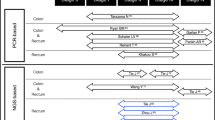
Opinion statement
Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) has already shown clinically relevant results in early-stage colon cancer patient management. Its prognostic value is by far much stronger than that of the available clinico-pathological biomarkers, therefore, has the potential to personalize the treatment after radical surgery through intensifying or de-intensifying the adjuvant therapy. Further developments and improvements should be pursued by (a) optimizing ctDNA assays and (b) validating its clinical utility in the different stages of this disease. Two main avenues of ctDNA testing are being pursued: tumor-informed vs tumor-agnostic assays. Two main clinical trial designs are under study: ctDNA-based strategy and ctDNA-by-treatment interaction. The former needs large sample sizes to address the main questions of the studies; thus, the target delta benefit may be the main challenge in these trial designs. The latter may be challenged by unavoidable contamination bias. To date, several clinical trials are ongoing worldwide. We believe that this large number of trials may provide an excellent common database for the demonstration of surrogacy of ctDNA for the classical 3-year disease-free survival endpoint. This would mark a huge methodological improvement to speed up new drug testing and development in the adjuvant treatment of this disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Ignatiadis M, Sledge GW, Jeffrey SS. Liquid biopsy enters the clinic - implementation issues and future challenges. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021;18:297–312.
Montagut C, Vidal J. Liquid biopsy for precision adjuvant chemotherapy in colon cancer. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:2330–1.
Dasari A, Morris VK, Allegra CJ, Atreya C, Benson AB III, Boland P, Chung K, Copur MS, Corcoran RB, Deming DA, Dwyer A, Diehn M, Eng C, George TJ, Gollub MJ, Goodwin RA, Hamilton SR, Hechtman JF, Hochster H, et al. ctDNA applications and integration in colorectal cancer: an NCI Colon and Rectal-Anal Task Forces whitepaper. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020;17:757–70.
Pessoa LS, Heringer M, Ferrer VP. ctDNA as a cancer biomarker: a broad overview. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2020;155:103109.
Mandel P, Metais P. Nuclear Acids In Human Blood Plasma. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1948;142:241–3.
Tie J, Wang Y, Cohen J, Li L, Hong W, Christie M, Wong HL, Kosmider S, Wong R, Thomson B, Choi J, Fox A, Field K, Burge M, Shannon J, Kotasek D, Tebbutt NC, Karapetis C, Underhill C, et al. Circulating tumor DNA dynamics and recurrence risk in patients undergoing curative intent resection of colorectal cancer liver metastases: A prospective cohort study. PLoS Med. 2021;18:e1003620.
Nakamura Y, Yoshino T. Clinical utility of analyzing circulating tumor DNA in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncologist. 2018;23:1310–8.
Bettegowda C, Sausen M, Leary RJ, et al. Detection of circulating tumor DNA in early- and late-stage human malignancies. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6:224ra224.
• Taieb J, Taly V, Vernerey D, et al. Analysis of circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) from patients enrolled in the IDEA-FRANCE phase III trial: rognostic and predictive value for adjuvant treatment duration. Ann Oncol. 2019;30:v867. The largest prospective study to investigate the prognostic impact of ctDNA, although with a lower prognostic value of ctDNA than that reported by other studies
Pascual J, Attard G, Bidard FC, Curigliano G, de Mattos-Arruda L, Diehn M, Italiano A, Lindberg J, Merker JD, Montagut C, Normanno N, Pantel K, Pentheroudakis G, Popat S, Reis-Filho JS, Tie J, Seoane J, Tarazona N, Yoshino T, Turner NC. ESMO recommendations on the use of circulating tumour DNA assays for patients with cancer: a report from the ESMO Precision Medicine Working Group. Ann Oncol. 2022;33:750–68.
Parikh AR, Van Seventer EE, Siravegna G, et al. Minimal residual disease detection using a plasma-only circulating tumor DNA assay in patients with colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27:5586–94.
Siravegna G, Mussolin B, Buscarino M, Corti G, Cassingena A, Crisafulli G, Ponzetti A, Cremolini C, Amatu A, Lauricella C, Lamba S, Hobor S, Avallone A, Valtorta E, Rospo G, Medico E, Motta V, Antoniotti C, Tatangelo F, et al. Clonal evolution and resistance to EGFR blockade in the blood of colorectal cancer patients. Nat Med. 2015;21:795–801.
