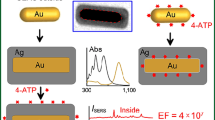
Abstract
Herein, we systematically investigated the synthesis of hollow gold nanourchins characterized by multiple sharp tips with extremely small radii of 5–10 nm radiating from central cores. The two-step-based approach was exploited to produce hollow Au nanourchins. The pre-synthesized Ag nanospheres were used as sacrificial templates in the galvanic replacement with HAuCl4 precursor to assist the formation of hollow cores. Subsequently, ascorbic acid was added to trigger the co-reduction reactions to promote the growth of multiple sharp tips. The hollow Au nanourchins exhibit tunable morphology and optical response in the visible to near-infrared regions (725–1040 nm), simply by adjusting different reaction parameters, including the amounts of Ag seed, HAuCl4 precursor, and ascorbic acid. Notably, the hollow Au nanourchins demonstrate a remarkably potent bactericidal efficiency against E. coli, surpassing that of spiky Au nanoparticles with solid cores. A better antibacterial activities were also observed for hollow Au nanourchins with shorter tips as compared to those with longer tips. Furthermore, the synthesized particles display a significant SERS enhancement toward the detection of Rhodamine B (10−4 M) even under off-resonance conditions. These findings highlight the potential of the hollow Au nanourchins as multifunctional materials for sensing and biological applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abolghasemi-Fakhri Z, Amjadi M (2021) Gold nanostar@ graphene quantum dot as a new colorimetric sensing platform for detection of cysteine. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 261:120010
Blanch AJ, Döblinger M, Rodríguez-Fernández J (2015) Simple and rapid high-yield synthesis and size sorting of multibranched hollow gold nanoparticles with highly tunable NIR plasmon resonances. Small 11:4550–4559
Chatterjee H, Rahman DS, Sengupta M, Ghosh SK (2018) Gold nanostars in plasmonic photothermal therapy: The role of tip heads in the thermoplasmonic landscape. J Phys Chem C 122:13082–13094
Cheeseman S, Christofferson AJ, Kariuki R, Cozzolino D, Daeneke T, Crawford RJ, Truong VK, Chapman J, Elbourne A (2020) Antimicrobial metal nanomaterials: from passive to stimuli-activated applications. Adv Sci 7:1902913
Ding X, Yuan P, Gao N, Zhu H, Yang YY, Xu Q-H (2017) Au-Ag core-shell nanoparticles for simultaneous bacterial imaging and synergistic antibacterial activity. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med 13:297–305
Dizaj SM, Lotfipour F, Barzegar-Jalali M, Zarrintan MH, Adibkia K (2014) Antimicrobial activity of the metals and metal oxide nanoparticles. Mater Sci Eng C 44:278–284
Feng Y, Chen Q, Yin Q, Pan G, Tu Z, Liu L (2019) Reduced graphene oxide functionalized with gold nanostar nanocomposites for synergistically killing bacteria through intrinsic antimicrobial activity and photothermal ablation. ACS Appl Biol Mater 2:747–756
González-Rubio G, Díaz-Núñez P, Rivera A, Prada A, Tardajos G, González-Izquierdo J, Bañares L, Llombart P, Macdowell LG, Alcolea Palafox M (2017) Femtosecond laser resha** yields gold nanorods with ultranarrow surface plasmon resonances. Science 358:640–644
Gu X, Xu Z, Gu L, Xu H, Han F, Chen B, Pan X (2021) Preparation and antibacterial properties of gold nanoparticles: a review. Environ Chem Lett 19:167–187
Guan G, Win KY, Yao X, Yang W, Han MY (2021) Plasmonically modulated gold nanostructures for photothermal ablation of bacteria. Adv Healthcare Mater 10:2001158
Guarino-Hotz M, Allen ALC, Wang A, Zou S, Zhang JZ (2022) Near-infrared light absorbing silver-coated hollow gold nanostars for surface-enhanced raman scattering detection of bovine serum albumin using cap** ligand exchange. J Phys Chem C 126:1026–1035
Hong X, Wen J, **ong X, Hu Y (2016) Shape effect on the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized via a microwave-assisted method. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:4489–4497
Hou F, Zhu Y, Zou Q, Zhang C, Wang H, Liao Y, Wang Q, Yang X, Yang Y (2019) One-step preparation of multifunctional alginate microspheres loaded with in situ-formed gold nanostars as a photothermal agent. Mater Chem Front 3:2018–2024
Kelly KL, Coronado E, Zhao LL, Schatz GC (2003) The optical properties of metal nanoparticles: the influence of size, shape, and dielectric environment. J Phys Chem B 107:668–677
Lee D, Yoon S (2016) Effect of nanogap curvature on SERS: a finite-difference time-domain study. J Phys Chem C 120:20642–20650
Lee J, Hua B, Park S, Ha M, Lee Y, Fan Z, Ko H (2014) Tailoring surface plasmons of high-density gold nanostar assemblies on metal films for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nanoscale 6:616–623
