Abstract
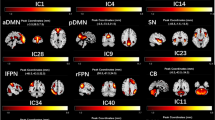
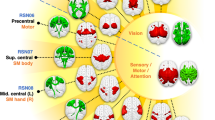
Wilson’s disease patients with neurological symptoms have motor symptoms and cognitive deficits, including frontal executive, visuospatial processing, and memory impairments. Although the brain structural abnormalities associated with Wilson’s disease have been documented, it remains largely unknown how Wilson’s disease affects large-scale functional brain networks. In this study, we investigated functional brain networks in Wilson’s disease. Particularly, we analyzed resting state functional magnetic resonance images of 30 Wilson’s disease patients and 26 healthy controls. First, functional brain networks for each participant were extracted using an independent component analysis method. Then, a computationally efficient pattern classification method was developed to identify discriminative brain functional networks associated with Wilson’s disease. Experimental results indicated that Wilson’s disease patients, compared with healthy controls, had altered large-scale functional brain networks, including the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex and basal ganglia network, the middle frontal gyrus, the dorsal striatum, the inferior parietal lobule, the precuneus, the temporal pole, and the posterior lobe of cerebellum. Classification models built upon these networks distinguished between neurological WD patients and HCs with accuracy up to 86.9% (specificity: 86.7%, sensitivity: 89.7%). The classification scores were correlated with the United Wilson’s Disease Rating Scale measures and durations of disease of the patients. These results suggest that Wilson’s disease patients have multiple aberrant brain functional networks, and classification scores derived from these networks are associated with severity of clinical symptoms.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aikath, D., Gupta, A., Chattopadhyay, I., Hashmi, M. A., Gangopadhyay, P. K., Das, S. K., & Ray, K. (2006). Subcortical white matter abnormalities related to drug resistance in Wilson disease. Neurology, 67(67), 878–880.
Ala, A., Walker, A. P., Ashkan, K., Dooley, J. S., & Schilsky, M. L. (2007). Wilson's disease. The Lancet, 369(9559), 397–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(07)60196-2.
Alexander, G. E., & Crutcher, M. D. (1990). Functional architecture of basal ganglia circuits: Neural substrates of parallel processing. Trends in Neurosciences, 13(7), 266–271.
Algin, O., Taskapilioglu, O., Hakyemez, B., Ocakoglu, G., Yurtogullari, S., Erer, S., & Parlak, M. (2010). Structural and neurochemical evaluation of the brain and pons in patients with Wilson's disease. Japanese Journal of Radiology, 28(9), 663–671. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-010-0491-4.
Andrews-Hanna, J. R., Smallwood, J., & Spreng, R. N. (2014). The default network and self-generated thought: Component processes, dynamic control, and clinical relevance. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1316, 29–52. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.12360.
Beckmann, C. F., DeLuca, M., Devlin, J. T., & Smith, S. M. (2005). Investigations into resting-state connectivity using independent component analysis, Investigations into resting-state connectivity using independent component analysis. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, 360(1457), 1001–1013. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2005.1634.
Blackburn, H. L., & Benton, A. L. (1957). Revised administration and scoring of the digit span test. Journal of Consulting Psychology, 21(2), 139–143.
Bodurka, J., Ye, F., Petridou, N., Murphy, K., & Bandettini, P. A. (2007). Map** the MRI voxel volume in which thermal noise matches physiological noise-implications for fMRI. Neuroimage, 34(2), 542–549.
Bressler, S. L., & Menon, V. (2010). Large-scale brain networks in cognition: Emerging methods and principles. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 14(6), 277–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2010.04.004.
Calhoun, V. D., Liu, J., & Adali, T. (2009). A review of group ICA for fMRI data and ICA for joint inference of imaging, genetic, and ERP data. Neuroimage, 45(1 Suppl), S163–S172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.10.057.
Center, U. O. U. H. S. (2001). Hyperbrain glossary of terms. University of Utah Health Sciences Center.
Chabardès, S., Kahane, P., Minotti, L., Hoffmann, D., & Benabid, A.-L. (2002). Anatomy of the temporal pole region. Epileptic Disorders, 4(1), 9–16.
Ciric, R., Wolf, D. H., Power, J. D., Roalf, D. R., Baum, G. L., Ruparel, K., Shinohara, R. T., Elliott, M. A., Eickhoff, S. B., Davatzikos, C., Gur, R. C., Gur, R. E., Bassett, D. S., & Satterthwaite, T. D. (2017). Benchmarking of participant-level confound regression strategies for the control of motion artifact in studies of functional connectivity. Neuroimage, 154, 174–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.03.020.
