Abstract
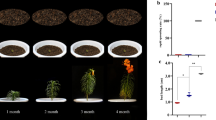
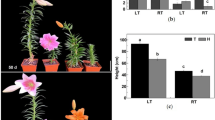
Lilium davidii var. unicolor is an important variety of lily with high economic, ornamental and medicinal values. It is one of the best lilies which are edible in China. Here, we study the physiological changes of L. davidii var. unicolor at different growth stage (vegetative stage, early bloom stage, full bloom stage, late bloom stage, early dry stage and dormancy stage) and metabolomics analysis of mother bulb at three different stages (full bloom stage, late bloom stage and early dry stage). The fast changes in plant height and number of daughter bulbs occurred from vegetative stage to full bloom stage and then became slow in the followed stages. The fresh weight of daughter bulb increased significantly from vegetative stage to dormancy stage, and fresh weight of mother bulb increased obviously from vegetative stage to full bloom stage. Plant fresh weight increased first and then decreased. Non-targeted metabolomics were used to analyze the metabolism of mother bulbs at three stages. A total of 141 differential metabolites were identified. According to the metabolic pathways identified in KEGG database, we found that 15 differential metabolites were enriched in multiple metabolic pathways, including l-aspartic acid, l-valine, trehalose, arbutin, and salicylic acid. Furthermore, we found that the chlorophyll contents, maximal photochemical efficiency and actual photochemical efficiency all have the maximum value at full bloom stage and the carbohydrate content also changed significantly from full bloom stage to early dry stage, which were consistent with the results of metabolomics. Thus, we can conclude that full bloom stage to early dry stage is the key period and this period involves many differential metabolites, which play an important role in L. davidii var. unicolor growth.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akram MN, Verpoorte R, Pomahačová B (2021) Effect of bulb age on alkaloid contents of narcissus pseudonarcissus bulbs. S Afr J Bot 136:182–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2020.07.034
Ali Q, Ashraf M, Anwar F, Al-Qurainy F (2012) Trehalose-induced changes in seed oil composition and antioxidant potential of maize grown under drought stress. J Am Oil Chem Soc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-012-2032-z
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase Beta Vulg. Plant Physiol 24:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.24.1.1
Bartwal A, Mall R, Lohani P, Guru SK, Arora S (2012) Role of secondary metabolites and brassinosteroids in plant defense against environmental stresses. J Plant Growth Regul 32:216–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-012-9272-x
Chang L, **ao YM, She LF, **a YP (2013) Analysis of gene expression and enzyme activities related to starch metabolism in Lycoris sprengeri bulbs of different sizes. Sci Hortic 161:118–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2013.07.005
Clark MF, RML, MosheBar-Joseph. (1986) ELISA Techniques. Methods Enzymol. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(86)18114-6
Doaa MR, Basha A, El-Aila H (2015) Response of foliar spraying with amino acids and integrated use of Nitrogen fertilizer on radish (Raphanus sativus L.) Plant. J Chemtech Res 8:135–140
Eastmond PJ, Graham IA (2003) Trehalose metabolism: a regulatory role for trehalose-6-phosphate? Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:231–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1369-5266(03)00037-2
Gallie DR (2013) L-ascorbic acid: a multifunctional molecule supporting plant growth and development. Scientifica (cairo) 2013:795964. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/795964
Gharib FAE-L (2007) Effect of Salicylic acid on the growth, metabolic activities and oil content of basil and marjoram. Int J Agri Biol 9(2):294–301
Guidi L, Lo Piccolo E, Landi M (2019) Chlorophyll fluorescence, photoinhibition and abiotic stress: does it make any difference the fact to be a c3 or c4 species? Front Plant Sci 10:174. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00174
Gunnaiah R, Kushalappa AC, Duggavathi R, Fox S, Somers DJ (2012) Integrated metabolo-proteomic approach to decipher the mechanisms by which wheat QTL (Fhb1) contributes to resistance against Fusarium graminearum. PLoS ONE 7:e40695. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0040695
Hall R, Beale M, Fiehn O, Hardy N, Bino SR (2002) Plant metabolomics: the missing link in functional genomics strategies. Plant Cell 14:1437–1440
Hongmei S, Tianlai Li, Yunfei Li (2005) Changes of carbohydrate and amylase in lily bulb during bulb development. Bull Bot Res 25(1):59–63
Hu H, Wang J, Hu Y, **e J (2020) Nutritional component changes in **angfen 1 banana at different developmental stages. Food Funct 11:8286–8296. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0fo00999g
Kawagishi K, Miura T (1996) Growth characteristics and effect of nitrogen and potassium topdressing on thickening growth of bulbs in spring-planted edible lily (lilium leichtlinii var. maximowiczii baker). Jpn J Crop Sci 65:51–57
