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2017.11.039
Shiroodi, S. G., Nesaei, S., Ovissipour, M., Al-Qadiri, H. M., Rasco, B., & Sablani, S. (2016). Biodegradable polymeric films incorporated with nisin: Characterization and efficiency against Listeria monocytogenes. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 9, 958–969. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1684-3
Singh, A., Duche, R. T., Wandhare, A. G., Sian, J. K., Singh, B. P., Sihag, M. K., Singh, K. S., Sangwan, V., Talan, S., & Panwar, H. (2022). Milk-derived antimicrobial peptides: Overview, applications, and future perspectives. Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins, 15(1), 44–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-022-10004-y
Thirunavookarasu, N., Kumar, S., Anandharaj, A., & Rawson, A. (2023). Enhancing functional properties of soy protein isolate—rice starch complex using ultrasonication and its characterization. Food and Bioprocess Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03280-1
Umeda, K., Ono, H. K., Wada, T., Motooka, D., Nakamura, S., Nakamura, H., & Hu, D. L. (2021). High production of egc2-related staphylococcal enterotoxins caused a food poisoning outbreak. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 357, 109366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2021.109366
Vasilchenko, A. S., Rogozhin, E. A., Vasilchenko, A. V., Kartashova, O. L., & Sycheva, M. V. (2016). Novel haemoglobin‐derived antimicrobial peptides from chicken (Gallus gallus) blood: purification, structural aspects and biological activity. Journal of applied microbiology, 121(6), 1546–1557. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13286
Vukomanović, M., Žunič, V., Kunej, Š, Jančar, B., Jeverica, S., Podlipec, R., & Suvorov, D. (2017). Nano-engineering the antimicrobial spectrum of lantibiotics: Activity of nisin against gram negative bacteria. Scientific Reports, 7, 4324. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-04670-0
Wang, H., Niu, M., Xue, T., Ma, L., Gu, X., Wei, G., Li, F., & Wang, C. (2022). Development of antibacterial peptides with efficient antibacterial activity, low toxicity, high membrane disruptive activity and a synergistic antibacterial effect. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 10(11), 1858–1874. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1tb02852a
Wang, J., Ma, M., Yang, J., Chen, L., Yu, P., Wang, J., Gong, D., Deng, S., Wen, X., & Zeng, Z. (2018). In vitro antibacterial activity and mechanism of monocaprylin against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Journal of Food Protection, 81(12), 1988–1996. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-18-248
Wu, J., Abbas, H. M. K., Li, J., Yuan, Y., Liu, Y., Wang, G., & Dong, A. W. (2019). Cell membrane-interrupting antimicrobial peptides from Isatis indigotica fortune isolated by a Bacillus subtilis expression system. Biomolecules, 10(1), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010030
Yang, S., Dai, J., Aweya, J. J., Lin, R., Weng, W., **e, Y., & **, R. (2023a). The antibacterial activity and pickering emulsion stabilizing effect of a novel peptide, sa6, isolated from salt-fermented Penaeus vannamei. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 16, 1312–1323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-023-03000-9
Yang, S., **ng, Y., Gao, J., **, R., Lin, R., Weng, W., **e, Y., & Aweya, J. J. (2023b). Lacticaseibacillus paracasei fermentation broth identified peptide, Y2Fr, and its antibacterial activity on Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Microbial Pathogenesis, 182, 106260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2023.106260
Yang, S., Yuan, Z., Aweya, J. J., Huang, S., Deng, S., Shi, L., Zheng, M., Zhang, Y., & Liu, G. (2021). Low-intensity ultrasound enhances the antimicrobial activity of neutral peptide TGH2 against Escherichia coli. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 77, 105676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2021.105676
Ye, P., Wang, J., Liu, M., Li, P., & Gu, Q. (2021). Purification and characterization of a novel bacteriocin from Lactobacillus paracasei ZFM54. LWT - Food Science and Technology, 143, 111125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111125
Zhang, Q. Y., Yan, Z. B., Meng, Y. M., Hong, X. Y., Shao, G., Ma, J. J., Cheng, X. R., Liu, J., Kang, J., & Fu, C. Y. (2021). Antimicrobial peptides: Mechanism of action, activity and clinical potential. Military Medical Research, 8(1), 48. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40779-021-00343-2
Zhang, S., Qiu, B., Zhu, J., Khan, M. Z. H., & Liu, X. (2018). Investigation of the interaction of 2,4-dimethoxy-6,7-dihydroxyphenanthrene with alpha-glucosidase using inhibition kinetics, CD, FT-IR and molecular docking methods. Spectrochimica Acta Part a: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 203, 13–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2018.05.077
Funding
This work was sponsored by Fujian Provincial Department of Science and Technology, China (2023N5008), Bureau of Ocean and Fisheries of Fujian Province, High Quality Development Special Project (FJHYF-L-2023–17).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.X.: Experiments, Data analysis, Writing-original draft. W.L.: Experiments, Software. J.J.A.: Experiments, Writing-review & editing. R.J.: Visualization. R.L.: Software, Validation. D.L.: Methodology. W.W.: Software. S.Y.: Supervision, Resources, Writing-review & editing. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
**ng, Y., Li, W., Aweya, J.J. et al. Lacticaseibacillus paracasei-Derived Antibacterial Peptide NGJ1D and Its Mechanism of Action Against Staphylococcus aureus. Food Bioprocess Technol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-024-03419-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-024-03419-8