Abstract
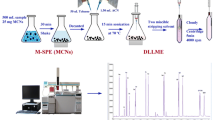
For the first time in this study, a sample preparation approach named self-effervescence-assisted dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction linked to dispersive liquid–liquid micro-extraction was evolved. This approach was applied to extract and preconcentrate some esteric compounds in plastic-bottled sparkling water samples. MIL-53 (Cr) was exploited as an adsorbent in the introduced method. In the procedure, releasing CO2 gas molecules from the sample after the addition of the mixture of metal–organic framework and Na2SO4 facilitated the sorption of analytes onto the sorbent. Vortexing was also implemented to increase extraction recoveries. After the sorption process, a mL level of 2-propanol was applied to desorb the target compounds. The obtained 2-propanol phase was then mixed with µL-level of 1,2-dibromoethane solvent as an extractant and injected into 5 mL of deionized water. Centrifugation of the formed milky solution induced sedimentation of 10 ± 0.5 µL of the organic phase containing the analytes. Injection of 1.0 µL of the stated phase into a gas chromatograph equipped with a flame ionization detector commenced the separation, detection, and determination of the analytes in the studied matrix. The obtained linear ranges in this survey were wide. Also, the linearities of the calibration curves drawn for the analytes were pleasant (r2 ≥ 0.995). Moreover, reaching low limits of detection and quantification documented as 0.96–1.40 and 3.17–4.62 µg L−1, respectively, were the highlights of the study. As the finding of the research, di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate was detected and quantified as 33 ± 2 μg L−1 (n = 3) in the surveyed plastic-bottled sparkling water.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Most data generated during this study are included in this published article. The rest of them are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- DLLME:
-
Dispersive liquid–liquid micro-extraction
- DSPE:
-
Dispersive solid phase extraction
- EF:
-
Enrichment factor
- FID:
-
Flame ionization detector
- GC:
-
Gas chromatography
- LOD:
-
Limit of detection
- LOQ:
-
Limit of quantification
- LR:
-
Linear range
- MOF:
-
Metal organic framework
- MS:
-
Mass spectrometry
- RSD:
-
Relative standard deviation
- SEADµSPE:
-
self-effervescence-assisted dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction
References
Abeele JVD, Brouwers J, Deloose E, Tack J, Augustijns P (2017) The effect of sparkling water on intraluminal formulation behavior and systemic drug performance. J Pharm Sci 106:2472–2482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xphs.2017.03.039
Afshari A, Gunnarsen L, Clausen PA, Hansen V (2004) Emission of phthalates from PVC and other materials. Indoor Air 14(2):120–128. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1600-0668.2003.00220.x
Arena A, Zoccali M, Mondello L, Tranchida PQ (2022) Direct analysis of phthalate esters in vegetable oils by means of comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography combined with triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. Food Chem 396:133721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.13372
Bustamante-Montes LP, Hernandez-Valero MA, Flores-Pimentel D, Garcia-Fabila M, Amaya-Chavez A, Barr DB, Borja-Aburto VH (2013) Prenatal exposure to phthalates is associated with decreased anogenital distance and penile size in male newborns. J Develop Origin Health Disease 4(4):300–306. https://doi.org/10.1017/S2040174413000172
Dan A, Zhang Sh, Chen Zh, Dong J, Zheng W, Tu Y, Lin Z, Cai Z (2023) Facile synthesis of Cu2+-immobilized magnetic covalent organic frameworks for highly efficient enrichment and sensitive determination of five phthalate monoesters from mouse plasma with HPLC-MS/MS. Talanta 253:123923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123923
EPA, Environmental Protection Agency Fed. Reg., Part 12, 40 CFR Part 141, National Primary Drinking Water Regulations, US Washington, DC, 1991.