Li A, Tang L, Song D, Song S, Ma W, Xu L, Kuang H, Wu X, Liu L, Chen X (2016) A SERS-active sensor based on heterogeneous gold nanostar core–silver nanoparticle satellite assemblies for ultrasensitive detection of aflatoxinB1. Nanoscale 8:1873–1878
Li Y, Zhai M, Xu H (2019) Controllable synthesis of sea urchin-like gold nanoparticles and their optical characteristics. Appl Surf Sci 498:143864
Liang F, ** D, Ma P, Wang D, Yang Q, Song D, Wang X (2015) Rapid determination of rhodamine B in chili powder by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Anal Lett 48:1918–1929
Liu M, **ang R, Lee Y, Otsuka K, Ho Y-L, Inoue T, Chiashi S, Delaunay J-J, Maruyama S (2018) Fabrication, characterization, and high temperature surface enhanced Raman spectroscopic performance of SiO 2 coated silver particles. Nanoscale 10:5449–5456
Lyu Z, **e M, Aldama E, Zhao M, Qiu J, Zhou S, **a Y (2019) Au@ Cu core-shell nanocubes with controllable sizes in the range of 20–30 nm for applications in catalysis and plasmonics. ACS Appl Nano Mater 2:1533–1540
Millstone JE, Hurst SJ, Métraux GS, Cutler JI, Mirkin CA (2009) Colloidal gold and silver triangular nanoprisms. Small 5:646–664
Mousavi SM, Zarei M, Hashemi SA, Ramakrishna S, Chiang W-H, Lai CW, Gholami A (2020) Gold nanostars-diagnosis, bioimaging and biomedical applications. Drug Metab Rev 52:299–318
Personick ML, Mirkin CA (2013) Making sense of the mayhem behind shape control in the synthesis of gold nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 135:18238–18247
Piktel E, Suprewicz Ł, Depciuch J, Chmielewska S, Skłodowski K, Daniluk T, Król G, Kołat-Brodecka P, Bijak P, Pajor-Świerzy A (2021) Varied-shaped gold nanoparticles with nanogram killing efficiency as potential antimicrobial surface coatings for the medical devices. Sci Rep 11:12546
Ray P, Lodha T, Biswas A, Sau TK, Ramana CV (2022) Particle specific physical and chemical effects on antibacterial activities: A comparative study involving gold nanostars, nanorods and nanospheres. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 634:127915
Shamaila S, Zafar N, Riaz S, Sharif R, Nazir J, Naseem S (2016) Gold nanoparticles: an efficient antimicrobial agent against enteric bacterial human pathogen. Nanomaterials 6:71
Tran NT, Li A, Chen P, Wang Y, Li S, Liedberg B (2017) Gold mesoflowers with a high density of multilevel long sharp tips: synthesis and characterization. J Mater Chem C 5:4884–4891
Tran V, Thiel C, Svejda JT, Jalali M, Walkenfort B, Erni D, Schlücker S (2018) Probing the SERS brightness of individual Au nanoparticles, hollow Au/Ag nanoshells, Au nanostars and Au core/Au satellite particles: single-particle experiments and computer simulations. Nanoscale 10:21721–21731
Tran NT, Liao H, Feng X, Xu ZZ, Liedberg B (2020) Synthesis of highly branched hollow trimetallic PdAgCu nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 31:185601
Wang Y, Wan J, Miron RJ, Zhao Y, Zhang Y (2016) Antibacterial properties and mechanisms of gold–silver nanocages. Nanoscale 8:11143–11152
Wang H, Song Z, Li S, Wu Y, Han H (2019a) One stone with two birds: functional gold nanostar for targeted combination therapy of drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:32659–32669
Wang H, Pu Y, Shan B, Li M (2019b) Combining experiments and theoretical modeling to interrogate the anisotropic growth and structure–plasmonic property relationships of gold nanostars. Inorg Chem 58:12457–12466
Weiner RG, Smith AF, Skrabalak SE (2015) Synthesis of hollow and trimetallic nanostructures by seed-mediated co-reduction. Chem Commun 51:8872–8875
Xu K, Zhou R, Takei K, Hong M (2019) Toward flexible surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) sensors for point-of-care diagnostics. Adv Sci 6:1900925
Yang Y-T, Hsu I-L, Cheng T-Y, Wu W-J, Lee C-W, Li T-J, Cheung CI, Chin Y-C, Chen H-C, Chiu Y-C (2019) Off-resonance SERS nanoprobe-targeted screen of biomarkers for antigens recognition of bladder normal and aggressive cancer cells. Anal Chem 91:8213–8220
Zhang A, Feng J, Yan J, Hu M, Zhang L, Zeng H (2022) Laser resha** of gold nanoparticles for highly sensitive SERS detection of ciprofloxacin. Appl Surf Sci 583:152543
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Ho Chi Minh City University of Technology and Education (HCMUTE) for financial support. The authors also sincerely thank Dr. Thanh-Binh Nguyen, Ms. Minh-Nhan Thi Nguyen and Ms. Yen-Linh Hoang Nguyen for their helps.
Funding
This work is financially supported by Ho Chi Minh City University of Technology and Education under the program “HCMUTE Key research projects” (T2023-12).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tran, N.T., Nguyen, TG., Le, MT. et al. Highly branched and hollow gold nanourchins for bacterial killing and off-resonance SERS sensing. Chem. Pap. 77, 7505–7514 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-023-03077-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-023-03077-8