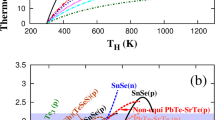
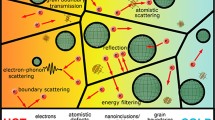
Abstract
In this review, an attempt was made to introduce the traditional concepts and materials in thermoelectric application and the recent development in searching high-performance thermoelectric materials. Due to the use of nanostructural engineering, thermoelectric materials with a high figure of merit are designed, leading to their blooming application in the energy field. One dimensional nanotubes and nanoribbons, two-dimensional planner structures, nanocomposites, and heterostructures were summarized. In addition, the state-of-the-art theoretical calculation in the prediction of thermoelectric materials was also reviewed, including the molecular dynamics (MD), Boltzmann transport equation, and non-equilibrium Green’s function. The combination of experimental fabrication and first-principles prediction significantly promotes the discovery of new promising candidates in the thermoelectric field.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Snyder G J, Toberer E S. Complex thermoelectric materials. Nature Materials, 2008, 7(2): 105–114
Zebarjadi M, Esfarjani K, Dresselhaus M S, Ren Z F, Chen G. Perspectives on thermoelectrics: from fundamentals to device applications. Energy & Environmental Science, 2012, 5(1): 5147–5162
Tan G, Zhao L D, Kanatzidis M G. Rationally designing highperformance bulk thermoelectric materials. Chemical Reviews, 2016, 116(19): 12123–12149
Zhao D L, Tan G. A review of thermoelectric cooling: materials, modeling and applications. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2014, 66(1–2): 15–24
Riffat S B, Ma X. Thermoelectrics: a review of present and potential applications. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2003, 23(8): 913–935
Ma W, Zhang X. Study of the thermal, electrical and thermoelectric properties of metallic nanofilms. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2013, 58(1–2): 639–651
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Huang C, Lin G, Chen J. Thermoelectric performance and optimization of three-terminal quantum dot nanodevices. Energy, 2016, 95: 593–601
Zhang Y, Huang C, Wang J, Lin G, Chen J. Optimum energy conversion strategies of a nano-scaled three-terminal quantum dot thermoelectric device. Energy, 2015, 85: 200–207
Page A, Van der Ven A, Poudeu P F P, Uher C. Origins of phase separation in thermoelectric (Ti, Zr, Hf)NiSn half-Heusler alloys from first principles. Journal of Materials Chemistry. A, Materials for Energy and Sustainability, 2016, 4(36): 13949–13956
Sellitto A, Cimmelli V A, Jou D. Thermoelectric effects and size dependency of the figure-of-merit in cylindrical nanowires. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2013, 57(1): 109–116
Zhao L D, Tan G, Hao S, He J, Pei Y, Chi H, Wang H, Gong S, Xu H, Dravid V P, Uher C, Snyder G J, Wolverton C, Kanatzidis M G. Ultrahigh power factor and thermoelectric performance in holedoped single-crystal SnSe. Science, 2016, 351(6269): 141–144
Mi X Y, Yu X, Yao K L, Huang X, Yang N, Lü J T. Enhancing the thermoelectric figure of merit by low-dimensional electrical transport in phonon-glass crystals. Nano Letters, 2015, 15(8): 5229–5234
Hicks L D, Dresselhaus M S. Thermoelectric figure of merit of a one-dimensional conductor. Physical Review B: Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 1993, 47(24): 16631–16634
Hicks L D, Dresselhaus M S. Effect of quantum-well structures on the thermoelectric figure of merit. Physical Review B: Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 1993, 47(19): 12727–12731
Venkatasubramanian R, Siivola E, Colpitts T, O’Quinn B. Thinfilm thermoelectric devices with high room-temperature figures of merit. Nature, 2001, 413(6856): 597–602
