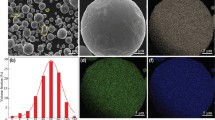
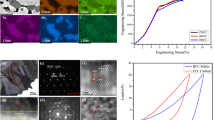
Abstract
CoCuFeMnNi bulk nanocrystalline alloy was prepared by mechanical alloying (MA) and spark plasma sintering (SPS). The effects of sintering parameters, such as temperature, heating rate, sintering pressure, pressing time, and cooling mode on the compressive strength of bulk sintered alloys were analyzed, and the effects of sintering temperature and pressing time on the magnetic properties of the alloys were investigated. The compressive strength test results show that the compressive strength of the alloy first increases and then decreases with the increase of heating rate and pressing time. A model was established to study the mechanisms of mechanical properties of the CoCuFeMnNi alloy. The strengthening mechanisms such as grain refinement strengthening, solid solution strengthening, and cluster strengthening of CoCuFeMnNi alloy was quantitatively analyzed. The magnetic test results show that the prepared CoCuFeMnNi amorphous alloy powder and its bulk alloy are typical soft magnetic materials. The saturation magnetic induction strength of the bulk alloy increases with the increase of sintering temperature and pressing time. However, the coercivity first decreases and then increases.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Li, A. Wang, and C.T. Liu, J. Alloy. Compd. 694, 55. (2017).
T.T. Zuo, M. Zhang, P.K. Liaw, and Y. Zhang, Intermetallics 100, 1. (2018).
F. Alijani, M. Reihanian, and K. Gheisari, J. Alloy. Compd. 773, 623. (2019).
Z.Q. Fu, B.E. Macdonald, A.D. Dupuy, X. Wang, T.C. Monson, R.E. Delaney, C.J. Pearce, K. Hu, Z.F. Jiang, Y.Z. Zhou, J.M. Schoenung, W.P. Chen, and E.J. Lavernia, Appl. Mater. Today. 15, 590. (2019).
X.W. Nie, M.D. Cai, and S. Cai, Int. J. Refractory Met. Hard Mater 98, 105568. (2021).
H. Shokrollahi and K. Janghorban, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 189, 1. (2007).
R. Agarwal, R. Sonkusare, S.R. Jha, N.P. Gurao, K. Biswas, and N. Nayan, Mater. Des. 157, 539. (2018).
K. Biswas Tazuddin and N.P. Gurao, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 657, 224. (2016).
X.W. Nie and Q. Lu, Ceram. Int. 47, 19700. (2021).
A. Tazuddin, N.P. Gurao, and K. Biswas, J. Alloys Compd. 697, 434. (2017).
R. Sonkusare, P.D. Janani, N.P. Gurao, S. Sarkar, S. Sen, K.G. Pradeep, and K. Biswas, Mater. Chem. Phys. 210, 269. (2018).
A. Takeuchi, T. Wada, and Y. Zhang, Intermetallics 82, 107. (2017).
S.M. Oh and S.I. Hong, Mater. Chem. Phys. 210, 120. (2018).
R. Sonkusare, N. Khandelwal, P. Ghosh, K. Biswas, and N.P. Gurao, J. Mater. Res. 34, 732 (2019).
R. Sonkusare, K. Biswas, N. A. Hamdany, H.G. Brokmeier, and R. Kalsar, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 782, 139187. (2020).
R. Sonkusare, R. Jain, K. Biswas, V. Parameswaran, and N.P. Gurao, J. Alloys Compd. 823, 153763. (2020).
N. Prasad, N. Bibhanshu, N. Nayan, G.S. Avadhani, and S. Suwas, Journal of Materials Research 34, 744. (2019).
B. E. MacDonald, Z. Fu, X. Wang, Z. Li, W. Chen, Y. Zhou, D. Raabe, J. Schoenung, H. Hahn, and E.J. Lavernia, Acta Mater. 181, 25. (2019).
F. Bahadur, K. Biswas, and N.P. Gurao, International Journal of Fatigue 130, 105258. (2020).
S. H. Shim, S. M. Oh, J. Lee, S.K. Hong, and S.I. Hong, Materials Science & Engineering A,762, 138129. (2019).
X. Nie, and J. **ong, JOM 73, 2525. (2021).
Y. Zou, Journal of Materials Research, 33, 3035. (2018).
A.S. Sharma,S. Yadav,K. Biswas,and B. Basu, Materials Science and Engineering: R 131, 1. (2018).
