Abstract
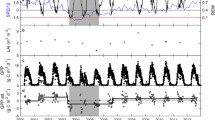
Non-photosynthetic components within a forest ecosystem account for a large proportion of the canopy but are not involved in photosynthesis. Therefore, the accuracy of gross primary production (GPP) estimates is expected to improve by removing these components. However, their influence in GPP estimations has not been quantitatively evaluated for deciduous forests. Several vegetation indices have been used recently to estimate the fraction of photosynthetically active radiation absorbed by photosynthetic components (\({FAPAR}_{green}\)) for partitioning \({APAR}_{green}\) (photosynthetically active radiation absorbed by photosynthetic components). In this study, the enhanced vegetation index (EVI) estimated \({FAPAR}_{green}\) and to separate the photosynthetically active radiation absorbed by photosynthetic components (\({APAR}_{green}\)) from total APAR observations (\({APAR}_{total}\)) at two deciduous forest sites. The eddy covariance-light use efficiency (EC-LUE) algorithm was employed to evaluate the influence of non-photosynthetic components and to test the performance of \({APAR}_{green}\) in GPP estimation. The results show that the influence of non-photosynthetic components have a seasonal pattern at deciduous forest sites, large differences are observed with normalized root mean square error (RMSE*) values of \({APAR}_{green}\)-based GPP and \({APAR}_{total}\)-based GPP between tower-based GPP during the early and end stages, while slight differences occurred during peak growth seasons. In addition, daily GPP estimation was significantly improved using the \({APAR}_{green}\)-based method, giving a higher coefficient of determination and lower normalized root mean square error against the GPP estimated by the \({APAR}_{total}\)-based method. The results demonstrate the significance of partitioning \({APAR}_{green}\) from \({APAR}_{total}\) for accurate GPP estimation in deciduous forests.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal DA, Humphrey M, Beekwilder NF, Jackson KR, Goode MM, Ingen C (2010) A data-centered collaboration portal to support global carbon-flux analysis. Concurr Comput Pract Exp 22(17):2323–2334. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpe.1600
Asner GP, Wessman CA, Archer S (1998) Scale dependence of absorption of photosynthetically active radiation in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol Appl 8(4):1003–1021. https://doi.org/10.1890/1051-0761(1998)008[1003:SDOAOP]2.0.CO;2
Baret F, Weiss M, Allard D, Garrigue S, Leroy M, Jeanjean H, Fernandes R, Myneni R, Privette J, Morisette J (2021) VALERI: a network of sites and a methodology for the validation of medium spatial resolution land satellite products. https://hal.inrae.fr/hal-03221068. Accessed 29 Jan 2022
Beer C, Reichstein M, Tomelleri E, Ciais P, Jung M, Carvalhais N, Rödenbeck C, Arain MA, Baldocchi D, Bonan GB (2010) Terrestrial gross carbon dioxide uptake: global distribution and covariation with climate. Science 329(5993):834–838. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1184984
Bounoua L, Collatz G, Los S, Sellers P, Dazlich D, Tucker C, Randall D (2000) Sensitivity of climate to changes in NDVI. J Clim 13(13):2277–2292
Chason JW, Baldocchi DD, Huston MA (1991) A comparison of direct and indirect methods for estimating forest canopy leaf area. Agric For Meteorol 57(1–3):107–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-1923(91)90081-Z
Chen JM (1996) Canopy architecture and remote sensing of the fraction of photosynthetically active radiation absorbed by boreal conifer forests. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 34(6):1353–1368. https://doi.org/10.1109/36.544559
Chen SY, Liu LY, Zhang X, Liu XJ, Chen XD, Qian XJ, Xu Y, **e DH (2019) Retrieval of the fraction of radiation absorbed by photosynthetic components (FAPARgreen) for forest using a triple-source leaf-wood-soil layer approach. Remote Sens 11(21):2471. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11212471
Cheng YB, Zhang QY, Lyapustin AI, Wang YJ, Middleton EM (2014) Impacts of light use efficiency and fPAR parameterization on gross primary production modeling. Agric For Meteorol 189–190:187–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2014.01.006
