Abstract
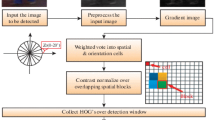
It is novel to apply three-dimensional (3D) light field imaging technology to recognize two-dimensional (2D) fake pedestrians. In this paper, we propose a parallel support vector machine (SVM) method based on 3D light field imaging (light field camera) and machine learning techniques. A light field (LF) camera with robust sensors, which is able to record rich 3D information, is used as hardware equipment. Histogram of oriented gradient (HOG) feature extraction algorithm and SVM classification method are used to recognize the real and 2D fake pedestrians efficiently. Besides, we carry out an experiment on our improved LF pedestrian dataset. The experimental results of parameter optimization study show that in the case of 400 training samples (200 positive samples and 200 negative samples), 120 to 420 testing samples, and an HOG cellsize as 8×8, the best recognition accuracy with polynomial kernel function is improved by more than 2% compared with the previous method. The best accuracy is 99.17%. Otherwise, the recognition accuracy of more than 98.00% will be obtained even under other experimental conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BILAL M. Algorithmic optimisation of histogram intersection kernel support vector machine-based pedestrian detection using low complexity features[J]. IET computer vision, 2017, 11(5): 350–357.
LI F, ZHANG R, YOU F. Fast pedestrian detection and dynamic tracking for intelligent vehicles within V2V cooperative environment[J]. IET image processing, 2017, 11(10): 833–840.
BRAUN M, KREBS S, FLOHR F, et al. Eurocity persons: a novel benchmark for person detection in traffic scenes[J]. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, 2019, 41(8): 1844–1861.
BILAL M, KHAN A, KHAN M U K, et al. A low-complexity pedestrian detection framework for smart video surveillance systems[J]. IEEE transactions on circuits and systems for video technology, 2016, 27(10): 2260–2273.
LIU S, LI Y F. Precision 3-D motion tracking for binocular microscopic vision system[J]. IEEE transactions on industrial electronics, 2019, 66(12): 9339–9349.
SEPAS-MOGHADDAM A, PEREIRA F, CORREIA P L. Ear recognition in a light field imaging framework: a new perspective[J]. IET biometrics, 2018, 7(3): 224–231.
JEON H G, PARK J, CHOE G, et al. Depth from a light field image with learning-based matching costs[J]. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, 2018, 41(2): 297–310.
MIGNARD-DEBISE L, IHRKE I. A vignetting model for light field cameras with an application to light field microscopy[J]. IEEE transactions on computational imaging, 2019, 5(4): 585–595.
ANAND C, JAINWAL K, SARKAR M. A three-phase, one-tap high background light subtraction time-of-flight camera[J]. IEEE transactions on circuits and systems I: regular papers, 2019, 66(6): 2219–2229.
DING Y, ZHAO Y, CHEN X, et al. Stereoscopic image quality assessment by analysing visual hierarchical structures and binocular effects[J]. IET image processing, 2019, 13(10): 1608–1615.
LFP (light field photography) file reader[EB/OL]. (2014)[2021-05-20]. http://code.behnam.es/pythonlfp-reader.
JIA C, SHI F, ZHAO Y, et al. Identification of pedestrians from confused planar objects using light field imaging[J]. IEEE access, 2018, 6: 39375–39384.
DENG F, GUO S, ZHOU R, et al. Sensor multifault diagnosis with improved support vector machines[J]. IEEE transactions on automation science and engineering, 2015, 14(2): 1053–1063.
RAGHAVENDRA R, RAJA K B, BUSCH C. Presentation attack detection for face recognition using light field camera[J]. IEEE transactions on image processing, 2015, 24(3): 1060–1075.
Lytro Inc[EB/OL]. (2014-06-02)[2021-05-20]. http://www.lytro.com/.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Statements and Declarations
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest related to this article.
This work has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61906133, 62020106004, 92048301 and 61703304).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, C., Zhang, Y., Shi, F. et al. Light field imaging based on a parallel SVM method for recognizing 2D fake pedestrians. Optoelectron. Lett. 18, 48–53 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11801-022-1047-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11801-022-1047-4