Goldsmid H J, Douglas R W. The use of semiconductors in thermoelectric refrigeration. British Journal of Applied Physics, 1954, 5(11): 386–390
Wright D A. Thermoelectric properties of bismuth telluride and its alloys. Nature, 1958, 181(4612): 834
Bergvall P, Beckman O. Thermoelectric properties of nonstoichiometric bismuth-antimony-telluride alloys. Solid-State Electronics, 1963, 6(2): 133–136
Champness C H, Chiang P T, Parekh P. Thermoelectric properties of Bi2Te3-Sb2Te3 alloys. Canadian Journal of Physics, 1965, 43(4): 653–669
Yim W M, Rosi F D. Compound tellurides and their alloys for peltier cooling—a review. Solid-State Electronics, 1972, 15(10): 1121–1140
Sugihara S, Suzuki H, Kawashima S, Fujita M, Kajikawa N, Shiraishi K, Sekine R. Thermoelectric properties and electronic structures for impurity-doped Bi2Te3. In: Proceedings of the 1998 17th International Conference on Thermoelectrics. Nagoya, Japan, 1998, 59–63
Chung D Y, Hogan T, Brazis P, Rocci-Lane M, Kannewurf C, Bastea M, Uher C, Kanatzidis M G. CsBi4Te6: a high-performance thermoelectric material for low-temperature applications. Science, 2000, 287(5455): 1024–1027
Chung D Y, Hogan T P, Rocci-Lane M, Brazis P, Ireland J R, Kannewurf C R, Bastea M, Uher C, Kanatzidis M G. A new thermoelectric material: CsBi4Te6. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2004, 126(20): 6414–6428
Jiang J, Chen L, Bai S, Yao Q, Wang Q. Thermoelectric properties of textured p-type (Bi,Sb)2Te3 fabricated by spark plasma sintering. Scripta Materialia, 2005, 52(5): 347–351
Poudel B, Hao Q, Ma Y, Lan Y, Minnich A, Yu B, Yan X, Wang D, Muto A, Vashaee D, Chen X, Liu J, Dresselhaus MS, Chen G, Ren Z. High-thermoelectric performance of nanostructured bismuth antimony telluride bulk alloys. Science, 2008, 320(5876): 634–638
Fan S, Zhao J, Guo J, Yan Q, Ma J, Hng H H. p-Type Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3 nanocomposites with enhanced figure of merit. Applied Physics Letters, 2010, 96(18): 182104
Chen S, Logothetis N, Ye L, Liu J. A high performance Ag alloyed nano-scale n-type Bi2Te3 based thermoelectric material. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2015, 2(2): 610–619
Caillat T, Fleurial J P, Borshchevsky A. Preparation and thermoelectric properties of semiconducting Zn4Sb3. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 1997, 58(7): 1119–1125
Jang K W, Kim I H, Lee J I, Choi G S. Thermoelectric properties of Zn4–xSb3 with x = 0–0.5. Diffusion and Defect Data, Solid State Data. Part B, Solid State Phenomena, 2007, 124–126: 1019–1022
Liu Y B, Zhou S M, Yuan X Y, Lou S Y, Gao T, Shi X J, Wu X P. Synthesis and high-performance thermoelectric properties of beta- Zn4Sb3 nanowires. Materials Letters, 2012, 84: 116–119
Zou T, Qin X, Zhang Y, Li X, Zeng Z, Li D, Zhang J, **n H, **e W, Weidenkaff A. Enhanced thermoelectric performance of β- Zn4Sb3 based nanocomposites through combined effects of density of states resonance and carrier energy filtering. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(1): 17803
Loffe A F. Semiconductor Thermoelements and Thermoelectric Cooling. London: Infosearch, Ltd, 1957
Fritts R W. Lead telluride alloys and junctions. In: Cadoff I B, Miller E, eds. Thermoelectric Materials and Devices. New York: Reinhold Publishing Corporation, 1960, 143–162
Mahan G D. Good thermoelectrics. Solid State Physics, 1998, 51: 81–157
Wang H, Li J F, Nan C W, Zhou M, Liu W, Zhang B P, Kita T. High-performance Ag0.8Pb18 + xSbTe20 thermoelectric bulk materials fabricated by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 88(9): 092104
Heremans J P, Jovovic V, Toberer E S, Saramat A, Kurosaki K, Charoenphakdee A, Yamanaka S, Snyder G J. Enhancement of thermoelectric efficiency in PbTe by distortion of the electronic density of states. Science, 2008, 321(5888): 554–557