Collatz GJ (1991) Physiological and environmental regulation of stomatal conductance, photosynthesis and transpiration: a model that includes a laminar boundary layer. Agric For Meteorol 54(2–4):107–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-1923(91)90002-8
DAAC O (2018) MODIS and VIIRS land products global subsetting and visualization tool. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA
Delpierre N, Berveiller D, Granda E, Dufrêne E (2016) Wood phenology, not carbon input, controls the interannual variability of wood growth in a temperate oak forest. New Phytol 210(2):459–470. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13771
Farquhar GD, Caemmerer S, Berry JA (1980) A biochemical model of photosynthetic CO2 assimilation in leaves of C3 species. Planta 149(1):78–90
Ferster CJ, Trofymow JT, Coops NC, Chen BZ, Black TA (2015) Comparison of carbon-stock changes, eddy-covariance carbon fluxes and model estimates in coastal Douglas-fir stands in British Columbia. For Ecosyst 2(1):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40663-015-0038-3
Field CB, Randerson JT, Malmström CM (1995) Global net primary production: combining ecology and remote sensing. Remote Sens Environ 51(1):74–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/0034-4257(94)00066-V
Gitelson AA (2019) Remote estimation of fraction of radiation absorbed by photosynthetically active vegetation: generic algorithm for maize and soybean. Remote Sens Lett 10(3):283–291. https://doi.org/10.1080/2150704X.2018.1547445
Gitelson AA, Viña A, Verma SB, Rundquist DC, Arkebauer TJ, Keydan G, Leavitt B, Ciganda V, Burba GG, Suyker AE (2006) Relationship between gross primary production and chlorophyll content in crops: implications for the synoptic monitoring of vegetation productivity. J Geophys Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JD006017
Gitelson AA, Peng Y, Arkebauer TJ, Suyker AE (2015) Productivity, absorbed photosynthetically active radiation, and light use efficiency in crops: implications for remote sensing of crop primary production. J Plant Physiol 177:100–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2014.12.015
Hanan NP, Kabat P, Dolman AJ, Elbers JA (1998) Photosynthesis and carbon balance of a Sahelian fallow savanna. Glob Chang Biol 4(5):523–538. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2486.1998.t01-1-00126.x
Hanan NP, Burba G, Verma SB, Berry JA, Suyker A, Walter-Shea EA (2002) Inversion of net ecosystem CO2 flux measurements for estimation of canopy PAR absorption. Glob Chang Biol 8(6):563–574. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2486.2002.00488.x
Huete A, Liu HQ, Batchily K, Leeuwen W (1997) A comparison of vegetation indices over a global set of TM images for EOS-MODIS. Remote Sens Environ 59(3):440–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(96)00112-5
Huete A, Didan K, Miura T, Rodriguez EP, Gao X, Ferreira LG (2002) Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens Environ 83(1–2):195–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(02)00096-2
Keenan TF, Prentice IC, Canadell JG, Williams CA, Wang H, Raupach M, Collatz GJ (2016) Recent pause in the growth rate of atmospheric CO2 due to enhanced terrestrial carbon uptake. Nat Commun 7(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13428
Korson L, Drost-Hansen W, Millero FJ (1969) Viscosity of water at various temperatures. J Phys Chem 73(1):34–39. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100721a006
Kurachi N, Hagihara A, Hozumi K (1989) Effect of light interception by non-photosynthetic organs on canopy photosynthetic production. Ecol Res 4(2):187–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02347151
Lambers H, Chapin FS, Pons TL (2008) Plant physiological ecology. Springer
Landsberg J, Waring R, Coops N (2003) Performance of the forest productivity model 3-PG applied to a wide range of forest types. For Ecol Manag 172(2–3):199–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1127(01)00804-0
Liu ZJ, Wu CY, Peng DL, Wang SS, Gonsamo A, Fang B, Yuan WP (2017) Improved modeling of gross primary production from a better representation of photosynthetic components in vegetation canopy. Agric For Meteorol 233:222–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2016.12.001