Gong J, Hendifar A, Gangi A, et al. Clinical applications of minimal residual disease assessments by tumor-informed and tumor-uninformed circulating tumor DNA in colorectal cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13:4547.
•• Tie J, Cohen JD, Lahouel K, et al. Circulating tumor DNA analysis guiding adjuvant therapy in stage II colon cancer. N Engl J Med. 2022;386:2261–72. The first randomized trial to demonstrate the non-inferiority of ctDNA-guided approach with similar 2-yr RFS rate compared to standard approach for stage II colon cancer patients
Tie J, Cohen JD, Lo SN, Wang Y, Li L, Christie M, Lee M, Wong R, Kosmider S, Skinner I, Wong HL, Lee B, Burge ME, Yip D, Karapetis CS, Price TJ, Tebbutt NC, Haydon AM, Ptak J, et al. Prognostic significance of postsurgery circulating tumor DNA in nonmetastatic colorectal cancer: individual patient pooled analysis of three cohort studies. Int J Cancer. 2021;148:1014–26.
Reinert T, Henriksen TV, Christensen E, Sharma S, Salari R, Sethi H, Knudsen M, Nordentoft I, Wu HT, Tin AS, Heilskov Rasmussen M, Vang S, Shchegrova S, Frydendahl Boll Johansen A, Srinivasan R, Assaf Z, Balcioglu M, Olson A, Dashner S, et al. Analysis of plasma cell-free DNA by ultradeep sequencing in patients with stages I to III colorectal cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2019;5:1124–31.
** S, Zhu D, Shao F, Chen S, Guo Y, Li K, Wang Y, Ding R, Gao L, Ma W, Lu T, Li D, Zhang Z, Cai S, Liang X, Song H, Ji L, Li J, Zheng Z, et al. Efficient detection and post-surgical monitoring of colon cancer with a multi-marker DNA methylation liquid biopsy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021;118
Taieb J, Taly V, Henriques J, Bourreau C, Mineur L, Bennouna J, Desrame J, Louvet C, Lepere C, Mabro M, Egreteau J, Bouche O, Mulot C, Hormigos K, Chaba K, Mazard T, de Gramont A, Vernerey D, André T, Laurent-Puig P. Prognostic value and relation with adjuvant treatment duration of ctDNA in stage III colon cancer: a post hoc analysis of the PRODIGE-GERCOR IDEA-France Trial. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27:5638–46.
Brierley JD, Gospodarowicz MK, Wittekind C, editors. TNM classification of malignant tumours. 8th ed. Oxford: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 2016.
Argilés G, Tabernero J, Labianca R, Hochhauser D, Salazar R, Iveson T, Laurent-Puig P, Quirke P, Yoshino T, Taieb J, Martinelli E, Arnold D, ESMO Guidelines Committee. Electronic address: clinicalguidelines@esmo.org Localised colon cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2020;31:1291–305.
NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) Colon Cancer Version 1.2022 — February 25, 2022, NCCN.org.
Sobrero A, Puccini A, Bregni G, Bruzzi P. The urgent need to improve the tools to assess clinical benefit and value of cancer treatment. Eur J Cancer. 2017;83:324–8.
Shergill A, Parikh AR. Investigating the use of circulating tumor DNA in early-stage colon cancer. Oncology. October 17, 2022;36(10):620–6.
Tie J, Wang Y, Tomasetti C, et al. Circulating tumor DNA analysis detects minimal residual disease and predicts recurrence in patients with stage II colon cancer. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8:346ra392.
Schøler LV, Reinert T, Ørntoft MW, et al. Clinical implications of monitoring circulating tumor DNA in patients with colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23:5437–45.
Huang K, Qu H, Zhang X, Huang T, Sun X, He W, Li M, Lin L, Xu M, Chen S, **a L. Circulating tumor DNA sequencing for colorectal cancers: a comparative analysis of colon cancer and rectal cancer data. Cancer Biomark. 2019;26:313–22.