Delaveau, P., Salgado-Pineda, P., Fossati, P., Witjas, T., Azulay, J. P., & Blin, O. (2010). Dopaminergic modulation of the default mode network in Parkinson's disease. European Neuropsychopharmacology: The Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology, 20(11), 784–792.
Du, Y., & Fan, Y. (2013). Group information guided ICA for fMRI data analysis. Neuroimage, 69, 157–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.11.008.
Dupont, S. (2002). Investigating temporal pole function by functional imaging. Epileptic Disorders International Epilepsy Journal with Videotape, 4 Suppl 1(Suppl 1), S17.
Fan, Y., Liu, Y., Jiang, T., Liu, Z., Hao, Y., & Liu, H. (2010). Discriminant analysis of resting-state functional connectivity patterns on the Grassmann manifold. 7623, 76231J, https://doi.org/10.1117/12.844495.
Fan, Y., Liu, Y., Wu, H., Hao, Y., Liu, H., Liu, Z., & Jiang, T. (2011). Discriminant analysis of functional connectivity patterns on Grassmann manifold. Neuroimage, 56(4), 2058–2067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.03.051.
Frota, N. A. F., Caramelli, P., & Barbosa, E. R. (2009). Cognitive impairment in Wilson’s disease. Dementia & Neuropsychologia, 3(1), 16–21.
Gjerris, A., Bech, P., Bøjholm, S., Bolwig, T., Kramp, P., Clemmesen, L., et al. (1983). The Hamilton anxiety scale: Evaluation of homogeneity and inter-observer reliability in patients with depressive disorders. Journal of Affective Disorders, 5(2), 163–170.
Gong, Y. (1992). Wechsler adult intelligence scale-revised in China version. Changsha: Hunan Medical College.
Gray, M. A., Egan, G. F., Ando, A., Churchyard, A., Chua, P., Stout, J. C., & Georgiou-Karistianis, N. (2013). Prefrontal activity in Huntington's disease reflects cognitive and neuropsychiatric disturbances: The IMAGE-HD study. Experimental Neurology, 239, 218–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2012.10.020.
Habas, C., Kamdar, N., Nguyen, D., Prater, K., Beckmann, C. F., Menon, V., & Greicius, M. D. (2009). Distinct cerebellar contributions to intrinsic connectivity networks. The Journal of Neuroscience, 29(26), 8586–8594. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1868-09.2009.
Han, Y., Zhang, F., Tian, Y., Hu, P., Li, B., & Wang, K. (2014). Selective impairment of attentional networks of alerting in Wilson's disease. PLoS One, 9(6), e100454. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0100454.
Han, Y., Cheng, H., Toledo, J. B., Wang, X., Li, B., Wang, K., et al. (2016). Impaired functional default mode network in patients with mild neurological Wilson's disease. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, 30, 46–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2016.06.018.
Hanlly, J., Dewick, H., Davies, A., Playeer, J., & Turnbull, C. (1990). Verbal fluency in Parkinson's disease. Neuropsychologia, 28(7), 737–741.
Hawkins, R. A., Mazziotta, J. C., & Phelps, M. E. (1987). Wilson's disease studied with FDG and positron emission tomography. Neurology, 37(11), 1707–1711.
Hegde, S., Sinha, S., Rao, S. L., Taly, A. B., & Vasudev, M. (2010). Cognitive profile and structural findings in Wilson's disease: A neuropsychological and MRI-based study. Neurology India, 58(5), 708–713.
Henry, J. D., & Crawford, J. R. (2004). Verbal fluency deficits in Parkinson's disease: A meta-analysis. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 10(04), 608–622.
Jadav, R., Saini, J., Sinha, S., Bagepally, B., Rao, S., & Taly, A. B. (2013). Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and its clinical correlates in drug naive Wilson's disease. Metabolic Brain Disease, 28(3), 455–462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-013-9407-1.
Japee, S., Holiday, K., Satyshur, M. D., Mukai, I., & Ungerleider, L. G. (2015). A role of right middle frontal gyrus in reorienting of attention: A case study. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 9, 23. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsys.2015.00023.
Juan, C.-J., Chen, C.-Y., Liu, Y.-J., Chung, H.-W., Chin, S.-C., Hsueh, C.-J., Chu, H., & Zimmerman, R. A. (2005). Acute putaminal necrosis and white matter demyelination in a child with subnormal copper metabolism in Wilson disease: MR imaging and spectroscopic findings. Neuroradiology, 47(6), 401–405.
