Abstract
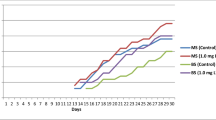
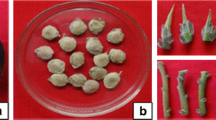
The habitat of the endemic, endangered, and medically important plant, Stachys cretica subsp. kutahyensis belongs to the family Lamiaceae, is threatened by human influence. This study used a shoot tip explant to standardize a simple and proper micropropagation system for relict endemic plant species. Murashige Skoog medium with different concentrations of gibberellic acid and juglone was used for in vitro germination. Seedlings from in vitro germinated plantlets were used as explant sources in tissue culture studies. The highest shoot average per explant (4.60 shoots) and shoot length (2.70 cm) was determined in MS medium with 2.0 mg/L 6-benzyl amino purine with 100% response in all treatments. This study used different rooting mediums: Murashige Skoog and modified Murashige Skoog media. The effects of Murashige Skoog and different concentrations of indole butyric acid, naphthaleneacetic acid, juglone, and modified MS, and different concentrations of juglone were investigated on rooting development. Elongated shoots were successfully rooted in the Mod MS medium with 10–7 M juglone. Rooted plantlets were gradually transferred to the soil by adapted external conditions. The transfer of S. cretica subsp. kutahyensis plants, adapted to the soil and field conditions (Tavşanlı/Nusretler), successfully carried out. This protocol can be used for conservation studies of endemic, endangered, and medicinally important plant species.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Ahmed R, Anis M (2014) Rapid in vitro propagation system through shoot tip cultures of Vitex trifolia L.-an important multipurpose plant of the Pacific traditional Medicine. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 20:385–392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-014-0233-7
Akbar MA, Roy SK (2006) Effects of liquid medium on rooting and acclimation of regenerated microshoots of Banana (Musa sapientum L.) cv. Sagar. Plant Tissue Cult Biotech 16(1):11–18. https://doi.org/10.3329/ptcb.v16i1.1100
Akçiçek E (2010) A new subspecies of Stachys cretica (section Eriostomum, Lamiaceae) from Turkey. Turk J Bot 34(2):131–136. https://doi.org/10.3906/bot-0911-225
Akçiçek E, Güner Ö (2022) A new subspecies of Stachys cretica (Lamiaceae) from western Turkey. Phytotaxa 539(3):257–264. https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.539.3.4
Akın B (2020) Tissue culture techniques of medicinal ve aromatic plants: History, cultivation and micropropagation. J Sci Rep - A 45:253–266
Akın B, Kocaçalışkan İ (2011) In vitro propagation of Arabis drabiformis Boiss. (Brassiaceae) an endemic rare species of Uludağ mountain (Bursa-Turkey). Afr J Biotechnol 10:18356–18361. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB11.2831
Akın B, Kocaçalışkan I, Güleryüz G (2014) Micropropagation of Erodium sibthorpianum subsp. sibthorpianum, an endemic threatened species of Uludağ Mountain (Bursa-Turkey). Turkish J Botany 38(1):148–155. https://doi.org/10.3906/bot-1304-24
Akin B, Kocacaliskan I (2016) Effect of juglone on seed germination and seedling growth of endemic species Aubrietaolympica and Arabisdrabiformis in tissue culture conditions. Phyton Annales Rei Botanicae 56(1):121–128. https://doi.org/10.12905/0380
Anish NP, Dan M, Bejoy M (2008) Conservation using in vitro progenies of the threatened ginger- Boesenbergia pulcherrima (Wall.) Kuntze. Int J Bot 4(1):93–98. https://doi.org/10.3923/ijb.2008.93.98
Arasoglu T, Mansuroglu B, Derman S, Gumus B, Kocyigit B, Acar T, Kocacaliskan I (2016) Enhancement of antifungal activity of juglone (5-Hydroxy-1, 4naphthoquinone) using a poly (d, l-lactic-co-glycolic acid)(PLGA) nanoparticle system. J Agric Food Chem 64(38):7087–7094. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.6b03309
Arasoglu T, Derman S, Mansuroglu B, Yelkenci G, Kocyigit B, Gumus B, Acar T, Kocacaliskan I (2017) Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of juglone encapsulated PLGA nanoparticles. J Appl Microbiol 123(6):1407–1419. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13601
Baba B (1995) Ekonomik öneme sahip endemiklerin doku kültür teknikleri ile çoğaltılması. Doktora tezi, Ege Üniversitesi, Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü, İzmir, 58 s (in Turkish)
Babaoğlu M, Gürel E, Özcan S (2002) Bitki biyoteknolojisi: I. Doku kültürü ve uygulamaları. Selçuk Üniversitesi Vakfı Yayınları, Konya (in Turkish)
Bamel K, Gupta R (2022) Juglone promotes shooting and inhibits rooting in leaf explants of in vitro raised tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L. var. Pusa Ruby) seedlings. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol - Plant 58:942–949. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-022-10277-6
Benabderrahim MA, Sarikurkcu C, Elfalleh W, Ozer MS, Ceylan O (2021) Phenolic composition and biological activities of Turkish endemic plant: Stachys cretica subsp. kutahyensis. S Afr J Bot 138:124–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2020.12.012
