Abstract
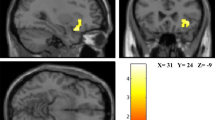
Quality of life is an important issue concerning people all over the world and affecting patients in the mental health field. When considering the potential neural links between quality of life and the brain, a brain network that comes into mind is the default mode network (DMN). Its architecture and function has been investigated in relation to various research fields including social and emotional cognition, meditation and neuropsychiatric disorders as well as happiness. In this cross-sectional study we investigated the relationship between various quality of life domains (physiological, psychological, social and environmental) and the functional connectivity of the default mode network at rest in a sample of 42 healthy working female managers. The results indicate that there is a significant association between the social quality of life domain and the functional connectivity of the default mode network. Post-hoc analysis revealed that high social quality of life scores were associated with right-left lateral parietal hypoconnectivity. By adopting a wide ranging perspective, our study approaches to fundamental research about quality of life but so far only applied on a female subgroup. As far as we know, it is the first to analyze the neuronal correlates of quality of life in the brain and therefore sets an initial step in its investigation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexopoulos, G. S., Hoptman, M. J., Kanellopoulos, D., Murphy, C. F., Lim, K. O., & Gunning, F. M. (2012). Functional connectivity in the cognitive control network and the default mode network in late-life depression. Journal of Affective Disorders, 139(1), 56–65.
Beer, J. S. (2007). The default self: feeling good or being right? Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 11(5), 187–189.
Berlim M. T., Fleck M. P. (2007) Quality of life and major depression. In: Ritsner M. S., Awad A. G. (Eds.), Quality of Life Impairment in Schizophrenia, Mood and Anxiety Disorders. Dordrecht: Springer.
Biswal, B., Yetkin, F, Z., Haughton, V, M., Hyde, J, S. (1995) Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magn Reson Med 34(4), 537–41.
Brewer, J. A., Worhunsky, P. D., Gray, J. R., Tang, Y. Y., Weber, J., & Kober, H. (2011). Meditation experience is associated with differences in default mode network activity and connectivity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108(50), 20254–20259.
Buckner, R. L., Andrews-Hanna, J. R., & Schacter, D. L. (2008). The brain's default network. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1124(1), 1–38.
Davidson, R. J., & McEwen, B. S. (2012). Social influences on neuroplasticity: stress and interventions to promote well-being. Nature Neuroscience, 15(5), 689–695.
Davidson, R. J., Kabat-Zinn, J., Schumacher, J., Rosenkranz, M., Muller, D., Santorelli, S. F., Urbanowski, F., Harrington, A., Bonus, K., & Sheridan, J. F. (2003). Alterations in brain and immune function produced by mindfulness meditation. Psychosomatic Medicine, 65(4), 564–570.
Fox, M. D., Snyder, A. Z., Vincent, J. L., Corbetta, M., van, Essen, D. C., Raichle, M. E. (2005). The human brain is intrinsically organized into dynamic, anticorrelated functional networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102, 9673–9678.
Greicius, M. D., Krasnow, B., Reiss, A. L., & Menon, V. (2003). Functional connectivity in the resting brain: a network analysis of the default mode hypothesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 100(1), 253–258.
Hallquist, M. N., Hwang, K., & Luna, B. (2013). The nuisance of nuisance regression: spectral misspecification in a common approach to resting-state fMRI preprocessing reintroduces noise and obscures functional connectivity. Neuroimage, 82, 208–225.
Hankin, B. L., & Abramson, L. Y. (2001). Development of gender differences in depression: An elaborated cognitive vulnerability–transactional stress theory. Psychological Bulletin, 127(6), 773–796.
Iacoboni, M., Lieberman, M. D., Knowlton, B. J., Molnar-Szakacs, I., Moritz, M., Throop, C. J., & Fiske, A. P. (2004). Watching social interactions produces dorsomedial prefrontal and medial parietal BOLD fMRI signal increases compared to a resting baseline. Neuroimage, 21(3), 1167–1173.
Katschnig, H. (2006). Quality of life in mental disorders: challenges for research and clinical practice. World Psychiatry, 5(3), 139–145.
Killingsworth, M. A., & Gilbert, D. T. (2010). A wandering mind is an unhappy mind. Science, 330(6006), 932–932.
Kriegeskorte, N., Simmons, W. K., Bellgowan, P. S., & Baker, C. I. (2009). Circular analysis in systems neuroscience: the dangers of double dip**. Nature Neuroscience, 12(5), 535–540.
Lanius, R. A., Bluhm, R. L., Coupland, N. J., Hegadoren, K. M., Rowe, B., Theberge, J., et al. (2010). Default mode network connectivity as a predictor of post-traumatic stress disorder symptom severity in acutely traumatized subjects. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 121(1), 33–40.
Lieberman, M. D. (2007). Social cognitive neuroscience: a review of core processes. Annual Review of Psychology, 58, 259–289.
Luo, Y., Huang, X., Yang, Z., Li, B., Liu, J., & Wei, D. (2014). Regional homogeneity of intrinsic brain activity in happy and unhappy individuals. PLoS One, 9(1), e85181.
Luo, Y., Kong, F., Qi, S., You, X., & Huang, X. (2015). Resting-state functional connectivity of the default mode network associated with happiness. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 11(3), 516–524.
Luo, Y., Qi, S., Chen, X., You, X., Huang, X., & Yang, Z. (2017). Pleasure attainment or self-realization: The balance between two forms of well-beings are encoded in default mode network. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 12(10), 1678–1686.
Lynch, C. J., Uddin, L. Q., Supekar, K., Khouzam, A., Phillips, J., & Menon, V. (2013). Default mode network in childhood autism: posteromedial cortex heterogeneity and relationship with social deficits. Biological Psychiatry, 74(3), 212–219.