Biswas K, He J, Blum I D, Wu C I, Hogan T P, Seidman D N, Dravid V P, Kanatzidis M G. High-performance bulk thermoelectrics with all-scale hierarchical architectures. Nature, 2012, 489(7416): 414–418
Wu D, Zhao L D, Tong X, Li W, Wu L, Tan Q, Pei Y, Huang L, Li J F, Zhu Y, Kanatzidis M G, He J. Superior thermoelectric performance in PbTe-PbS pseudo-binary: extremely low thermal conductivity and modulated carrier concentration. Energy & Environmental Science, 2015, 8(7): 2056–2068
Chen Z, Jian Z, Li W, Chang Y, Ge B, Hanus R, Yang J, Chen Y, Huang M, Snyder G J, Pei Y. Lattice dislocations enhancing thermoelectric PbTe in addition to band convergence. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(23): 1606768
Dismukes J P, Ekstrom L, Steigmeier E F, Kudman I, Beers D S. Thermal and electrical properties of heavily doped Ge-Si alloys up to 1300°K. Journal of Applied Physics, 1964, 35(10): 2899–2907
Fleurial J P, Vandersande J, Scoville N, Bajgar C, Beaty J. Progress in the optimization of n-type and p-type SiGe thermoelectric materials. AIP Conference Proceedings, 1993, 271: 759–764
Kleint C A, Heinrich A, Muehl T, Hecker J. Structural properties of strain symmetrized silicon/germanium (111) superlattices. In: IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS 2001). Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2001, Z8131–Z8136
Joshi G, Lee H, Lan Y, Wang X, Zhu G, Wang D, Gould R W, Cuff D C, Tang M Y, Dresselhaus M S, Chen G, Ren Z. Enhanced thermoelectric figure-of-merit in nanostructured p-type silicon germanium bulk alloys. Nano Letters, 2008, 8(12): 4670–4674
Bathula S, Jayasimhadri M, Gahtori B, Singh N K, Tyagi K, Srivastava A K, Dhar A. The role of nanoscale defect features in enhancing the thermoelectric performance of p-type nanostructured SiGe alloys. Nanoscale, 2015, 7(29): 12474–12483
Polvani D A, Meng J F, Chandra Shekar N V, Sharp J, Badding J V. Large improvement in thermoelectric properties in pressuretuned p-type Sb1.5Bi0.5Te3. Chemistry of Materials, 2001, 13(6): 2068–2071
Sidorenko N A, Ivanova L D. Bi-Sb solid solutions: potential materials for high-efficiency thermoelectric cooling to below 180 K. Inorganic Materials, 2001, 37(4): 331–335
Zhao X B, Ji X H, Zhang Y H, Zhu T J, Tu J P, Zhang X B. Bismuth telluride nanotubes and the effects on the thermoelectric properties of nanotube-containing nanocomposites. Applied Physics Letters, 2005, 86(6): 062111
Tang X, **e W, Li H, Zhao W, Zhang Q, Niino M. Preparation and thermoelectric transport properties of high-performance p-type Bi2Te3 with layered nanostructure. Applied Physics Letters, 2007, 90(1): 012102
Cao Y Q, Zhao X B, Zhu T J, Zhang X B, Tu J P. Syntheses and thermoelectric properties of Bi2Te3/Sb2Te3 bulk nanocomposites with laminated nanostructure. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 92(14): 143106
Yan X, Poudel B, Ma Y, Liu W S, Joshi G, Wang H, Lan Y, Wang D, Chen G, Ren Z F. Experimental studies on anisotropic thermoelectric properties and structures of n-type Bi2Te2.7Se0.3. Nano Letters, 2010, 10(9): 3373–3378
Zhang G, Kirk B, Jauregui L A, Yang H, Xu X, Chen Y P, Wu Y. Rational synthesis of ultrathin n-type Bi2Te3 nanowires with enhanced thermoelectric properties. Nano Letters, 2012, 12(1): 56–60
Guo Q, Chan M, Kuropatwa B A, Kleinke H. Enhanced thermoelectric properties of variants of Tl9SbTe6 and Tl9BiTe6. Chemistry of Materials, 2013, 25(20): 4097–4104
Hong M, Chen Z G, Yang L, Zou J. BixSb2–xTe3 nanoplates with enhanced thermoelectric performance due to sufficiently decoupled electronic transport properties and strong wide-frequency phonon scatterings. Nano Energy, 2016, 20: 144–155
Pan Y, Li J F. Thermoelectric performance enhancement in n-type Bi2(TeSe)3 alloys owing to nanoscale inhomogeneity combined with a spark plasma-textured microstructure. NPG Asia Materials, 2016, 8(6): e275