Bhattacharjee R (1980) Taxonomic studies in Stachys II: A new infrageneric classification of Stachys L. Notes from Royal Botanic Garden 38(1):65–96
Chandra B, Palni LMS, Nandi SK (2006) Propagation and conservation of Picrorhiza kurrooa Royle ex Benth.: an endangered Himalayan medicinal herb of high commercial value. Biodivers Conserv 15(7):2325–2338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-005-0770-z
Clark AM, Jurgens TM, Hufford CD (1990) Antimicrobial activity of juglone. Phytother Res 4(1):11–14. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.2650040104
Cuenca S, Amo-Marco JB, Parra R (1999) Micropropagation from inflorescence stems of Spanish endemic plant Centaurea paui Loscos ex Willk. (Compositae). Plant Cell Rep 18:674–679. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002990050641
Decker EL, Frank W, Sarnighausen E, Reski R (2006) Moss systems biology en route: phytohormones in physcomitrella development. Plant Biol 8:397–406. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-923952
Díaz-Sala C (2021) Adventitious root formation in tree species. Plants 10(3):486. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10030486
Efferth T (2019) Biotechnology applications of plant callus cultures. Engineering 5(1):50–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2018.11.006
Erdağ B, Emek Y (2005) In vitro micropropagation of Anthemis xylopoda O. Schwarz, a critically endangered species from Turkey. Pak J Biol Sci 8(5):691–695. https://doi.org/10.3923/pjbs.2005.691.695
Fay MF (1992) Conservation of rare and endangered plants using in vitro methods. In Vitro Cell Dev-Biol 28:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02632183
George EF, Hall MA, de Klerk GJM (2008) The components of plant tissue culture media II. Organic additions, osmotic and pH effects, and support systems. In: George EF, Hall MA, de Klerk GJM (eds) Plant propagation by tissue culture, vol 1. The Background, Springer Dordrecht, pp 115–173. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-5005-3_4
Goren AC, Piozzi F, Akcicek E, Kılıç T, Çarıkçı S, Mozioğlu E, Setzer WN (2011) Essential oil composition of twenty-two Stachys species (mountain tea) and their biological activities. Phytochem Lett 4(4):448–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2011.04.013
Gümüşçü A, Çöçü S, Uranbey S, İpek A, Çalışkan M, Arslan N (2008) In vitro micro-propagation of endangered ornamental plant Neotchihatchewia isatidea (Boiss.) Rauschert. Afr J Biotechnol 7(3):234–238. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB07.721
Güner Ö (2022) Stachys istanbulensis (Lamiaceae) a new species from Turkey: evidence from morphological, micromorphological and molecular analysis. Turk J Bot 46:624–635. https://doi.org/10.55730/1300-008X.2737
Güner Ö, Özdöl T, Yıldırım H (2023) A New Rupicolous Species from West of Türkiye: Stachys cuhacioglui (Lamiaceae). Türler ve Habitatlar 4(2):98–109. https://doi.org/10.53803/turvehab.1339346
Işık K (2011) Rare and endemic species: why are they prone to extinction? Turk J Bot 35(4):411–417. https://doi.org/10.3906/bot-1012-90
Işıkalan Ç, Orcan P, Akbaş F, Namlı S, Kuru İS, Buluş Ş (2020) Effect of cytokinins on in vitro propagation of Ajuga xylorrhiza Kit Tan (Critically Endangered), Endemic to Turkey. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol-Plant 56:911–914. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-020-10082-z
IUCN (2022) The IUCN Red List Guidelines version 2022–15.1. https://www.iucnredlist.org. Cited July 2022
JMP (2005) JMP SAS Statistical Analysis System. Cary, North Carolina, USA
Khanavi M, Hajimahmoodi M, Cheraghi-Niroomand M, Kargar Z, Ajani Y, Hadjiakhoondi A, Oveisi MR (2009) Comparison of the antioxidant activity and total phenolic contents in some Stachys species. Afr J Biotechnol 8(6):1143–1147
Khawar KM, Ozel CA, Ulug A, Sur I, Kızılates E, Uzuntas F, Arslan O (2008) In vitro adventitious shoot proliferation of İsatic aucheri Boiss. (Turkish Woad) from petiole explants. Res J Agric Biol Sci 4(4):327–330
Kocaçalışkan İ, Bingöl NA (2017) Biyoistatistik. Nobel Akademik Yayıncılık, Ankara (in Turkish)
Kocaçalışkan I, Terzi I (2001) Allelopathic effects of walnut leaf extracts and juglone on seed germination and seedling growth. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 76(4):436–440. https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.2001.11511390
Mayerni R, Warnita A, Chan SROS (2020) Direct organogenesis in local clones of Patchouli Plant (Pogostemon cablin Benth) in vitro. Indones J Crop Sci (JERAMI) 3(1):16–19. https://doi.org/10.25077/jijcs.3.1.16-19.2020
Milewska-Hendel A, Polak M, Sala K, Zieleźnik-Rusinowska P, Gawecki R, Kurczyńska E (2017) Morpho-histological analysis of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) plants after treatment with juglone. Acta Agrobot 70(2):1701. https://doi.org/10.5586/aa.1701
