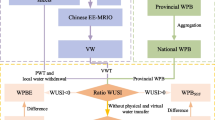
Abstract
Virtual water trade (VWT) provides a new perspective for alleviating water crisis and has thus attracted widespread attention. However, the heterogeneity of virtual water trade inside and outside the river basin and its influencing factors remains further study. In this study, for better investigating the pattern and heterogeneity of virtual water trade inside and outside provincial regions along the Yellow River Basin in 2015 using the input-output model (MRIO), we proposed two new concepts, i.e., virtual water surplus and virtual water deficit, and then used the Logarithmic Mean Divisia Index (LMDI) model to identify the inherent mechanism of the imbalance of virtual water trade between provincial regions along the Yellow River Basin and the other four regions in China. The results show that: 1) in provincial regions along the Yellow River Basin, the less developed the economy was, the larger the contribution of the agricultural sector in virtual water trade, while the smaller the contribution of the industrial sector. 2) Due to the large output of agricultural products, the upstream and midstream provincial regions of the Yellow River Basin had a virtual water surplus, with a net outflow of virtual water of 2.7 × 108 m3 and 0.9 × 108 m3, respectively. 3) provincial regions along the Yellow River Basin were in a virtual water deficit with the rest of China, and the decisive factor was the active degree of trade with the outside. This study would be beneficial to illuminate the trade-related water use issues in provincial regions along the Yellow River Basin, which has far-reaching practical significance for alleviating water scarcity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan J A, 1993. Fortunately there are substitutes for water otherwise our hydro-political futures would be impossible. In: Priorities for Water Resources Allocation and Management. London: ODA, 13–26.
Allan J A, 1998. Virtual water: a strategic resource global solutions to regional deficits. Groundwater, 36(4): 545–546. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.1998.tb02825.x
Bazrafshan O, Etedali H R, Moshizi Z G N et al., 2019. Virtual water trade and water footprint accounting of Saffron production in Iran. Agricultural Water Management, 213: 368–374. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2018.10.034
Bazrafshan O, Zamani H, Etedali H R et al., 2020. Improving water management in date palms using economic value of water footprint and virtual water trade concepts in Iran. Agricultural Water Management, 229: 105941. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2019.105941
Bhave A G, Conway D, Dessai S et al., 2018. Water resource planning under future climate and socioeconomic uncertainty in the Cauvery River Basin in Karnataka, India. Water Resources Research, 54(2): 708–728. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/2017wr020970
Boretti A, Rosa L, 2019. Reassessing the projections of the World Water Development Report. npj Clean Water, 2(1): 15. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-019-0039-9
Brindha K, 2020. Virtual water flows, water footprint and water savings from the trade of crop and livestock products of Germany. Water and Environment Journal, 34(4): 656–668. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/wej.12601
Cazcarro I, Schyns J F, Arto I et al., 2022. Nations’ water footprints and virtual water trade of wood products. Advances in Water Resources, 164: 104188. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2022.104188
Chen W M, Wu S M, Lei Y L et al., 2018. Virtual water export and import in China’s foreign trade: a quantification using input-output tables of China from 2000 to 2012. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 132: 278–290. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.02.017
D’Ambrosio E, Gentile F, De Girolamo A M, 2020. Assessing the sustainability in water use at the basin scale through water footprint indicators. Journal of Cleaner Production, 244: 118847. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118847
Du Y Y, Fang K, Zhao D D et al., 2022. How far are we from possible ideal virtual water transfer? Evidence from assessing vulnerability of global virtual water trade. Science of the Total Environment, 828: 154493. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154493
Fu Y C, Zhao J Y, Wang C L et al., 2018. The virtual water flow of crops between intraregional and interregional in China. Agricultural Water Management, 208: 204–213. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2018.06.023
Guan D B, Meng J, Reiner D M et al., 2018. Structural decline in China’s CO2 emissions through transitions in industry and energy systems. Nature Geoscience, 11(8): 551–555. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-018-0161-1
Han Y P, Jia D D, Zhuo L et al., 2018. Assessing the water footprint of wheat and maize in Haihe River Basin, Northern China (1956–2015). Water, 10(7): 867. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/w10070867
Hoekstra A Y, 2016. A critique on the water-scarcity weighted water footprint in LCA. Ecological Indicators, 66: 564–573. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.02.026
Hoekstra A Y, 2017. Water footprint assessment: evolvement of a new research field. Water Resources Management, 31(10): 3061–3081. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1618-5
Li M, Tian Q S, Yu Y et al., 2021. Virtual water trade in the Yellow River Economic Belt: a multi-regional input-output model. Water, 13(6): 748. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/w13060748
Liu W F, Antonelli M, Kummu M et al., 2019. Savings and losses of global water resources in food-related virtual water trade. WIREs:Water, 6(1): e1320. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/wat2.1320
Leontief W, Duchin F, 1992. The Future Impact of Automation on Workers. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Ma W J, Opp C, Yang D W, 2020. Past, present, and future of virtual water and water footprint. Water, 12(11): 3068. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/w12113068
Meng J, Mi Z F, Guan D B et al., 2018. The rise of South-South trade and its effect on global CO2 emissions. Nature Communications, 9: 1871. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04337-y
Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China, 2016. China Water Resources Bulletin 2015. Bei**g: China Water Power Press.
