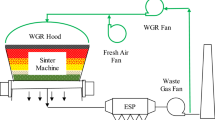
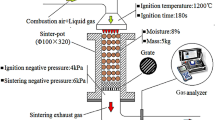
Abstract
It is of great significance for cleaner production to substitute bio-energy for fossil fuels in iron ore sintering. However, with the replacement ratio increasing, the consistency of heat front and flame front is broken, and the thermal utilizing efficiency of fuel is reduced, which results in the decrease of yield and tumble index of sinter. Circulating flue gas to sintering bed as biochar replacing 40% coke, CO in flue gas can be reused so as to increase the thermal utilizing efficiency of fuels, and the consistency of two fronts is recovered for the circulating flue gas containing certain CO2, H2O and lower O2, which contributes to increasing the maximum temperature, extending the high temperature duration time of sintering bed, and results in improving the output and quality of sinter. In the condition of circulating 40% flue gas, the sintering with biomass fuels is strengthened, and the sintering indexes with biomass fuel replacing 40% coke breeze are comparative to those of using coke breeze completely.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
XU **g-li. Energy consumption and energy conservation measures of sinter production [C]// National Conference Proceedings on Raw Iron, Kunming: The Chinese Society for Metals, 2005: 25–28.
DAWSON PR. Recent developments in iron ore sintering [J]. Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 1993;20(2): 135–143.
GAN Min, FAN **ao-hui and CHEN Xu-ling. Reduction of pollutant emission in iron ore sintering process by applying biomass fuels [J]. ISIJ International, 2012, 52(9): 1574–1578.
GARCIA C F, AYAA N. Possible actions for the minimization of the environmental impact of the iron ore sintering fumes [J]. Revista de Metalurgia, 2004, 40(4): 243–246.
LONG Hong-ming. Emission reduction of dioxin in iron ore sintering process by adding urea as inhibitor [J]. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2011, 38(4): 258–262.
PETER S, BODO LH, Gerhard E. Measures to reduce CO2 and other emissions in the steel industry in germany and Europe [J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2009, 16: 42–50.
LOVEL R, VINING K, DELL’AMICO M. Iron ore sintering with charcoal [J]. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy, 2007, 116(2): 85–92.
MOHAMMAD Z, MARIA MP, TREVOR, A T F. Biomass for iron ore sintering [J]. Mineral Engineering, 2010 (7): 1–7.
PENG Zhi-jian, ZHEN Yin-zhu. Study of additives on iron ore energy saving and emission reduction of iron ore sintering [C]// Annual Conference on Sintering & Pelltizing Technology, Changsha: National Infrrmation Network of Sintering & Pelletizing, 2009: 32–36.
JIANG Zheng-wu. Study on combustion process of biomass fuels and characteristics of their ash [J]. Journal of Materials Review, 2010, 24(4): 66–80.
LIU Jian-yu, CHEN Rong-yao. Direct combustion of biomass fuel characteristics analysis [J]. Journal of Northeast Agriculture University, 2001, 32(2): 290–294. (in Chinese)
WEI Xue-feng. Mechanism of biomass fuel combustion by catalyst [J]. Journal of Henan University of Science and Technology (Natural Science), 2009, 30(2), 32–34. (in Chinese)
CHEN **. Exploitation and utilization of bio-energy [J]. Journal of Process in Chemistry, 2007, 19(7): 1091–1096.
GUO Rui-chao, TANG Jun-rong. The statue and vision for utilization of lignified biomass energy [J]. Journal of Forest Inventory and Planning, 2007, 32(1): 90–94
SUN Yong-ming. The status and future of bioenergy and biomass utilization in China [J]. Journal of Renewable Energy, 2006(2): 77–82.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Projects(51174253, 51304245) supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gan, M., Fan, Xh., Jiang, T. et al. Fundamental study on iron ore sintering new process of flue gas recirculation together with using biochar as fuel. J. Cent. South Univ. 21, 4109–4114 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-014-2405-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-014-2405-6