Dharmaiah P, Kim H S, Lee C H, Hong S J. Influence of powder size on thermoelectric properties of p-type 25%Bi2Te3–75%Sb2Te3 alloys fabricated using gas-atomization and spark-plasma sintering. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 686: 1–8
Hsu K F, Loo S, Guo F, Chen W, Dyck J S, Uher C, Hogan T, Polychroniadis E K, Kanatzidis MG. Cubic AgPbmSbTe2 + m: bulk thermoelectric materials with high figure of merit. Science, 2004, 303(5659): 818–821
Wang H, Li J F, Nan C W, Zhou M, Liu W, Zhang B P, Kita T. High-performance Ag0.8Pb18 + xSbTe20 thermoelectric bulk materials fabricated by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 88(9): 092104
Johnsen S, He J, Androulakis J, Dravid V P, Todorov I, Chung D Y, Kanatzidis M G. Nanostructures boost the thermoelectric performance of PbS. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(10): 3460–3470
Pei Y, Shi X, LaLonde A, Wang H, Chen L, Snyder G J. Convergence of electronic bands for high performance bulk thermoelectrics. Nature, 2011, 473(7345): 66–69
Zhang Q, Yang S, Zhang Q, Chen S, Liu W, Wang H, Tian Z, Broido D, Chen G, Ren Z. Effect of aluminum on the thermoelectric properties of nanostructured PbTe. Nanotechnology, 2013, 24(34): 345705
Zhang Y, Wang H, Kräemer S, Shi Y, Zhang F, Snedaker M, Ding K, Moskovits M, Snyder G J, Stucky G D. Surfactant-free synthesis of Bi2Te3-Te micro-nano heterostructure with enhanced thermoelectric figure of merit. ACS Nano, 2011, 5(4): 3158–3165
Zhao L D, Lo S H, Zhang Y, Sun H, Tan G, Uher C, Wolverton C, Dravid V P, Kanatzidis M G. Ultralow thermal conductivity and high thermoelectric figure of merit in SnSe crystals. Nature, 2014, 508(7496): 373–377
Sevinçli H, Sevik C, Çağın T, Cuniberti G. A bottom-up route to enhance thermoelectric figures of merit in graphene nanoribbons. Scientific Reports, 2013, 3(1): 1228
Yamini S A, Wang H, Ginting D, Mitchell D R, Dou S X, Snyder G J. Thermoelectric performance of n-type (PbTe)0.75(PbS)0.15(PbSe)0.1 composites. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(14): 11476–11483
Lu Z W, Li J Q, Wang C Y, Li Y, Liu F S, Ao W Q. Effects of Mn substitution on the phases and thermoelectric properties of Ge0.8Pb0.2Te alloy. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 621: 345–350
Zhao L D, Zhang X, Wu H, Tan G, Pei Y, **ao Y, Chang C, Wu D, Chi H, Zheng L, Gong S, Uher C, He J, Kanatzidis MG. Enhanced thermoelectric properties in the counter-doped SnTe system with strained endotaxial SrTe. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(7): 2366–2373
Li J C, Li D, Qin X Y, Zhang J. Enhanced thermoelectric performance of p-type SnSe doped with Zn. Scripta Materialia, 2017, 126: 6–10
Boukai A I, Bunimovich Y, Tahir-Kheli J, Yu J K, Goddard W A III, Heath J R. Silicon nanowires as efficient thermoelectric materials. Nature, 2008, 451(7175): 168–171
Hochbaum A I, Chen R, Delgado R D, Liang W, Garnett E C, Najarian M, Majumdar A, Yang P. Enhanced thermoelectric performance of rough silicon nanowires. Nature, 2008, 451(7175): 163–167
Miao L, Tanemura S, Huang R, Liu C Y, Huang C M, Xu G. Large Seebeck coefficients of protonated titanate nanotubes for hightemperature thermoelectric conversion. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2010, 2(8): 2355–2359
Li Z, Chen Y, Li J F, Chen H, Wang L, Zheng S, Lu G. Systhesizing SnTe nanocrystals leading to thermoelectric performance enhancement via an ultra-fast microwave hydrothermal method. Nano Energy, 2016, 28: 78–86
Yang L, Yang N, Li B. Thermoelectric properties of nanoscale three dimensional Si phononic crystals. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2016, 99: 102–106
He D, Zhao W, Mu X, Zhou H, Wei P, Zhu W, Nie X, Su X, Liu H, He J, Zhang Q. Enhanced thermoelectric performance of heavyfermion YbAl3 via multi-scale microstructures. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 725: 1297–1303