Kim, H. J., Kim, S. J., Kim, H. S., Choi, C. G., Kim, N., Han, S., Jang, E. H., Chung, S. J., & Lee, C. S. (2013). Alterations of mean diffusivity in brain white matter and deep gray matter in Parkinson's disease. Neuroscience Letters, 550, 64–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2013.06.050.
Leinweber, B., Möller, J. C., Scherag, A., Reuner, U., Günther, P., Lang, C. J., et al. (2008). Evaluation of the unified Wilson's disease rating scale (UWDRS) in German patients with treated Wilson's disease. Movement Disorders, 23(1), 54–62.
Levisohn, L., Croningolomb, A., & Schmahmann, J. D. (2000). Neuropsychological consequences of cerebellar tumour resection in children: Cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome in a paediatric population. Brain A Journal of Neurology, 123(Pt 5)(5), 1041.
Li, P., **g, R. X., Zhao, R. J., Ding, Z. B., Shi, L., Sun, H. Q., Lin, X., Fan, T. T., Dong, W. T., Fan, Y., & Lu, L. (2017). Electroconvulsive therapy-induced brain functional connectivity predicts therapeutic efficacy in patients with schizophrenia: A multivariate pattern recognition study. NPJ Schizophrenia, 3, 21. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41537-017-0023-7.
Magalhaes, A. C. A., Caramelli, P., Menezes, J. R., Lo, L. S., Bacheschi, L. A., Barbosa, E. R., Rosemberg, L. A., & Magalhaes, A. (1994). Wilson's disease: MRI with clinical correlation. [journal article]. Neuroradiology, 36(2), 97–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00588068.
Mesulam, M. (2009). Defining neurocognitive networks in the BOLD New World of computed connectivity. Neuron, 62(1), 1–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2009.04.001.
Miller, I. W., Bishop, S., Norman, W. H., & Maddever, H. (1985). The modified Hamilton rating scale for depression: Reliability and validity. Psychiatry Research, 14(2), 131–142.
Mironov, A. (1993). Decreased signal intensity of the putamen and the caudate nucleus in Wilson disease of the brain. Neuroradiology, 35(2), 166–166.
Mochizuki, H., Kamakura, K., Masaki, T., Okano, M., Nagata, N., Inui, A., Fujisawa, T., & Kaji, T. (1997). Atypical MRI features of Wilson's disease: High signal in globus pallidus on T1-weighted images. Neuroradiology, 39(3), 171–174.
Muhlau, M., Wohlschlager, A. M., Gaser, C., Valet, M., Weindl, A., Nunnemann, S., et al. (2009). Voxel-based morphometry in individual patients: A pilot study in early Huntington disease. [controlled clinical trial]. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 30(3), 539–543. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A1390.
Nichols, T. E., & Holmes, A. P. (2002). Nonparametric permutation tests for functional neuroimaging: A primer with examples. Human Brain Map**, 15(1), 1–25.
Nobili, F., Abbruzzese, G., Morbelli, S., Marchese, R., Girtler, N., Dessi, B., Brugnolo, A., Canepa, C., Drosos, G. C., Sambuceti, G., & Rodriguez, G. (2009). Amnestic mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease: A brain perfusion SPECT study. Movement Disorders Official Journal of the Movement Disorder Society, 24(3), 414–421.
Portala, K., Levander, S., Westermark, K., Ekselius, L., & von Knorring, L. (2001). Pattern of neuropsychological deficits in patients with treated Wilson's disease. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, 251(6), 262–268.
Potgieser, A. R., van der Hoorn, A., Meppelink, A. M., Teune, L. K., Koerts, J., & de Jong, B. M. (2014). Anterior temporal atrophy and posterior progression in patients with Parkinson's disease. Neuro-Degenerative Diseases, 14(3), 125–132.
Pruim, R. H. R., Mennes, M., van Rooij, D., Llera, A., Buitelaar, J. K., & Beckmann, C. F. (2015). ICA-AROMA: A robust ICA-based strategy for removing motion artifacts from fMRI data. Neuroimage, 112, 267–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.02.064.
Quarantelli, M., Salvatore, E., Giorgio, S. M., Filla, A., Cervo, A., Russo, C. V., et al. (2013). Default-mode network changes in Huntington's disease: An integrated MRI study of functional connectivity and morphometry. PLoS One, 8(8), e72159.
Roberts, E. A., Schilsky, M. L., & American Association for Study of Liver, D. (2008). Diagnosis and treatment of Wilson disease: An update. [practice guideline]. Hepatology, 47(6), 2089–2111. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.22261.
Rosas, H. D., Hevelone, N. D., Zaleta, A. K., Greve, D. N., Salat, D. H., & Fischl, B. (2005). Regional cortical thinning in preclinical Huntington disease and its relationship to cognition. Neurology, 65(5), 745–747. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000174432.87383.87.