Khademi O, Ashtari M, Razavi F (2019) Effects of salicylic acid and ultrasound treatments on chilling injury control and quality preservation in banana fruit during cold storage. Sci Hortic 249:334–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.02.018
Klerk De (2012) Micropropagation of bulbous crops: technology and present state. Floric Ornam Biotechnol 6:1–8
Kolbe A, Tiessen A, Schluepmann H, Paul M, Ulrich S, Geigenberger P (2005) Trehalose 6-phosphate regulates starch synthesis via posttranslational redox activation of adp-glucose pyrophosphorylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:11118–11123
Lazare S, Bechar D, Fernie AR, Brotman Y, Zaccai M (2019) The proof is in the bulb: glycerol influences key stages of lily development. Plant J 97:321–340. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14122
Li YF (2007) Carbohydrate metabolism changes in the growth process of planted Lanzhou lily bulb after low temperature storage. J Anhui Agr Sci 35:7262–7263
Li Q, Song J (2019) Analysis of widely targeted metabolites of the euhalophyte Suaeda salsa under saline conditions provides new insights into salt tolerance and nutritional value in halophytic species. BMC Plant Biol 19:388. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-2006-5
Li X, Wang C, Cheng J, Zhang J, da Silva JA, Liu X, Duan X, Li T, Sun H (2014) Transcriptome analysis of carbohydrate metabolism during bulblet formation and development in Lilium davidii var unicolor. BMC Plant Biol 14:358. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-014-0358-4
Li W, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Wang R, Guo Z, **e Z (2020) Impacts of drought stress on the morphology, physiology, and sugar content of Lanzhou lily (Lilium davidii var unicolor). Act Physiol Plant 42:127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-020-03115-y
Liao WB, Huang GB, Yu JH, Zhang ML (2012) Nitric oxide and hydrogen peroxide alleviate drought stress in marigold explants and promote its adventitious root development. Plant Physiol Biochem 58:6–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2012.06.012
Liu X, Yang G (2012) Adventitious shoot regeneration of oriental lily (Lilium orientalis) and genetic stability evaluation based on ISSR marker variation. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol-Plant 48:172–179. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-012-9429-0
Liu P, Weng R, Xu Y, Pan Y, Wang B, Qian Y, Qiu J (2020) Distinct quality changes of garlic bulb during growth by metabolomics analysis. J Agric Food Chem 68:5752–5762. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c01120
Lunn JE, Feil R, Hendriks JH, Gibon Y, Morcuende R, Osuna D, Scheible WR, Carillo P, Hajirezaei MR, Stitt M (2006) Sugar-induced increases in trehalose 6-phosphate are correlated with redox activation of ADPglucose pyrophosphorylase and higher rates of starch synthesis in Arabidopsis Thaliana. Biochem J 397:139–148. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20060083
Meng J, Xu T, Hu F, Song C, Zhang L, Zhang Z (2015) Melatonin treatment of pre-veraison grape berries to increase size and synchronicity of berries and modify wine aroma components. Food Chem 185:127–134
Paul MJ, Jhurreea D, Zhang Y, Primavesi LF, Delatte T, Schluepmann H, Wingler A (2010) Upregulation of biosynthetic processes associated with growth by trehalose 6-phosphate. Plant Signal Behav 5:386–392. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.5.4.10792
Pengfei W, Qianqian W, **anen L, Minjian Q (2012) Metabolites research of corydalis yanhusuo tubers with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Chin Bull Bot 47:149–154. https://doi.org/10.3724/sp.J.1259.2012.00149
Pradhan M, Tripathy P, Mandal P, Sahoo BB, Pradhan R, Mishra SP, Mishra HN (2016) Effect of salicylic acid on growth and bulb yield of onion (Allium Cepa L). Int J Bio-Resource Stress Manag 7(4):960–963. https://doi.org/10.23910/IJBSM/2016.7.4.1429
Rai VK (2002) Role of amino acids in plant responses to stresses. Biol Plant 45:481–487. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022308229759
Robinson AR, Dauwe R, Mansfield SD (2018) Assessing the between-background stability of metabolic effects arising from lignin-related transgenic modifications, in two Populus hybrids using non-targeted metabolomics. Tree Physiol 38:378–396. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpx110
Sirikantaramas S, Yamazaki M, Saito K (2013) Camptothecin. New Light on Alkaloid Biosynthesis and Future Prospects. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 139–161
Sun HM, Li TL, Li YF (2005) Physiology Mechanism of metabolisms in the middle scales of Lilium davidii var. unicolor bulbs stored at low temperature for dormancy-release. Agri Sci China 4:521–527
Tian X, **e J, Yu J (2020) Physiological and transcriptomic responses of Lanzhou Lily (Lilium davidii, var unicolor) to cold stress. PLoS ONE 15(1):e0227921. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0227921
