Abstract
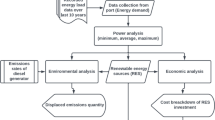
Air pollution from ship** is becoming a critical issue, particularly in dense hub port cities. One proposed solution to minimize ship-based emissions at ports is the implementation of an Onshore Power Supply (OPS) system. OPS allows ships to shut off their auxiliary engines and instead connect to the port grid. While there have been numerous studies conducted on ports in Europe and the United States, little research has been done on Egyptian ports. Therefore, this paper aims to investigate the feasibility of implementing OPS at Port Said West Port in Egypt, aligning with Egypt Vision 2030’s goals for addressing climate change. The research primarily focuses on analyzing data collected from calling ships to generate socio-economic and cost-effectiveness analyses of OPS. To further enhance the environmental benefits of OPS, the paper proposes the use of solar energy as the OPS electricity source. The findings of the study revealed that by relying on the national grid, emissions can be reduced by 28%. Moreover, it is predicted that this reduction could reach 100% if electricity generation is solely based on solar energy. Additionally, the economic analysis demonstrates promising profitability, with a payback period of approximately two years.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acciaro M, Vanelslander T, Sys C, Ferrari C, Roumboutsos A, Giuliano G, Kapros S (2014) Environmental sustainability in seaports: a framework for successful innovation. Maritime Policy & Management, 41(5): 480–500. https://doi.org/10.1080/03088839.2014.932926
Adamo F, Andria G, Cavone G, De Capua C, Lanzolla AML, Morello R, Spadavecchia M (2014) Estimation of ship emissions in the port of Taranto. Measurement, 47, 982–988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2013.09.012
American Bureau of Ship** (ABS) (2021) Retrieved online from https://ww2.eagle.org/en.html (Accessed 13 May 2021)
Andria G, Attivissimo F, Cavone G, Lanzolla AML, Spadavecchia M (2014) Environmental impact of the marine transport in port of Taranto. 5th IMEKO TC19 Symposium on Environmental Instrumentation and Measurements, 16–19. IMEKO-International Measurement Federation Secretariat
Badino A, Borelli D, Gaggero T, Rizzuto E, Schenone C (2012) Noise emitted from ships: impact inside and outside the vessels. Procedia - Social and Behavioural Sciences. 48: 868–879. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.06.1064
Ballini F, Bozzo R (2015) Air pollution from ships in ports: The socio-economic benefit of cold-ironing technology. Research in Transportation Business & Management, 17: 92–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rtbm.2015.10.007
Bassam AM, Phillips AB, Turnock SR, Wilson PA (2023) A solar energy-based shore side power system for a ferry service across the Suez Canal, Ships and Offshore Structures, https://doi.org/10.1080/17445302.2023.2245187
Bullock S, Hoolohan C, Larkin A (2023) Accelerating ship** decarbonization: A case study on UK shore power. Heliyon 9.7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17475
CARB (2007) Technical support document: Initial statement of reasons for the proposed rulemaking-Regulations to reduce emissions from diesel auxiliary engines on ocean-going vessels while at-berth at a California port. Sacramento, CA: California Air Resources Board. Retrieved from http://www.arb.ca.gov/regact/2007/shorepwr07/shorepwr07.html
CARB (2011) Initial statement of reasons for proposed rulemaking-Proposed amendments to the regulations fuel sulfur and other operational requirements for ocean-going vessels within California waters and 24 nautical miles of the California baseline. Sacramento, CA: California Air Resources Board. http://www.arb.ca.gov/regact/2011/shorepwr11/shorepwr11.html
Chang CC, Wang CM (2012) Evaluating the effects of green port policy: Case study of Kaohsiung harbour in Taiwan. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 17(3), 185–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2011.11.006
Cheng K, Chang Y, Kuang Y, Ling Q, Zou Z, Huang R (2022) Multiple-Year Changes (2014–2018) in Particulate Vanadium Linked to Ship** Regulations in the World’s Largest Port Region. ACS Earth and Space Chemistry. 6: 415–420. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsearthspacechem.1c00402
Climate Data (2019) Climate-data. org, Port Said Climate: Average temperature, weather by month. Available at: https://en.climate-data.org/africa/egypt/port-said-governorate/port-said-504/ (Accessed: 02 October 2023)
Corbett JJ, Winebrake JJ, Green EH, Kasibhatla P, Eyring V, Lauer A (2007) Mortality from ship emissions: a global assessment. Environ Sci Techno, 41(24): 8512–8518. https://doi.org/10.1021/es071686z
De Jonge E, Hugi C, Cooper D (2005) European commission directorate general environment service contract on ship emissions: Assignment, abatement and market-based instruments. Task 2a-Shore-Side Electricity Final Report ENTEC UK Limited.