Tarazona N, Gimeno-Valiente F, Gambardella V, Zuñiga S, Rentero-Garrido P, Huerta M, Roselló S, Martinez-Ciarpaglini C, Carbonell-Asins JA, Carrasco F, Ferrer-Martínez A, Bruixola G, Fleitas T, Martín J, Tébar-Martínez R, Moro D, Castillo J, Espí A, Roda D, Cervantes A. Targeted next-generation sequencing of circulating-tumor DNA for tracking minimal residual disease in localized colon cancer. Ann Oncol. 2019;30:1804–12.
Tie J, Cohen JD, Wang Y, Christie M, Simons K, Lee M, Wong R, Kosmider S, Ananda S, McKendrick J, Lee B, Cho JH, Faragher I, Jones IT, Ptak J, Schaeffer MJ, Silliman N, Dobbyn L, Li L, et al. Circulating tumor DNA analyses as markers of recurrence risk and benefit of adjuvant therapy for stage III colon cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2019;5:1710–7.
Wang Y, Li L, Cohen JD, Kinde I, Ptak J, Popoli M, Schaefer J, Silliman N, Dobbyn L, Tie J, Gibbs P, Tomasetti C, Kinzler KW, Papadopoulos N, Vogelstein B, Olsson L. Prognostic potential of circulating tumor DNA measurement in postoperative surveillance of nonmetastatic colorectal cancer. JAMA Oncology. 2019;5:1118–23.
Benhaim L, Bouché O, Normand C, Didelot A, Mulot C, le Corre D, Garrigou S, Djadi-Prat J, Wang-Renault SF, Perez-Toralla K, Pekin D, Poulet G, Landi B, Taieb J, Selvy M, Emile JF, Lecomte T, Blons H, Chatellier G, et al. Circulating tumor DNA is a prognostic marker of tumor recurrence in stage II and III colorectal cancer: multicentric, prospective cohort study (ALGECOLS). Eur J Cancer. 2021;159:24–33.
Chen G, Peng J, **ao Q, Wu HX, Wu X, Wang F, Li L, Ding P, Zhao Q, Li Y, Wang D, Shao Y, Bao H, Pan Z, Ding KF, Cai S, Wang F, Xu RH. Postoperative circulating tumor DNA as markers of recurrence risk in stages II to III colorectal cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14:80.
Henriksen TV, Tarazona N, Frydendahl A, Reinert T, Gimeno-Valiente F, Carbonell-Asins JA, Sharma S, Renner D, Hafez D, Roda D, Huerta M, Roselló S, Madsen AH, Løve US, Andersen PV, Thorlacius-Ussing O, Iversen LH, Gotschalck KA, Sethi H, et al. Circulating tumor DNA in stage III colorectal cancer, beyond minimal residual disease detection, toward assessment of adjuvant therapy efficacy and clinical behavior of recurrences. Clin Cancer Res. 2022;28:507–17.
Tie J, Cohen J, Lahouel K, et al. 318MO - circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) dynamics, CEA and sites of recurrence for the randomised DYNAMIC study: adjuvant chemotherapy (ACT) guided by ctDNA analysis in stage II colon cancer (CC). Ann Oncol. 2022;33(suppl_7):S136–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/annonc/annonc1048.
Iveson TJ, Sobrero AF, Yoshino T, Souglakos I, Ou FS, Meyers JP, Shi Q, Grothey A, Saunders MP, Labianca R, Yamanaka T, Boukovinas I, Hollander NH, Galli F, Yamazaki K, Georgoulias V, Kerr R, Oki E, Lonardi S, et al. Duration of adjuvant doublet chemotherapy (3 or 6 months) in patients with high-risk stage II colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39:631–41.
Andre T, de Gramont A, Vernerey D, et al. Adjuvant fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin in stage II to III colon cancer: updated 10-year survival and outcomes according to BRAF mutation and mismatch repair status of the MOSAIC study. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:4176–87.
Group QC. Adjuvant chemotherapy versus observation in patients with colorectal cancer: a randomised study. Lancet. 2007;370:2020–9.
Naidoo M, Gibbs P, Tie J. ctDNA and adjuvant therapy for colorectal cancer: time to re-invent our treatment paradigm. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13:346.
