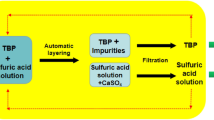
Abstract
Ammonium sulfate is used as a fertilizer because it supplies nitrogen and sulfur for plant nutrients. It can be obtained by three processes: as recovery from coke oven, a by-product from caprolactum and gypsum process. Natural gypsum fulfills the demands of the cement industries and is used by farmers as a direct fertilizer for reconditioning of alkaline solids for reducing alkalinity and improving crop production. The present study aims to synthesize ammonium sulfate from low-grade naturally occurring gypsum found in Rajasthan, India. Ammonium sulfate was prepared by adding a fixed amount of natural gypsum with an appropriate quantity of ammonium carbonate in distilled water at varying temperatures for different contact times in a batch reactor. The characterization of the natural gypsum and product was done by using Scanning Electron Microscopy, Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, Fourier Transform Infrared, X-ray Fluorescence and X-ray Diffraction. Effect of various operating parameters including temperature (30–60 °C) and contact time (1–6 h) on product yield was studied. The maximum yield of ~ 44.7% was observed at 4 h and 50 °C. The dosage of natural gypsum was 100 gm. Design-Expert software was also applied to study the influence of both the operating parameters, and it was analyzed that maximum yield of 43.5% fit well with R2 value of 0.96. Therefore, low-grade natural gypsum could be used as effective source for manufacturing ammonium sulfate.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler HH, Kerr PF (1965) Variations in infrared spectra, molecular symmetry and site symmetry of sulfate minerals. Am Mineral 50:132–147
Anbalagan G, Mukundakumari S, Murugesan KS, Gunasekaran S (2009) Infrared, optical absorption, and EPR spectroscopic studies on natural gypsum. Vib Spectrosc 50:226–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vibspec.2008.12.004
Blaney DL, McCord TB (1995) Indications of sulfate minerals in the Martan soil from Earth-based spectroscopy. J Geophys Res 100:433–441
Chandara C, Azizli KAM, Ahmad ZA, Sakai E (2009) Use of waste gypsum to replace natural gypsum as set retarders in portland cement. Waste Manag 29:1675–1679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2008.11.014
Chiang K, Chou P, Hua C, Chien K, Cheeseman C (2009) Lightweight bricks manufactured from water treatment sludge and rice husks. J Hazard Mater 171:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.144
Chou MIM, Bruinius JA, Li YC, Rostam-Abadi M, Lytle JM (1968) Manufacture of ammonium sulfate from gypsum. Prepr Pap Am Chem Soc Div Fuel Chem 40:423–548
Chou MIM, Bruinius JA, Benig V, Chou SFJ, Carty RH (2005) Producing ammonium sulfate from flue gas desulfurization by-products. Energy Sour 27:1061–1071. https://doi.org/10.1080/00908310490479510
Cooper CD, Mustard JF (2002) Spectroscopy of loose and cemented sulfate-bearing soils: implications for duricrust on Mars. Icarus 158:42–55. https://doi.org/10.1006/icar.2002.6874
Cordell GB (1968) Reaction kinetics of the production of ammonium sulfate from anhydrite. Ind Eng Chem Process Des Dev 7:278–285. https://doi.org/10.1021/i260026a022
Hardy WL, Snell FD (1957) Ammonium sulfate by the gypsum process. Ind Eng Chem 49:57A-58A. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie50566a005
Kandil AHT, Cheira MF, Gado HS, Soliman MH, Akl HM (2017) Ammonium sulfate preparation from phosphogypsum waste. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 10:24–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2016.11.001
Pedersen BF, Semmingsen D (1982) Neutron diffraction refinement of the structure of gypsum, CaSO4·2H2O. Acta Crystallogr Sect B 38:1074–1077. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0567740882004993
Powlson DS, Dawson CJ (2022) Use of ammonium sulphate as a sulphur fertilizer: implications for ammonia volatilization. Soil Use Manag 38:622–634. https://doi.org/10.1111/sum.12733
Reddy KS, Naidu MVS, Vani PM, Padmaja D, Kavitha P, K, PPR (2011) Manures, fertilizers and agricultural chemicals. SSAC-321. https://rajneeshrajoria.weebly.com/uploads/4/9/0/6/49069889/manures_fertilizers_and_agrochemicals.pdf
Strydom CA, Potgieter JH (1999) Dehydration behaviour of a natural gypsum and a phosphogypsum during milling. Thermochim Acta 332:89–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6031(99)00083-0
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Material Research Centre (MRC); Malaviya National Institute of Technology (MNIT), Jaipur, India for the characterization of natural gypsum and final product using SEM, EDS, XRD and FT-IR analysis. The authors thank Sophisticated Instrumentation Centre for Applied Research and Testing (SICART), Anand Gujarat, India, for the XRF analysis.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A., Dubey, S. Utilization of natural gypsum for the preparation of ammonium sulfate. Chem. Pap. 77, 2707–2716 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02660-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02660-9