Det Norske Veritas (DNV) (2021) Retrieved online from https://vesselregister.dnv.com/vesselregister/(Accessed 13 May 2021)
EMICS Circular (2018) EMICS Egypt. Retrieved online from https://www.emicsegypt.com/ (Accessed 15 May 2021)
Essen H, van Wijngaarden L, van Sutter D, Bieler C, Maffii S, Fiorello D, Fermi F, Parolin R, Schroten A, Brambilla M (2020) Handbook on the external costs of transport: version 2019-1.1. Publications Office of the European Union. https://doi.org/10.2832/51388
Esteve Pérez J, Gutiérrez Romero JE (2015) Renewable energy supply to ships at port. SARTI. https://raco.cat/index.php/Instrumentation/article/view/316007
Gilbert P, Bows-Larkin A, Mander S, Walsh C (2015) Technologies for the high seas: meeting the climate challenge. Carbon Management, 5(4): 447–461. https://doi.org/10.1080/17583004.2015.1013676
Gore K, Rigot-Müller P, Coughlan J (2023) Cost-benefit assessment of shore side electricity: An Irish perspective. Journal of environmental management, 326(Pt B): 116755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116755
Guo B, Gissey GC (2019) Cost Pass-through in the British Wholesale Electricity Market: Implications of Brexit and the ETS reform. Energy Policy Research Group, University of Cambridge. http://www.jstor.org/stable/resrep30333
Gutierrez-Romero J, Esteve-Pérez J, Zamora B (2019) Implementing Onshore Power Supply from renewable energy sources for requirements of ships at berth. Applied Energy. 255. 113883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.113883
Huang L, Wen Y, Geng X, Zhou C, **ao C, Zhang F (2017) Estimation and spatio-temporal analysis of ship exhaust emission in a port area. Ocean Engineering. 140: 401–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2017.06.015
IMO (2020) Fourth IMO greenhouse gas study. MEPC 75/7/15: Reduction of GHG Emissions from Ships-Final report. https://www.imo.org/en/ourwork/Environment/Pages/Fourth-IMO-Greenhouse-Gas-Study-2020.aspx
Innes A, Monios J (2018) Identifying the unique challenges of installing cold ironing at small and medium ports-The case of Aberdeen. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment 62: 298–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2018.02.004
IRENA (2021) Renewable Capacity Statistics 2021. Technical Report, Abu Dhabi. https://www.irena.org/publications/2021/March/Renewable-Capacity-Statistics-2021
Kotrikla AM, Lilas T, Nikitakos N (2017) Abatement of air pollution at an Aegean Island port utilizing shore side electricity and renewable energy. Marine Policy, 75: 238–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpol.2016.01.026
Kraemer I, Czermanski E (2020) Onshore power one option to reduce air emissions in ports. Sustainability Management Forum. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00550-020-00497-y
Kurt I, Boulougouris E, Pachakis D (2023) Comparative Technical-Economic Evaluation of Offshore Containerships Port Systems. Ships and Offshore Structures. https://doi.org/10.1080/17445302.2023.2226502
Lee H, Pham H, Chen M, Choo S (2021) Bottom-Up Approach Ship Emission Inventory in Port of Incheon Based on VTS Data. Advanced Transportation. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5568777
Maibach M, Schreyer C, Sutter D, Van Essen HP, Boon BH, Smokers R, Schroten A, Doll C, Pawlowska B, Bak M (2008) Handbook on estimation of external costs in the transport sector Internalisation Measures and Policies for All external Cost of Transport (IMPACT), Version 1.1. http://www.cedelft.nl/
Merk O (2014) Ship** emissions in ports. Paris: The International Transport Forum’s Discussion Paper. https://doi.org/10.1787/5jrw1ktc83r1-en
MFAT market report NZ (2021) The Importance of the Suez Canal to Global Trade Market Report Egypt: The New Zealand Embassy. https://www.mfat.govt.nz/assets/Trade/MFAT-Market-reports/The-Importance-of-the-Suez-Canal-to-Global-Trade-18-April-2021
Mohamed S, Salah-Eldine M (2020) Evaluating the sustainable green seaports (SGP) in Egypt: Case Study of Alexandria and Eldekhila Seaports, Journal of Alexandria University for Administrative Sciences, 57 (1). https://acjalexu.journals.ekb.eg/article_79839
Naty S, Viviano A, Foti E (2016) Wave Energy Exploitation System Integrated in the Coastal Structure of a Mediterranean Port. Sustainability. 8(12). https://doi.org/10.3390/su8121342
Ni P, Wang X, Li H (2020) A review on regulations, current status, effects and reduction strategies of emissions for marine diesel engines fuel. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.118477
Nippon Kaiji Kyokai (ClassNK) (2021) Retrieved online from https://www.classnk.or.jp/hp/en/index.html (Accessed 13 May 2021)
ODS register (2010) Noise from ships in ports Possibilities for noise reduction. Retrieved from https://mst.dk/media/mst/66165/978-87-92668-35-6
Paulauskas V, Filina-Dawidowicz L, Paulauskas D (2020) The Method to Decrease Emissions from Ships in Port Areas. Sustainability, 12(11): 4374. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12114374
Peng Y, Liu H, Li X, Huang J, Wang W (2020) Machine learning method for energy consumption prediction of ships in port considering green ports. Journal of Cleaner Production. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121564