Circulating tumour DNA analysis informing adjuvant chemotherapy in stage III colon cancer a multicentre phase II/III randomised controlled study (DYNAMIC-III). Australianclinicaltrials.gov identifier: ACTRN12617001566325. https://www.australianclinicaltrials.gov.au/anzctr/trial/ACTRN12617001566325.
Anandappa G, Starling N, Peckitt C, Bryant A, Begum R, Carter P, Hatt S, Khakoo SS, Turner A, Kidd S, Duncan J, Hobbis L, Giorgakoudi K, Smalley M, Lowery D, Wheatstone P, Chau I, Hubank M, Cunningham D. TRACC: Tracking mutations in cell-free DNA to predict relapse in early colorectal cancer—a randomized study of circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) guided adjuvant chemotherapy versus standard of care chemotherapy after curative surgery in patients with high-risk stage II or stage III colorectal cancer (CRC). J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:TPS4120.
Folprecht G, Reinacher-Schick A, Weitz J, Lugnier C, Kraeft AL, Wisser S, Aust DE, Weiss L, von Bubnoff N, Kramer M, Thiede C, Tannapfel A. The CIRCULATE Trial: circulating tumor DNA based decision for adjuvant treatment in colon cancer stage II evaluation (AIO-KRK-0217). Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2022;21:170–4.
Taieb J, Benhaim L, Laurent Puig P, et al. Decision for adjuvant treatment in stage II colon cancer based on circulating tumor DNA: the CIRCULATE-PRODIGE 70 trial. Dig Liver Dis. 2020;52:730–3.
Yukami H, Mishima S, Kotani D, Oki E, Taniguchi H, Nakamura Y, Kato T, Takemasa I, Yamanaka T, Shirasu H, Sawada K, Ebi H, Aleshin A, Billings P, Rabinowitz M, Mori M, Yoshino T. P-120 Prospective observational study monitoring circulating tumor DNA in resectable colorectal cancer patients undergoing radical surgery: GALAXY study in CIRCULATE-Japan (trial in progress). Ann Oncol. 2020;31:S128–9.
Malla M, Loree JM, Kasi PM, Parikh AR. Using circulating tumor DNA in colorectal cancer: current and evolving practices. J Clin Oncol. 2022;40:2846–57.
Taniguchi H, Nakamura Y, Kotani D, Yukami H, Mishima S, Sawada K, Shirasu H, Ebi H, Yamanaka T, Aleshin A, Billings PR, Rabinowitz M, Oki E, Takemasa I, Kato T, Mori M, Yoshino T. CIRCULATE-Japan: circulating tumor DNA-guided adaptive platform trials to refine adjuvant therapy for colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci. 2021;112:2915–20.
Morris VK, Yothers G, Kopetz S, Jacobs SA, Lucas PC, Iqbal A, Boland PMK, Deming DA, Scott AJ, Lim HJ, Wolmark N, George TJ. NRG-GI005 (COBRA): phase II/III study of circulating tumor DNA as a predictive biomarker in adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with stage II colon cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:TPS261.
Masfarre L, Vidal J, Fernandez-Rodriguez C, Montagut C. ctDNA to guide adjuvant therapy in localized colorectal cancer (CRC). Cancers (Basel). 2021;13:2869.
Shirasu H, Taniguchi H, Matsuhashi N, et al. A randomized, double-blind, phase III study comparing trifluridine/tipiracil hydrochloride therapy versus placebo in resected colorectal cancer patients who are positive for blood circulating tumor DNA after standard adjuvant therapy (EPOC 1905): ALTAIR trial in CIRCULATE-Japan (trial in progress). J Clin Oncol. 2022;40:TPS215.
Lonardi S, Montagut C, Pietrantonio F, Elez E, Sartore-Bianchi A, Tarazona N, Sciallero S, Zampino MG, Mosconi S, Muñoz S, Lazzari L, Luraghi P, Siena S, Sobrero AF, Labianca R, Torri V, Bardelli A, Tabernero J, Marsoni S. The PEGASUS trial: Post-surgical liquid biopsy-guided treatment of stage III and high-risk stage II colon cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:TPS4124.
Nors J, Henriksen TV, Gotschalck KA, Juul T, Søgaard J, Iversen LH, Andersen CL. IMPROVE-IT2: implementing noninvasive circulating tumor DNA analysis to optimize the operative and postoperative treatment for patients with colorectal cancer – intervention trial 2. Study protocol. Acta Oncol. 2020;59:336–41.