National Bureau of Statistics of China, 2009. China Economic Census Yearbook 2008. Bei**g: China Statistics Press.
Pastor A V, Palazzo A, Havlik P et al., 2019. The global nexus of food-trade-water sustaining environmental flows by 2050. Nature Sustainability, 2(6): 499–507. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-019-0287-1
Qin Y, Mueller N D, Siebert S et al., 2019. Flexibility and intensity of global water use. Nature Sustainability, 2(6): 515–523. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-019-0294-2
Rosa L, Chiarelli D D, Rulli M C et al., 2020. Global agricultural economic water scarcity. Science Advances, 6(18): eaaz6031. doi: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaz6031
Rui D, Riaz N, Guoyong W et al., 2022. Agricultural water use efficiency and spatial spillover effect considering undesired output in China. Water Policy, 24(10): 1658–1675. doi: https://doi.org/10.2166/wp.2022.111
Schwarz J, Mathijs E, Maertens M, 2019. A dynamic view on agricultural trade patterns and virtual water flows in Peru. Science of the Total Environment, 683: 719–728. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.118
Sun S K, Yin Y L, Wu P T et al., 2019. Geographical evolution of agricultural production in China and its effects on water stress, economy, and the environment: the virtual water perspective. Water Resources Research, 55(5): 4014–4029. doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/2018WR023379
Vallino E, Ridolfi L, Laio F, 2021. Trade of economically and physically scarce virtual water in the global food network. Scientific Reports, 11: 22806. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-01514-w
Wu X D, Guo J L, Li C H et al., 2019. Global socio-hydrology: an overview of virtual water use by the world economy from source of exploitation to sink of final consumption. Journal of Hydrology, 573: 794–810. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.03.080
**e P X, Zhuo L, Yang X et al., 2020. Spatial-temporal variations in blue and green water resources, water footprints and water scarcities in a large river basin: a case for the Yellow River Basin. Journal of Hydrology, 590: 125222. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125222
Xu Z C, Li Y J, Herzberger A et al., 2019. Interactive national virtual water-energy nexus networks. Science of the Total Environment, 673: 128–135. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.298
Xu Z W, Yao L M, Zhang Q et al., 2020. Inequality of water allocation and policy response considering virtual water trade: a case study of Lanzhou City, China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 269: 122326. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122326
Xue J, Chen X, Ma J, 2022. Regional virtual water trade: the perspective of interprovincial trade in China. American Journal of Industrial and Business Management, 12(5): 1029–1046. doi: https://doi.org/10.4236/ajibm.2022.125054
Zhai M Y, Huang G H, Liu L R et al., 2019. Transfer of virtual water embodied in food: a new perspective. Science of the Total Environment, 659: 872–883. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccitotenv.2018.12.433
Zhang C, Anadon L D, 2014. A multi-regional input-output analysis of domestic virtual water trade and provincial water footprint in China. Ecological Economics, 100: 159–172. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2014.02.006
Zhang M, Qin J Y, Tan H et al., 2023. Education level of farmers, market-oriented reforms, and the utilization efficiency of agricultural water resources in China. Economic Change and Restructuring, 1–21. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10644-022-09474-5
Zhuo L, Mekonnen M M, Hoekstra A Y et al., 2016. Inter- and intra-annual variation of water footprint of crops and blue water scarcity in the Yellow River Basin (1961–2009). Advances in Water Resources, 87: 29–41. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2015.11.002
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MA Wei**g: conceptualization, methodology, supervision, writing-reviewing and editing; LI **angjie: conceptualization, methodology, software, visualization, writing original draft; KOU **gwen: methodology, software, visualization; LI Chengyi: methodology, software, visualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42201302), ‘Double First-Class’ University Construction Project of Lanzhou University (No. 561120213)
Supplementary
Tables S1–S2 could be found at http://egeoscien.neigae.ac.cn/article/2024/2.
Electronic Suplementary Material
11769_2024_1415_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Spatial Heterogeneity of Embedded Water Consumption from the Perspective of Virtual Water Surplus and Deficit in the Yellow River Basin, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, W., Li, X., Kou, J. et al. Spatial Heterogeneity of Embedded Water Consumption from the Perspective of Virtual Water Surplus and Deficit in the Yellow River Basin, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 34, 311–326 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-024-1415-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-024-1415-z