Mar, R. A. (2011). The neural bases of social cognition and story comprehension. Annual Review of Psychology, 62, 103–134.
Marongiu Ivarsson, S., & Ekehammar, B. (2001). Women’s entry into management: Comparing women managers and non-managers. Journal of Managerial Psychology, 16(4), 301–314.
McArtor, D. B., Lubke, G. H., & Bergeman, C. S. (2017). Extending multivariate distance matrix regression with an effect size measure and the asymptotic null distribution of the test statistic. Psychometrika, 82(4), 1052–1077.
Moran, J. M., Macrae, C. N., Heatherton, T. F., Wyland, C. L., & Kelley, W. M. (2006). Neuroanatomical evidence for distinct cognitive and affective components of self. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 18(9), 1586–1594.
Nakamura, J., & Csikszentmihalyi, M. (2014). The concept of flow. In Flow and the foundations of positive psychology (pp. 239–263). Dordrecht: Springer.
Northoff, G., & Bermpohl, F. (2004). Cortical midline structures and the self. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 8(3), 102–107.
Qin, P., & Northoff, G. (2011). How is our self related to midline regions and the default-mode network? Neuroimage, 57(3), 1221–1233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.05.028.
Rabin, J. S., Gilboa, A., Stuss, D. T., Mar, R. A., & Rosenbaum, R. S. (2010). Common and unique neural correlates of autobiographical memory and theory of mind. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 22(6), 1095–1111.
Ritsner, M. S., & Awad, A. G. (2007). Quality of life impairment in schizophrenia, mood and anxiety disorders (pp. 133–142). Dordrecht, Netherlands: Springer.
Satterthwaite, T. D., Vandekar, S. N., Wolf, D. H., Bassett, D. S., Ruparel, K., Shehzad, Z., Craddock, R. C., Shinohara, R. T., Moore, T. M., Gennatas, E. D., Jackson, C., Roalf, D. R., Milham, M. P., Calkins, M. E., Hakonarson, H., Gur, R. C., & Gur, R. E. (2015). Connectome-wide network analysis of youth with psychosis spectrum symptoms HHS public access. Molecular Psychiatry, 20(12), 1508–1515.
Shehzad, Z., Kelly, C., Reiss, P. T., Cameron, C. R., Emerson, J. W., McMahon, K., et al. (2014). A multivariate distance-based analytic framework for connectome-wide association studies. NeuroImage, 93(Pt 1), 74–94.
Sheline, Y. I., Barch, D. M., Price, J. L., Rundle, M. M., Vaishnavi, S. N., Snyder, A. Z., Mintun, M. A., Wang, S., Coalson, R. S., & Raichle, M. E. (2009). The default mode network and self-referential processes in depression. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 106(6), 1942–1947. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0812686106.
Skevington, S. M., Lotfy, M., & O’Connell, K. A. (2004). The World Health Organization’s WHOQOL-BREF quality of life assessment: psychometric properties and results of the international field trial a report from the WHOQOL group. Quality of Life Research, 13(2), 299–310.
Spreng, R. N., Mar, R. A., & Kim, A. S. N. (2009). The common neural basis of autobiographical memory, prospection, navigation, theory of mind, and the default mode: a quantitative meta-analysis. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 21(3), 489–510.
Takeuchi, H., Taki, Y., Nouchi, R., Hashizume, H., Sassa, Y., Sekiguchi, A., Kotozaki, Y., Nakagawa, S., Nagase, T., Miyauchi, C. M., & Kawashima, R. (2014). Anatomical correlates of quality of life: evidence from voxel-based morphometry. Human Brain Map**, 35(5), 1834–1846.
The Whoqol Group. (1998). The World Health Organization quality of life assessment (WHOQOL): development and general psychometric properties. Social Science & Medicine, 46(12), 1569–1585.
Topp, C. W., Østergaard, S. D., Søndergaard, S., & Bech, P. (2015). The WHO-5 well-being index: a systematic review of the literature. Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics, 84(3), 167–176.
Vincent, J. L., Snyder, A. Z., Fox, M. D., Shannon, B. J., Andrews, J. R., Raichle, M. E., & Buckner, R. L. (2006). Coherent spontaneous activity identifies a hippocampal-parietal memory network. Journal of Neurophysiology, 96(6), 3517–3531.
Vul, E., Harris, C., Winkielman, P., & Pashler, H. (2009). Reply to comments on “puzzlingly high correlations in fMRI studies of emotion, personality, and social cognition”. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 4(3), 319–324. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6924.2009.01132.x.
Whitfield-Gabrieli, S., & Nieto-Castanon, A. (2012). Conn: a functional connectivity toolbox for correlated and anticorrelated brain networks. Brain Connectivity, 2(3), 125–141. https://doi.org/10.1089/brain.2012.0073.
Wilson, S. M., Molnar-Szakacs, I., & Iacoboni, M. (2008). Beyond superior temporal cortex: intersubject correlations in narrative speech comprehension. Cerebral Cortex, 18(1), 230–242.
Zapala, M. A., & Schork, N. J. (2012). Statistical properties of multivariate distance matrix regression for high-dimensional data analysis. Frontiers in Genetics, 3, 190. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2012.00190.
Zapala, M. A., & Schork, N. J. (2006) Multivariate regression analysis of distance matrices for testing associations between gene expression patterns and related variables. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 103(51), 19430–5.
Funding
This study was funded by Natura Cosméticos S.A. and Instituto Israelita de Ensino e Pesquisa Albert Einstein.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PNG 34 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kraft, I., Balardin, J.B., Sato, J.R. et al. Quality of life is related to the functional connectivity of the default mode network at rest. Brain Imaging and Behavior 13, 1418–1426 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-9954-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-9954-5