Schlaug, G., Hefter, H., Engelbrecht, V., Kuwert, T., Arnold, S., Stöcklin, G., & Seitz, R. J. (1996). Neurological impairment and recovery in Wilson's disease: Evidence from PET and MRI. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 136(1), 129–139.
Sener, R. N. (2003). Diffusion MR imaging changes associated with Wilson disease. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 24(5), 965–967.
Sinha, S., Taly, A. B., Ravishankar, S., Prashanth, L. K., Venugopal, K. S., Arunodaya, G. R., Vasudev, M. K., & Swamy, H. S. (2006). Wilson's disease: Cranial MRI observations and clinical correlation. Neuroradiology, 48(9), 613–621. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0101-4.
Starosta-Rubinstein, S., Young, A. B., Kluin, K., Hill, G., Aisen, A. M., Gabrielsen, T., & Brewer, G. J. (1987). Clinical assessment of 31 patients with Wilson's disease. Correlations with structural changes on magnetic resonance imaging. Archives of Neurology, 44(4), 365–370.
Stoodley, C. J., & Schmahmann, J. D. (2009). Functional topography in the human cerebellum: A meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies. Neuroimage, 44(2), 489–501.
Tessitore, A., Esposito, F., Vitale, C., Santangelo, G., Amboni, M., Russo, A., Corbo, D., Cirillo, G., Barone, P., & Tedeschi, G. (2012). Default-mode network connectivity in cognitively unimpaired patients with Parkinson disease. Neurology, 79(23), 2226–2232.
Tuovinen, T., Rytty, R., Moilanen, V., Abou Elseoud, A., Veijola, J., Remes, A. M., & Kiviniemi, V. J. (2016). The effect of Gray matter ICA and coefficient of variation map** of BOLD data on the detection of functional connectivity changes in Alzheimer's disease and bvFTD. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 10, 680. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2016.00680.
Webb, W., & Adler, R. K. (2016). Neurology for the Speech-Language Pathologist-E-Book: Elsevier health sciences,297–312.
Wenisch, E., De Tassigny, A., Trocello, J.-M., Beretti, J., Girardot-Tinant, N., & Woimant, F. (2013). Cognitive profile in Wilson's disease: A case series of 31 patients. Revue Neurologique, 169(12), 944–949.
Westermark, K., Tedroff, J., Thuomas, K. Å., Hartvig, P., Långström, B., Andersson, Y., Hörnfeldt, K., & Aquilonius, S. M. (1995). Neurological Wilson's disease studied with magnetic resonance imaging and with positron emission tomography using dopaminergic markers. Movement Disorders, 10(5), 596–603.
Wetherill, R. R., Rao, H., Hager, N., Wang, J., Franklin, T. R., & Fan, Y. (2018). Classifying and characterizing nicotine use disorder with high accuracy using machine learning and resting-state fMRI. Addiction Biology, 0(0), https://doi.org/10.1111/adb.12644.
Wolf, R. C., Sambataro, F., Vasic, N., Wolf, N. D., Thomann, P. A., Saft, C., Landwehrmeyer, G. B., & Orth, M. (2012). Default-mode network changes in preclinical Huntington's disease. Experimental Neurology, 237(1), 191–198.
Yoneyama, N., Watanabe, H., Kawabata, K., Bagarinao, E., Hara, K., Tsuboi, T., Tanaka, Y., Ohdake, R., Imai, K., Masuda, M., Hattori, T., Ito, M., Atsuta, N., Nakamura, T., Hirayama, M., Maesawa, S., Katsuno, M., & Sobue, G. (2018). Severe hyposmia and aberrant functional connectivity in cognitively normal Parkinson's disease. PLoS One, 13(1), e0190072.
Zaheryany, S. M. S., Bidaki, R., Brujeni, N. H., Rezvani, M., & Shooshtari, M. H. (2012). Idiopathic thrombocytopenia and neurologic manifestations in a young female leading to the diagnosis of Wilson’s disease. Iranian Journal of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, 6(2), 96–99.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Basic Research Program of China (grant number 2015CB856404), National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 61473296), the Clinical Research Key Project of Anhui University of Chinese Medicine (grant number 2014lckf02006), the Anhui Provincial Science and Technology Project (grant number 15011d04009), and NIH grants (EB022573, DA039215, and DA039002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interests
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
**g, R., Han, Y., Cheng, H. et al. Altered large-scale functional brain networks in neurological Wilson’s disease. Brain Imaging and Behavior 14, 1445–1455 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-019-00066-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-019-00066-y