R.F. Zhao, B. Ren, G.P. Zhang, Z.X. Liu, B. Cai, and J. J. Zhang, Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 491, 165574. (2019).
Q. Li, G. Wang, X. P. Song, L. Fang, and R. Liu, Journal of Materials Processing Technology. 209, 3285. (2009).
Y. Zhang, P. Sharma, and A. Makino, Materials Transactions, 52, 2254. (2011)
S. Lee, H. Kato, T. Kubota, A. Makino, and A. Inoue, Intermet, 17, 218. (2009).
Z.Y. **ao, C.Y. Tang, H.D. Zhao, and D. Tong, J Non-Cryst Solids 358, 114. (2012).
J.Y. He, W.H. Liu, H. Wang, Y. Wu, X.J. Liu, T.G. Nieh, and Z.P. Lu, Acta Mater. 62, 105. (2014).
X. Yang and Y. Zhang, Mater. Chem. Phys. 132, 233. (2012).
S. Guo, C. Ng, J. Lu, and C.T. Liu, J. Appl. Phys. 109, 103505. (2011).
A. Sourav, S. Yebaji, and S. Thangaraju, Materials Science & Engineering A, 793, 139877. (2020).
Q. Liu, G. Wang, X. Sui, Y. Liu, X. Li, and J. Yang, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 35, 2600. (2019).
Y. Long, X.B. Liang, K. Su, H.Y. Peng, and X.Z. Li, J. Alloy. Compd. 780, 607. (2019).
B. Kang, J. Lee, H.J. Ryu, and S.H. Hong, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 712, 616. (2018).
Z.F. Lei, X.J. Liu, Y. Wu, H. Wang, S.H. Jiang, S.D. Wang, X.D. Hui, Y.D. Wu, B. Gault, P. Kontis, D. Raabe, L. Gu, Q.H. Zhang, H.W. Chen, H.T. Wang, J.B. Liu, K. An, Q.S. Zeng, T.G. Nieh, and Z.P. Lu, Nat. Mater. 563, 546. (2018).
Y. Zhang, T.T. Zuo, Z. Tang, M.C. Gao, K.A. Dahmen, P.K. Liaw, and Z.P. Lu, Prog. Mater. Sci. 61, 1. (2014).
X.W. Nie, Y. Du, and H.H. Xu, Phil. Mag. Lett. 91, 328. (2011).
U.F. Kocks, Metal. Mater. Trans. 1, 1121. (1970).
E. Fazakas, V. Zadorozhnyy, L.K. Varga, A. Inoue, D.V. Louzguine-Luzgin, F. Tian, and L. Vitos, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 47, 131. (2014).
H. Wen, T.D. Top**, D. Isheim, D.N. Seidman, and E.J. Lavernia, Acta Mater. 61, 2769. (2013).
S.Y. Sun, H.L. Shang, B.Y. Ma, F. Chen, and G.Y. Li, Comput. Mater. Sci. 142, 325. (2018).
Z.P. Wang, Q.H. Fang, J. Lia, B. Liu, and Y. Liu, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 34, 349. (2018).
J.Y. Pan, T. Dai, T. Lu, X.Y. Ni, J.W. Dai, and M. Li, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 738, 362. (2018).
T. Shanmugasundaram, E. Bouzy, and A.H. Chokshi, Mater. Sci. Eng. 639, 97. (2015).
P. Luo, D.T. McDonald, W. Xu, S. Palanisamy, M.S. Dargusch, and K. **a, Scr. Mater. 66, 785. (2012).
Z.M. Jiao, M.Y. Chu, H.J. Yang, Z.H. Wang, and J.W. Qiao, Mater. Sci. Technol. 31, 1244. (2015).
M. Li, J. Gazquez, A. Borisevich, R. Mishra, and K.M. Flores, Intermetallics 95, 110. (2018).
X. Nie, Y. Du, and H. Xu, Physica B 405, 4279. (2010).
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No.: 51304247), Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (Project No.: 2019JJ70050) and Scientific Research Project of Colleges and Universities in Hunan Province (Project No.: 19C0557).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XN devised the project and conceived of the presented idea. SM prepared the specimens and developed the experimental work and performed the mechanical testing and analysis. AM evaluated and analyzed the microstructures. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nie, X., Sheng, M. & Mabi, A. Effect of SPS Sintering Process on Compressive Strength and Magnetic Properties of CoCuFeMnNi Bulk Alloy. JOM 74, 2665–2675 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05277-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05277-1