Zhao W, Liu Z, Sun Z, Zhang Q, Wei P, Mu X, Zhou H, Li C, Ma S, He D, Ji P, Zhu W, Nie X, Su X, Tang X, Shen B, Dong X, Yang J, Liu Y, Shi J. Superparamagnetic enhancement of thermoelectric performance. Nature, 2017, 549(7671): 247–251
Pei Y, Lensch-Falk J, Toberer E S, Medlin D L, Snyder G J. High thermoelectric performance in PbTe due to large nanoscale Ag2Te precipitates and La do**. Advanced Functional Materials, 2011, 21(2): 241–249
Gahtori B, Bathula S, Tyagi K, Jayasimhadri M, Srivastava A K, Singh S, Budhani R C, Dhar A. Giant enhancement in thermoelectric performance of copper selenide by incorporation of different nanoscale dimensional defect features. Nano Energy, 2015, 13: 36–46
Ahmad S, Singh A, Bohra A, Basu R, Bhattacharya S, Bhatt R, Meshram K N, Roy M, Sarkar S K, Hayakawa Y, Debnath A K, Aswal D K, Gupta S K. Boosting thermoelectric performance of p-type SiGe alloys through in-situ metallic YSi2 nanoinclusions. Nano Energy, 2016, 27: 282–297
Kim G H, Hwang D H, Woo S I. Thermoelectric properties of nanocomposite thin films prepared with poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) poly(styrenesulfonate) and graphene. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2012, 14(10): 3530–3536
Tan X J, Liu H J, Wen Y W, Lv H Y, Pan L, Shi J, Tang X F. Thermoelectric properties of ultrasmall single-wall carbon nanotubes. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115(44): 21996–22001
Ouyang T, **ao H P, **e Y E, Wei X L, Chen Y P, Zhong J X. Thermoelectric properties of gamma-graphyne nanoribbons and nanojunctions. Journal of Applied Physics, 2013, 114(7): 073710
Wang C, Ouyang T, Chen Y, Zhou B, Zhong J. Thermoelectric properties of gamma-graphyne nanoribbon incorporating diamond- like quantum dots. Journal of Physics. D, Applied Physics, 2016, 49(13): 135303
Yang D, Lu C, Yin H, Herman I P. Thermoelectric performance of PbSe quantum dot films. Nanoscale, 2013, 5(16): 7290–7296
Guo R Q, Wang X J, Kuang Y D, Huang B L. First-principles study of anisotropic thermoelectric transport properties of IV–VI semiconductor compounds SnSe and SnS. Physical Review B: Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 2015, 92(11): 115202
Chen Z G, Han G, Yang L, Cheng L, Zou J. Nanostructured thermoelectric materials: current research and future challenge. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International, 2012, 22(6): 535–549
Ginting D, Lin C C, Rathnam L, Yun J H, Yu B K, Kim S J, Rhyee J S. High thermoelectric performance due to nanoinclusions and randomly distributed interface potentials in n-type (PbTe0.93–xSe0.07Clx)0.93(PbS)0.07 composites. Journal of Materials Chemistry. A, Materials for Energy and Sustainability, 2017, 5(26): 13535–13543
Zhang D, Yang J, Jiang Q, Zhou Z, Li X, **n J, Basit A, Ren Y, He X. Multi-cations compound Cu2CoSnS4: DFT calculating, band engineering and thermoelectric performance regulation. Nano Energy, 2017, 36: 156–165
Volz S G, Chen G. Molecular-dynamics simulation of thermal conductivity of silicon crystals. Physical Review B: Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 2000, 61(4): 2651–2656
Volz S G, Chen G. Molecular dynamics simulation of thermal conductivity of silicon nanowires. Applied Physics Letters, 1999, 75(14): 2056–2058
**e H, Ouyang T, Germaneau É, Qin G, Hu M, Bao H. Large tunability of lattice thermal conductivity of monolayer silicene via mechanical strain. Physical Review B: Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 2016, 93(7): 075404
Turney J E, Landry E S, McGaughey A J H, Amon C H. Predicting phonon properties and thermal conductivity from anharmonic lattice dynamics calculations and molecular dynamics simulations. Physical Review B: Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 2009, 79(6): 064301