Miyazaki J, Tan BH, Errington SG (2010) Eradication of endophytic bacteria via treatment for axillary buds of Petunia hybrida using Plant Preservative Mixture (PPM™). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 102:365–372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-010-9741-5
Moola AK, Kumari BDR (2019) Direct regeneration of plantlets from shoot tip explants of a vulnerable medicinal plant – Celastrus paniculatus Willd. J Applied Horticult 21(3):189–194. https://doi.org/10.37855/jah.2019.v21i03.32
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15(3):473–497. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1962.tb08052.x
Nadeem M, Palni LMS, Purohit AN, Pandey H, Nandi SK (2000) Propagation and conservation of Podophyllum hexandrum Royle: an important medicinal herb. Biol Conserv 92:121–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3207(99)00059-2
Nas MN, Read PE (2004) A hypothesis for the development of a defined tissue culture medium of higher plants and micropropagation of hazelnuts. Sci Hortic 101:189–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2003.10.004
Perica MC (2003) In vitro propagation of Centaurea rupestris L. Acta Biol Cracov Bot 45(2):127–130
Ram K, Shekhawat NS (2011) Micropropagation of commercially cultivated Henna (Lawsonia inermis) using nodal explants. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 17:281–289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-011-0069-3
Ramabulana AT, Steenkamp PA, Madala NE, Dubery IA (2021) Application of plant growth regulators modulates the profile of chlorogenic acids in cultured Bidens pilosa Cells. Plants (basel) 10(3):437. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10030437
Rao NK (2004) Plant genetic resources: Advancing conservation and use through biotechnology. Afr J Biotechnol 3(2):136–145. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB2004.000-2025
Salehi P, Sonboli A, Asghari B (2007) Chemical composition of the essential oil of Stachys acerosa and its antibacterial and antioxidant activities. Chem Nat Compd 43(3):339–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-007-0126-x
Sathyanarayana BN, Varghese Dalia B (2007) Plant Tissue Culture: Practices and New Experimental Protocols. IK International Publishing House, New Delhi, India
Senapati SK, Aparajita S, Rout GR (2013) Micropropagation and assessment of genetic stability in Celastrus paniculatus: An endangered medicinal plant. Biologia 68:627–632. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-013-0187-1
Sudheer WN, Praveen N, Al-Khayri JM, Jain SM (2022) Role of plant tissue culture medium components. In: Kumar A, Modi A, Singh M (eds) Rai A C. Advances in plant tissue culture, Academic Press, pp 51–83
Sudhersan C, AboEl-Nil M, Hussain J (2003) Tissue culture technology for the conservation and propagation of certain native plants. J Arid Environ 54:133–147. https://doi.org/10.1006/jare.2001.0884
Tomou EM, Barda C, Skaltsan H (2020) Genus Stachys: A review of traditional uses, phytochemistry and bioactivity. Medicines 7(10):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines7100063
Tundis R, Peruzzi L, Menichini F (2014) Phytochemical and biological studies of Stachys species in relation to chemotaxonomy: a review. Phytochemistry 102:7–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2014.01.023
Uyanık M (2017) Türkiye’de tehlike altindaki bazi endemik Salvia türlerinin in vitro çoğaltimi ve tarla şartlarina adaptasyonu. Doktora tezi, Ankara Üniversitesi, Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü, Ankara, 77 (in Turkish)
Wala BB, Jasrai YT (2003) Micropropagation of an endangered medicinal plant: Curculigo orchioides Gaertn. Plant Tissue Culture 13(1):13–19
Wochok ZS (1981) The role of tissue culture in preserving threatened and endangered plant species. Biol Conserv 20(2):83–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-3207(81)90019-7
Wu Y, Yi G, Yang H, Zhou B, Zeng J (2005) Basal medium with modified nitrogen source and other factors influence the rooting of banana. HortScience 40:428–430. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI.40.2.428
Yuniastuti E, Widodo CE, Delfianti MNI (2018) Effect of benzyl amino purine and indole-3-acetic acid on propagation of Sterculia foetida in vitro IOP Conf Ser. Earth Environ Sci 142:012011. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/142/1/012011
Zhang XP, Ma CX, Sun LR, Hao FS (2020) Roles and mechanisms of Ca2+ in regulating primary root growth of plants. Plant Signal Behav 15(5):1748283. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2020.1748283
Funding
No funds, grants, or other support were received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclore.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Akın, B., Bingöl, N.A. & Bulman, G.C. A first approach for the micropropagation of threatened endemic subspecies of Stachys cretica subsp. kutahyensis. Biologia 79, 1653–1661 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-024-01640-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-024-01640-6