Farajzadeh MA, Mohebbi A, Izadyar M, Afshar Mogaddam MA, Pezhhanfar S (2021) Facile preparation of nitrogen-doped amorphous carbon nanocomposite as an efficient sorbent in dispersive solid phase extraction. Int J Environ Anal Chem 101:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1867718
Farajzadeh MA, Pezhhanfar S, Mohebbi A, Afshar Mogaddam MR (2020) Detection and determination of some migrated chemicals from plastic containers into different drinks and liquids using dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction prior to gas chromatography. Anal Bioanal Chem Res 7:303–320. https://doi.org/10.22036/abcr.2020.196780.1380
Fasano E, Bono-Blay F, Cirillo T, Montuori P, Lacorte S (2012) Migration of phthalates, alkyl phenols, bisphenol A, and di(2-ethylhexyl)adipate from food packaging. Food Control 27:132–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2012.03.005
Ghisari M, Bonefeld-Jorgensen EC (2009) Effects of plasticizers and their mixtures on estrogen receptor and thyroid hormone functions. Toxicol Let 189:67–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2009.05.004
Goulas AE, Zygoura P, Karatapanis A, Georgantelis D, Kontominas MG (2007) Migration of di(2-ethylhexyl) adipate and acetyltributyl citrate plasti- cizers from food-grade PVC film into sweetened sesame paste (halawa tehi- neh): kinetic and penetration study. Food Chem Toxicol 45:585–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2006.10.003
Mirzajani R, Kardani F, Ramezani Z (2020) Fabrication of UMCM-1 based monolithic and hollow fiber-Metal-organic framework deep eutectic solvents/molecularly imprinted polymers and their use in solid phase microextraction of phthalate esters in yogurt, water and edible oil by GC-FID. Food Chem 314:126179–126191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126179
Nakamoto K (2008) Infrared and Raman spectra of inorganic and coordination compounds: part a: theory and applications in inorganic chemistry, 6th edn. Wiley
Peakall DB (1975) Phthalate esters: occurrence and biological effects. Res Rev 54:1–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-9857-1-1
Pezhhanfar S, Farajzadeh MA, Hosseini-Yazdi SA, Afshar Mogaddam MA (2022) Synthesis of MOF-70 based on diffusion method; microgram amount application as a highly efficient sorbent in dispersive micro solid phase extraction prior to dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the preconcentration and extraction of pesticides from fruit juices. J Iran Chem Soc 19:2407–2419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-021-02456-w
Pezhhanfar S, Farajzadeh MA, Hosseini-Yazdi SA, Afshar Mogaddam MR (2021a) An MOF-based dispersive micro solid phase extraction prior to dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for analyzing plasticizers. J Food Compos Anal 104:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2021.104174
Pezhhanfar S, Farajzadeh MA, Hosseini-Yazdi SA, Afshar Mogaddam MR (2021b) Application of an MOF-based dispersive micro solid phase extraction method followed by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for plasticizers’ detection and determination. New J Chem 45:18208–18220. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NJ03235F
Rezaee M, Yamini YS, Shariati A, Esrafili M, Shamsipur M (2009) Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction combined with high-performance liquid chromatography-UV detection as a very simple, rapid and sensitive method for the determination of bisphenol A in water samples. J Chromatogr A 1216:1511–1514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2008.12.091
Sampson J, de Korte D (2011) DEHP-plasticized PVC: relevance to blood services. Trans Med 21(2):73–83. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3148.2010.01056.x
Serre Ch, Millange F, Thouvenot Ch, Nogues M, Marsolier G, Louer D, Ferey G (2002) Very large breathing effect in the first nanoporous chromium(III)-based solids: MIL-53 or CrIII(OH). {O2C-C6H4-CO2}. HO2C-C6H4-CO2H}x.H2Oy. J Am Chem Soc 124:13519–13526. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0276974
Snijder CA, Roeleveld N, Velde E, Steegers EAP, Raat H, Hofman A, JaddoeVWV BA (2012) Occupational exposure to chemicals and fetal growth: the generation R study. Human Rep 27:910–920. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/der437
Wang B, Liu B, Yan Y (2021) Facile preparation of ZIF-8 MOF coated mesoporous magnetic nanoarticles to provide a magnetic solid phase extraction platform. J Anal Chem 76:430–441. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061934821040110
Wang C, Li YF (2016) Semen phthalate metabolites, semen quality parameters and serum reproductive hormones: a cross-sectional study in China. Environ Pollut 1:173–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.12.052
Wang R, Su P, Yang Y (2013) Optimization of ionic liquid-based microwave-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the determination of plasticizers in water by response surface methodology. Anal Method 5:1033–1039. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2AY26313K
Wang T, Zhang R, Li D, Su P, Yang Y (2019) Application of magnetized MOF-74 to phthalate esters extraction from Chinese liquor. J Sep Sci 42(8):1600–1609. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201801244
Wilkes CE, Summers JW, Daniels CA, Berard M (2005) PVC Handbook. Hanser, Munich
Wu X, Hong H, Liu X, Guan W, Meng L, Ye Y, Ma Y (2013) Graphene-dispersive solid-phase extraction of phthalate acid esters from environmental water. Sci Total Environ 444:224–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.11.060
Yamini Y, Faraji M, Adeli M (2015) Magnetic silica nanomaterials for solid-phase extraction combined with dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction of ultra-trace quantities of plasticizers. Microchim Acta 182:1491–1499. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1474-z
Yamini Y, Ghambarian M, Khalili-Zanjani MR, Faraji M, Shariati S (2009) Comparison of solidification of floating drop and homogenous liquid-liquid microextractions for the extraction of two plasticizers from the water kept in PET-bottles. J Sep Sci 32:3201–3208. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.200900280
Zhu Q, Jia J, Zhang K, Zhang H, Liao Ch, Jiang G (2019) Phthalate esters in indoor dust from several regions, China and their implications for human exposure. Sci Total Environ 652:1187–1194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.326
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to University of Tabriz for financial support.
Funding
This work was supported by University of Tabriz, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SP contributed to MOF synthesis, methodology, and characterization, analytical analysis and methodology, data analysis, and writing the manuscript. MAF contributed to analytical methodology and editing the manuscript. AM contributed to synthesis methodology and analytical analysis. SAH-Y contributed to synthesis methodology. MRAM contributed to analytical methodology.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Informed consent
Informed consent not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pezhhanfar, S., Farajzadeh, M.A., Mirzaahmadi, A. et al. Self-effervescence-assisted dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction combined with dispersive liquid–liquid micro-extraction for the extraction and preconcentration of some phthalate and adipate esters in sparkling water. Chem. Pap. 77, 4041–4055 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-023-02766-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-023-02766-8