Liu N, Oishi AC, Miniat CF, Bolstad P (2021) An evaluation of ECOSTRESS products of a temperate montane humid forest in a complex terrain environment. Remote Sens Environ 265:112662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2021.112662
Monteith J (1972) Solar radiation and productivity in tropical ecosystems. J Appl Ecol 9(3):747–766. https://doi.org/10.2307/2401901
Nestola E, Calfapietra C, Emmerton CA, Wong C, Thayer DR, Gamon JA (2016) Monitoring grassland seasonal carbon dynamics, by integrating MODIS NDVI, proximal optical sampling, and eddy covariance measurements. Remote Sens 8(3):260. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8030260
Nestola E (2017) Monitoring productivity of plant ecosystems: integration of optical, flux and ecophysiological measurements. Università degli studi della Tuscia—Viterbo. http://hdl.handle.net/2067/3094
Nilson T (1971) A theoretical analysis of the frequency of gaps in plant stands. Agric Meteorol 8:25–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-1571(71)90092-6
Nilson T (1999) Inversion of gap frequency data in forest stands. Agric For Meterol 98:437–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1923(99)00114-8
Peng Y, Gitelson AA, Sakamoto T (2013) Remote estimation of gross primary productivity in crops using MODIS 250 m data. Remote Sens Environ 128:186–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2012.10.005
Prentice IC, Dong N, Gleason SM, Maire V, Wright IJ (2014) Balancing the costs of carbon gain and water transport: testing a new theoretical framework for plant functional ecology. Ecol Lett 17(1):82–91. https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.12211
Prince SD, Goward SN (1995) Global primary production: a remote sensing approach. J Biogeogr 22:815–835. https://doi.org/10.2307/2845983
Raich J, Rastetter E, Melillo JM, Kicklighter DW, Steudler P, Peterson B, Grace A, Moore B, Vorosmarty CJ (1991) Potential net primary productivity in South America: application of a global model. Ecol Appl 1(4):399–429. https://doi.org/10.2307/1941899
Rödig E, Huth A, Bohn F, Rebmann C, Cuntz M (2017) Estimating the carbon fluxes of forests with an individual-based forest model. For Ecosyst 4(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40663-017-0091-1
Rossini M, Meroni M, Migliavacca M, Manca G, Cogliati S, Busetto L, Picchi V, Cescatti A, Seufert G, Colombo R (2010) High resolution field spectroscopy measurements for estimating gross ecosystem production in a rice field. Agric For Meteorol 150(9):1283–1296. https://doi.org/10.1016/jagrformet.2010.05.011
Ruimy A, Dedieu G, Saugier B (1996) TURC: a diagnostic model of continental gross primary productivity and net primary productivity. Glob Biogeochem Cycles 10(2):269–285. https://doi.org/10.1029/96GB00349
Running SW, Thornton PE, Nemani R, Glassy JM (2000) Global terrestrial gross and net primary productivity from the earth observing system. Springer, New York
Running SW, Nemani RR, Heinsch FA, Zhao MS, Reeves M, Hashimoto H (2004) A continuous satellite-derived measure of global terrestrial primary production. Bioscience 54(6):547–560. https://doi.org/10.1641/0006-3568(2004)054[0547:ACSMOG]2.0.CO;2
Schaaf C, Wang Z (2015) MCD43A4 MODIS/Terra+Aqua BRDF/Albedo Nadir BRDF adjusted ref daily L3 Global-500m V006. NASA EOSDIS land processes DAAC
Schaefer K, Collatz GJ, Tans P, Denning AS, Baker I, Berry J, Prihodko L, Suits N, Philpott A (2008) Combined simple biosphere/Carnegie-Ames-Stanford approach terrestrial carbon cycle model. J Geophys Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007JG000603
Sellers PJ, Tucker CJ, Collatz GJ, Los SO, Justice CO, Dazlich DA, Randall DA (1996) A revised land surface parameterization (SiB2) for atmospheric GCMs. Part II: the generation of global fields of terrestrial biophysical parameters from satellite data. J Clim 9(4):706–737
Wu CY, Munger JW, Niu Z, Kuang D (2010) Comparison of multiple models for estimating gross primary production using MODIS and eddy covariance data in Harvard Forest. Remote Sens Environ 114(12):2925–2939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2010.07.012
Wu GH, Guan KY, Jiang CY, Peng B, Kimm H, Chen M, Yang X, Wang S, Suyker AE, Bernacchi CJ (2020) Radiance-based NIRv as a proxy for GPP of corn and soybean. Environ Res Lett 15(3):034009. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ab65cc