Li W, Carrete J, Katcho N A, Mingo N. ShengBTE: a solver of the Boltzmann transport equation for phonons. Computer Physics Communications, 2014, 185(6): 1747–1758
Jiang J W, Wang J S, Li B W. A nonequilibrium Green’s function study of thermoelectric properties in single-walled carbon nanotubes. Journal of Applied Physics, 2011, 109(1): 014326
Chen K X, Wang X M, Mo D C, Lyu S S. Thermoelectric properties of transition metal dichalcogenides: from monolayers to nanotubes. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2015, 119(47): 26706–26711
Chen K X, Lyu S H, Wang X M, Fu Y X, Heng Y, Mo D C. Excellent thermoelectric performance predicted in two-dimensional buckled antimonene: a first-principles study. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2017, 121(24): 13035–13042
Fan D D, Liu H J, Cheng L, Jiang P H, Shi J, Tang X F. MoS2 nanoribbons as promising thermoelectric materials. Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 105(13): 133113
Zhang J, Liu H J, Cheng L, Wei J, Liang J H, Fan D D, Shi J, Tang X F, Zhang Q J. Phosphorene nanoribbon as a promising candidate for thermoelectric applications. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4(1): 6452
Wang X M, Lu S S. Thermoelectric transport in graphyne nanotubes. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2013, 117(38): 19740–19745
Chen K X, Luo Z Y, Mo D C, Lyu S S. WSe2 nanoribbons: new high-performance thermoelectric materials. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2016, 18(24): 16337–16344
He W, Zhang G, Zhang X, Ji J, Li G, Zhao X. Recent development and application of thermoelectric generator and cooler. Applied Energy, 2015, 143: 1–25
Gou X, **ao H, Yang S. Modeling, experimental study and optimization on low-temperature waste heat thermoelectric generator system. Applied Energy, 2010, 87(10): 3131–3136
Wang L. Thermopower and thermoconductance properties of zigzag edged graphene nanoribbon based thermoelectric module. Physics Letters, 2013, 377(21–22): 1486–1490
Sevinçli H, Cuniberti G. Enhanced thermoelectric figure of merit in edge-disordered zigzag graphene nanoribbons. Physical Review B: Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 2010, 81(11): 113401
Chang P H, Nikolić B K. Edge currents and nanopore arrays in zigzag and chiral graphene nanoribbons as a route toward high-ZT thermoelectrics. Physical Review B: Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 2012, 86(4): 041406
Yeo P S E, Sullivan M B, Loh K P, Gan C K. First-principles study of the thermoelectric properties of strained graphene nanoribbons. Journal of Materials Chemistry. A, Materials for Energy and Sustainability, 2013, 1(36): 10762–10767
Yu C, Choi K, Yin L, Grunlan J C. Light-weight flexible carbon nanotube based organic composites with large thermoelectric power factors. ACS Nano, 2011, 5(10): 7885–7892
Avery A D, Zhou B H, Lee J, Lee E S, Miller E M, Ihly R, Wesenberg D, Mistry K S, Guillot S L, Zink B L, Kim Y H, Blackburn J L, Ferguson A J. Tailored semiconducting carbon nanotube networks with enhanced thermoelectric properties. Nature Energy, 2016, 1(4): 16033
Hsin C L, Wingert M, Huang C W, Guo H, Shih T J, Suh J, Wang K, Wu J, Wu W W, Chen R. Phase transformation and thermoelectric properties of bismuth-telluride nanowires. Nanoscale, 2013, 5(11): 4669–4672
Jiang J W, Wang J S. Joule heating and thermoelectric properties in short single-walled carbon nanotubes: electron-phonon interaction effect. Journal of Applied Physics, 2011, 110(12): 124319
Si H G, Wang Y X, Yan Y L, Zhang G B. Structural, electronic, and thermoelectric properties of InSe nanotubes: first-principles calculations. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012, 116(6): 3956–3961