Tsavkelova E, Oeser B, Oren-Young L, Israeli M, Sasson Y, Tudzynski B, Sharon A (2012) Identification and functional characterization of indole-3-acetamide-mediated IAA biosynthesis in plant-associated Fusarium species. Fungal Genet Biol 49:48–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2011.10.005
Vm R, Re S, Tr S (2003) NMR-based metabolomics: a powerful approach for characterizing the effects of environmental stressors on organism health. Environ Sci Technol 37(21):4982–4989
Wan J, Zhang P, Wang R, Sun L, Ju Q, Xu J (2018) Comparative physiological responses and transcriptome analysis reveal the roles of melatonin and serotonin in regulating growth and metabolism in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol 18:362. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1548-2
Wang P, Wang Q, Li X, Qin M (2012) Metabolites research of Corydalis yanhusuo tubers with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Chinese Bull Bot 47:149–154
Wang A, Li R, Ren L, Gao X, Zhang Y, Ma Z, Ma D, Luo Y (2018) A comparative metabolomics study of flavonoids in sweet potato with different flesh colors (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam). Food Chem 260:124–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.03.125
Weckwerth W (2003) Metabolomics in systems biology. Annu Rev Plant Biol 54:669–689. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.54.031902.135014
Wen W, Li D, Li X, Gao Y, Li W, Li H, Liu J, Liu H, Chen W, Luo J, Yan J (2014) Metabolome-based genome-wide association study of maize kernel leads to novel biochemical insights. Nat Commun 5:3438. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4438
Wojciechowska E, Weinert CH, Egert B, Trierweiler B, Schmidt-Heydt M, Horneburg B, Graeff-Hönninger S, Kulling SE, Geisen R (2014) Chlorogenic acid, a metabolite identified by untargeted metabolome analysis in resistant tomatoes, inhibits the colonization by Alternaria alternata by inhibiting alternariol biosynthesis. Eur J Plant Pathol 139:735–747. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-014-0428-3
**a YP, Zheng HJ, Huang CH (2005) Studies on the bulb development and its physiological mechanisms in lilium oriental hybrids. Acta Hort 673:91–98
Yang YH, Zong JW, Huang P, Yang FL, Liang YH (2015) Time of pruning influences the growth and bulb yield of edible lily (Lilium davidiivar.unicolor) plants. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 88:721–726. https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.2013.11513030
Yang Q, **e Z, Wang X, Wang Y, Zhang Y, He Y, Li W, Lv WC (2018) Effect of slow-release iron fertilizer on iron-deficiency chlorosis, yield and quality of Lilium davidii var.unicolor in a two-year field experiment. Sci Cold Arid Regions 10:421–427
Zhao B, Zhang J, Guo X, Wang J (2013) Microwave-assisted extraction, chemical characterization of polysaccharides from Lilium davidii var. unicolor Salisb and its antioxidant activities evaluation. Food Hydrocoll 31:346–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2012.11.021
Zhao L, Liu H, Cai G, **a M (2014) Assessment of the genetic diversity and genetic relationships of Lilium in China using ISSR markers. Biochem Syst Ecol 55:184–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2014.03.024
Zheng RR, Wu Y, **a YP (2012) Chlorocholine chloride and paclobutrazol treatments promote carbohydrate accumulation in bulbs of Lilium oriental hybrids “Sorbonne.” J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 13:136–144. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1000425
Zhou ZL, Feng ZC, Fu CY, Zhang HL, **a JM (2012) Steroidal and phenolic glycosides from the bulbs of Lilium pumilum DC and their potential Na+/K+ ATPase inhibitory activity. Molecules 17:10494–10502. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules170910494
Zhu G, Wang S, Huang Z, Zhang S, Liao Q, Zhang C, Lin T, Qin M, Peng M, Yang C et al (2018) Rewiring of the fruit metabolome in tomato breeding. Cell 172(249–261):e212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program (2018YFD1000800); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31160398, 31860568, 31560563 and 32072559); the Research Fund of Higher Education of Gansu, China (No. 2018C-14 and 2019B-082); the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province, China (Nos. 1606RJZA073 and 1606RJZA077).
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China, Nos. 31160398, Weibiao Liao, 31860568, Weibiao Liao, 31560563, Weibiao Liao, 32072559, Weibiao Liao, the Research Fund of Higher Education of Gansu, China, No. 2018C-14, Weibiao Liao, 2019B-082, Weibiao Liao, the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province, China, Nos. 1606RJZA073, Weibiao Liao, 1606RJZA077, Weibiao Liao, National Key Research and Development Program, 2018YFD1000800, Weibiao Liao
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. Krolicka.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, Y., Wang, B., Gong, W. et al. Physiological and metabolic analysis in mother bulbs of Lilium davidii var. unicolor during growth and development. Acta Physiol Plant 44, 88 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-022-03419-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-022-03419-1