Yoshino T, Watanabe J, Shitara K, Yasui H, Ohori H, Shiozawa M, Yamazaki K, Oki E, Sato T, Naitoh T, Komatsu Y, Kato T, Hihara M, Soeda J, Yamamoto K, Akagi K, Ochiai A, Uetake H, Tsuchihara K, Muro K. Panitumumab (PAN) plus mFOLFOX6 versus bevacizumab (BEV) plus mFOLFOX6 as first-line treatment in patients with RAS wild-type (WT) metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC): results from the phase 3 PARADIGM trial. J Clin Oncol. 2022;40:LBA1.
Tomlinson JS, Jarnagin WR, DeMatteo RP, et al. Actual 10-year survival after resection of colorectal liver metastases defines cure. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:4575–80.
Kopetz S, Chang GJ, Overman MJ, Eng C, Sargent DJ, Larson DW, Grothey A, Vauthey JN, Nagorney DM, McWilliams RR. Improved survival in metastatic colorectal cancer is associated with adoption of hepatic resection and improved chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:3677–83.
Van Cutsem E, Verheul HM, Flamen P, et al. Imaging in colorectal cancer: progress and challenges for the clinicians. Cancers (Basel). 2016;8
Overman MJ, Vauthey J-N, Aloia TA, Conrad C, Chun YS, Pereira AAL, Jiang Z, Crosby S, Wei S, Raghav KPS, Morris VK, Tan M, Maslan A, Talasaz AA, Mortimer S, Kopetz S. Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) utilizing a high-sensitivity panel to detect minimal residual disease post liver hepatectomy and predict disease recurrence. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:3522.
Loupakis F, Sharma S, Derouazi M, et al. Detection of molecular residual disease using personalized circulating tumor DNA assay in patients with colorectal cancer undergoing resection of metastases. JCO Precis Oncol. 2021;5
Sargent DJ, Wieand HS, Haller DG, Gray R, Benedetti JK, Buyse M, Labianca R, Seitz JF, O'Callaghan CJ, Francini G, Grothey A, O'Connell M, Catalano PJ, Blanke CD, Kerr D, Green E, Wolmark N, Andre T, Goldberg RM, de Gramont A. Disease-free survival versus overall survival as a primary end point for adjuvant colon cancer studies: individual patient data from 20,898 patients on 18 randomized trials. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:8664–70.
Sargent D, Sobrero A, Grothey A, O'Connell MJ, Buyse M, Andre T, Zheng Y, Green E, Labianca R, O'Callaghan C, Seitz JF, Francini G, Haller D, Yothers G, Goldberg R, de Gramont A. Evidence for cure by adjuvant therapy in colon cancer: observations based on individual patient data from 20,898 patients on 18 randomized trials. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:872–7.
Sargent DJ, Patiyil S, Yothers G, Haller DG, Gray R, Benedetti J, Buyse M, Labianca R, Seitz JF, O'Callaghan CJ, Francini G, Grothey A, O'Connell M, Catalano PJ, Kerr D, Green E, Wieand HS, Goldberg RM, de Gramont A, ACCENT Group. End points for colon cancer adjuvant trials: observations and recommendations based on individual patient data from 20,898 patients enrolled onto 18 randomized trials from the ACCENT Group. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:4569–74.
Funding
Funding
Funding provided by AIRC IG 2018 to Alberto Sobrero.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Alberto Puccini, Valentino Martelli, Alessandro Pastorino, and Stefania Sciallero declare no conflict of interests. Alberto Sobrero has served as consultant/advisory board member for BMS Pierre Fabre Amgen Hutchmed MSD Servier; and received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers’ bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events: Roche Servier MSD BMS Amgen Merck Bayer Sanofi Pierre Fabre.
Human and Animal Rights
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Lower Gastrointestinal Cancers
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Puccini, A., Martelli, V., Pastorino, A. et al. ctDNA to Guide Treatment of Colorectal Cancer: Ready for Standard of Care?. Curr. Treat. Options in Oncol. 24, 76–92 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11864-022-01048-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11864-022-01048-x