Huang W, Da H, Liang G. Thermoelectric performance of MX2 (M = Mo, W; X = S, Se) monolayers. Journal of Applied Physics, 2013, 113(10): 104304
Huang W, Luo X, Gan C K, Quek S Y, Liang G. Theoretical study of thermoelectric properties of few-layer MoS2 and WSe2. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2014, 16(22): 10866–10874
Tahir M, Schwingenschlögl U. Tunable thermoelectricity in monolayers of MoS2 and other group-VI dichalcogenides. New Journal of Physics, 2014, 16(11): 115003
Wickramaratne D, Zahid F, Lake R K. Electronic and thermoelectric properties of few-layer transition metal dichalcogenides. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2014, 140(12): 124710
Lee C, Hong J, Whangbo M H, Shim J H. Enhancing the thermoelectric properties of layered transition-metal dichalcogenides 2H–MQ2 (M = Mo,W; Q = S, Se, Te) by layer mixing: density functional investigation. Chemistry of Materials, 2013, 25(18): 3745–3752
Bhattacharyya S, Pandey T, Singh A K. Effect of strain on electronic and thermoelectric properties of few layers to bulk MoS2. Nanotechnology, 2014, 25(46): 465701
Guo S D. Biaxial strain tuned thermoelectric properties in monolayer PtSe2. Journal of Materials Chemistry. C, Materials for Optical and Electronic Devices, 2016, 4(39): 9366–9374
Wang X M, Mo D C, Lu S S. On the thermoelectric transport properties of graphyne by the first-principles method. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2013, 138(20): 204704
Yang K, Cahangirov S, Cantarero A, Rubio A, D’Agosta R. Thermoelectric properties of atomically thin silicene and germanene nanostructures. Physical Review B: Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 2014, 89(12): 125403
Fei R, Faghaninia A, Soklaski R, Yan J A, Lo C, Yang L. Enhanced thermoelectric efficiency via orthogonal electrical and thermal conductances in phosphorene. Nano Letters, 2014, 14(11): 6393–6399
Lv H Y, Lu W J, Shao D F, Sun Y P. Enhanced thermoelectric performance of phosphorene by strain-induced band convergence. Physical Review B: Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 2014, 90(8): 085433
Medrano Sandonas L, Teich D, Gutierrez R, Lorenz T, Pecchia A, Seifert G, Cuniberti G. Anisotropic thermoelectric response in twodimensional puckered structures. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2016, 120(33): 18841–18849
Carrete J, Mingo N, Tian G, Ågren H, Baev A, Prasad P N. Thermoelectric properties of hybrid organic-inorganic superlattices. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012, 116(20): 10881–10886
Savelli G, Silveira Stein S, Bernard-Granger G, Faucherand P, Montès L, Dilhaire S, Pernot G. Titanium-based silicide quantum dot superlattices for thermoelectrics applications. Nanotechnology, 2015, 26(27): 275605
Duan J, Wang X, Lai X, Li G, Watanabe K, Taniguchi T, Zebarjadi M, Andrei E Y. High thermoelectric power factor in graphene/hBN devices. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(50): 14272–14276
Luo Y, Jiang Q, Yang J, Li W, Zhang D, Zhou Z, Cheng Y, Ren Y, He X, Li X. Simultaneous regulation of electrical and thermal transport properties in CuInTe2 by directly incorporating excess ZnX (X = S, Se). Nano Energy, 2017, 32: 80–87
Yin K, Su X, Yan Y, Tang H, Kanatzidis M G, Uher C, Tang X. Morphology modulation of SiC nano-additives for mechanical robust high thermoelectric performance Mg2Si1–xSnx/SiC nanocomposites. Scripta Materialia, 2017, 126: 1–5
Acknowledgements
Financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51676212) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, KX., Li, MS., Mo, DC. et al. Nanostructural thermoelectric materials and their performance. Front. Energy 12, 97–108 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11708-018-0543-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11708-018-0543-5