Sciberras EA, Zahawi B, Atkinson DJ (2015) Electrical characteristics of cold ironing energy supply for berthed ships. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2015.05.007
SCZONE (2021) West Port Said port. Retrieved from: https://sczone.eg/services/west-portsaid-port/ (Accessed 30 May 2021)
Seddiek I, Mosleh M, Banawan A (2014) Fuel saving and emissions cut through shore-side power concept for high-speed crafts at the red sea in Egypt. Journal of Marine Science and Application, 12: 463–472. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11804-013-1218-6
Seddiek I (2019) Application of renewable energy technologies for eco-friendly sea ports. Ships and Offshore Structures. 10.108017445302.2019.1696535
Seediek I, Elgohary M (2020) Assessment of renewable energy supply for green ports with a case study. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. 27(5): 5547–5558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07150-2
Ship and bunker (2022) Retrieved from https://shipandbunker.com/prices#MGO (Accessed 2 June 2022)
Slack B, Comtois C, Wiegmans B, Witte P (2018) Ships time in port. International Journal of Ship** and Transport Logistics. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJSTL.2018.10008534
SolarGIS Freemaps (2018) Global Horizontal Irradiation. Country maps: Egypt. Solar resource map 2018 Retrieved from https://solargis.com/maps-and-gis-data/download/egypt (Accessed 4 July 2022)
Stolz B, Held M, Georges G, Boulouchos K (2021) The CO2 reduction potential of shore-side electricity in Europe. Applied Energy, 285: 116425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.116425
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) (2017) Shore Power Technology Assessment at U. S. Ports. Transportation and Climate Division Office of Transportation and Air Quality U. S. Environmental Protection Agency. Retrieved from https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2017-05/documents/420r17004-2017-update
Tiwari GN, Arvind K (2016) Handbook of solar energy: theory, analysis and applications (energy systems in electrical engineering). Singapore: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-0807-8
Tseng P, Pilcher N (2015) A study of the potential of shore power for the port of Kaohsiung, Taiwan: to introduce or not to introduce. Research in Transportation Business & Management, 17: 83–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rtbm.2015.09.001
Tzannatos E (2010) Ship emissions and their externalities for the port of Piraeus-Greece. Atmospheric Environment. 44. 400–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.10.024
Wang L, Liang C, Shi J, Molavi A, Lim G, Zhang Y (2021) A bilevel hybrid economic approach for optimal deployment of onshore power supply in maritime ports. Applied energy, 292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.116892
Winkel R, Weddige U, Johnsen D, Hoen V, Papaefthimiou S (2016) Shore Side Electricity in Europe: Potential and environmental benefits. Energy Policy, 88: 584–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2015.07.013
Yarova N, Vorkunova O, Khoteyeva N (2017) Economic assessment of the alternative energy sources implementation for port enterprises. Economic Annals-XXI, 166(7–8): 46–50. https://doi.org/10.21003/ea.V166-09
Yıldırım Pekşen D, Alkan G (2018) Application of Alternative Maritime Power (AMP) Supply to Cruise Port. J. ETA Maritime Science, 6(4): 307–318. https://doi.org/10.5505/jems.2018.15870
Zhai Q, Cao H, Zhao X, Yuan C (2011) Cost Benefit Analysis of Using Clean Energy Supplies to Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Global Automotive Manufacturing. Energies 4, no. 10: 1478–1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/en4101478
Zis T, North R, Angeloudis P, Ochieng W, Harrison Bell M (2014) Evaluation of cold ironing and speed reduction policies to reduce ship emissions near and at ports. Maritime Economics & Logistics, 16(4): 371–398. https://doi.org/10.1057/mel.2014.6
Zis T (2019) Prospects of cold ironing as an emissions reduction option. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 119: 82–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tra.2018.11.003
Acknowledgement
The authors greatly acknowledge the support of Port Said West Port Authority in the Port Said branch towards the availability of the research data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interestThe authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Article Highlights
• Implementing Onshore Power Supply (OPS) at Port Said West Port reduces ship** emissions by 28%.
• Emissions reduction can reach near or 100% if solar energy is the primary OPS electricity source.
• OPS adoption at the targeted Egyptian port shows promising profitability.
• The barriers facing OPS-wide implementation in Egypt are outlined.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Makram, M., Bassam, A.M., Tawfik, A.A. et al. Assessment of Onshore Renewable Energy Power Supply for Ship’s Emissions Reduction in Port Said West Port. J. Marine. Sci. Appl. 23, 506–524 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11804-024-00423-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11804-024-00423-4