**ao XM, Braswell B, Zhang QY, Boles S, Frolking S, Moore B III (2003) Sensitivity of vegetation indices to atmospheric aerosols: continental-scale observations in Northern Asia. Remote Sens Environ 84(3):385–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(02)00129-3
**ao XM, Hollinger D, Aber J, Goltz M, Davidson EA, Zhang QY, Moore B III (2004) Satellite-based modeling of gross primary production in an evergreen needleleaf forest. Remote Sens Environ 89(4):519–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2003.11.008
**ao XM, Zhang QY, Braswell B, Urbanski S, Boles S, Wofsy S, Moore B III, Ojima D (2004b) Modeling gross primary production of temperate deciduous broadleaf forest using satellite images and climate data. Remote Sens Environ 91(2):256–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2004.03.010
**ao XM, Zhang QY, Saleska S, Hutyra L, Camargo PD, Wofsy S, Frolking S, Boles S, Keller M, Moore B III (2005) Satellite-based modeling of gross primary production in a seasonally moist tropical evergreen forest. Remote Sens Environ 94(1):105–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2004.08.015
Yan M, Li ZY, Tian X, Zhang L, Zhou Y (2019) Improved simulation of carbon and water fluxes by assimilating multi-layer soil temperature and moisture into process-based biogeochemical model. For Ecosyst 6(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40663-019-0171-5
Yuan WP, Liu SG, Zhou GS, Zhou GY, Tieszen LL, Baldocchi D, Bernhofer C, Gholz H, Goldstein AH, Goulden ML, Hollinger DY, Hu YM, Law BE, Stoy PC, Vesala T, Wofsy SC et al (2007) Deriving a light use efficiency model from eddy covariance flux data for predicting daily gross primary production across biomes. Agric For Meteorol 143(3–4):189–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2006.12.001
Yuan WP, Liu SG, Yu GR, Bonnefond JM, Chen JQ, Davis K, Desai AR, Goldstein AH, Gianelle D, Rossi F (2010) Global estimates of evapotranspiration and gross primary production based on MODIS and global meteorology data. Remote Sens Environ 114(7):1416–1431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2010.01.022
Yuan WP, Liu D, Dong WJ, Liu SG, Zhou GS, Yu GR, Zhao TB, Feng JM, Ma ZG, Chen JQ, Chen Y, Chen SP, Han SJ, Huang JP, Li LH, Liu HZ, Liu SM, Ma MG, Wang YF, **a JZ, Xu WF, Zhang Q, Zhao XQ, Zhao L (2014) Multiyear precipitation reduction strongly decreases carbon uptake over northern China. J Geophys Res Biogeosciences 119(5):881–896. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JG002608
Zhang QY, Cheng YB, Lyapustin AI, Wang YJ, Gao F, Suyker A, Shashi V, Middleton EM (2014) Estimation of crop gross primary production (GPP): fAPARchl versus MOD15A2 FPAR. Remote Sens Environ 153:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2014.07.012
Zheng Y, Shen RQ, Wang YW, Li XQ, Liu SG, Liang SL, Chen JM, Ju WM, Zhang L, Yuan WP (2020) Improved estimate of global gross primary production for reproducing its long-term variation, 1982–2017. Earth Syst Sci Data 12(4):2725–2746. https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-12-2725-2020
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the supprot of the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science for providing the AmeriFlux data and the European research framework programs (CarboEurope, FP6; CarboExtreme, FP7) for the flux and meteorological data for the FR-Fon site. We are further grateful for the data provided by the MODIS and VIIRS Land Products Global Subsetting and Visualization Tool.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Project funding: This research was funded by Innovative Research Program of the International Research Center of Big Data for Sustainable Development Goals (No. CBAS2022IRP01), the National Earth System Science Data Sharing Infrastructure (No. 2005DKA32300), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41825002).
The online version is available at http://www.springerlink.com.
Corresponding editor: Yanbo Hu.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Liu, L., Sui, L. et al. Improving GPP estimates by partitioning green APAR from total APAR in two deciduous forest sites. J. For. Res. 34, 915–927 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-022-01546-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-022-01546-6