Abstract
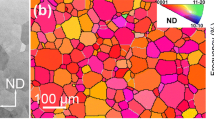
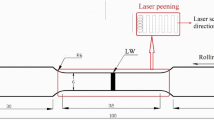
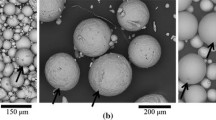
Laser peening without coating (LPwC) was carried out at multiple passes on Ti-6Al-4V at a power density of 6 GW cm−2. Tensile residual stress (65 MPa) was observed on the LPwC sample surface, without surface melting and re-solidification. Further, an oxide layer (TiO) had formed on the surface of the LPwC samples, without alpha case formation. Both these results have not been reported in Ti-6Al-4V. Secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) revealed the presence of oxide layer < 10 μm in thickness on LPwC samples. Acid pickling was used as a practical post-processing technique to eliminate the oxide layer, without causing hydrogen embrittlement. Laser peening induced a residual stress of −233 MPa at the surface and maximum residual stress of −552 MPa at a depth of 50 μm after pickling in Ti-6Al-4V samples. Further, high- and low-angle grain boundaries were found to have increased after peening, increasing further the strength of the alloy, as shown by microhardness profiles.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.R. Boyer, An Overview on the Use of Titanium in the Aerospace Industry, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1996, 213(1–2), p 103–114.
M. Geetha, A.K. Singh, R. Asokamani, and A.K. Gogia, Ti Based Biomaterials, the Ultimate Choice for Orthopaedic Implants - A Review, Prog. Mater. Sci. Elsevier Ltd, 2009, 54(3), p 397–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2008.06.004
N. Rao, Materials for Gas Turbines – An Overview, Adv. Gas Turbine Technol., 2011.
I. Inagaki, T. Takechi, Y. Shirai, and N. Ariyasu, Application and Features of Titanium for the Aerospace Industry, Nippon Steel Sumitomo Met. Tech. Rep., 2014, 106(106), p 22–27.
J. Breme, E. Eisenbarth, and V. Biehl, “Titanium and Its Alloys for Medical Applications,” Titan. Titan. Alloys, 2005.
E. Maleki and O.K. Unal, Reza Kashyzadeh, Efficiency Analysis of Shot Peening Parameters on Variations of Hardness, Grain Size and Residual Stress via Taguchi Approach, Met. Mater. Int., 2019, 25(6), p 1436–1447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-019-00290-7
S. Bagheri and M. Guagliano, Review of Shot Peening Processes to Obtain Nanocrystalline Surfaces in Metal Alloys, Surf. Eng., 2009, 25(1), p 3–14.
L. **e, Y. Wen, K. Zhan, L. Wang, C. Jiang, and V. Ji, Characterization on Surface Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V after Shot Peening, J. Alloys. Compd. Elsevier. B.V, 2016, 666, p 65–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.01.119
H. Liu, Y. Wei, C.K.I. Tan, D.T. Ardi, D.C.C. Tan, and C.J.J. Lee, XRD and EBSD Studies of Severe Shot Peening Induced Martensite Transformation and Grain Refinements in Austenitic Stainless Steel, Mater. Charact. Elsevier, 2020, 168, p 110574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2020.110574
J.P. Goulmy, P. Kanoute, E. Rouhaud, L. Toualbi, S. Kruch, V. Boyer, J. Badreddine, and D. Retraint, A Calibration Procedure for the Assessment of Work Hardening Part II: Application to Shot Peened IN718 Parts, Mater. Charact., 2021, 175, p 111068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2021.111068
Y. Sano, M. Obata, T. Kubo, N. Mukai, M. Yoda, K. Masaki, and Y. Ochi, Retardation of Crack Initiation and Growth in Austenitic Stainless Steels by Laser Peening without Protective Coating, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 417(1–2), p 334–340.
A.H. Clauer, B.P. Fairand, and B.A. Wilcox, Laser Shock Hardening of Weld Zones in Aluminum Alloys, Metall. Trans. A, 1977, 8(12), p 1871–1876.
B. Dhakal and S. Swaroop, Mechanical properties and deformation dependent microstructural aspects of laser shock peened 7075-T6 aluminum alloy without coating, Mater. Charact., 2022, 183, p 111620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2021.111620
S. Slawik, S. Bernarding, F. Lasagni, C. Navarro, A. Periñán, F. Boby, S. Migot-Choux, J. Domínguez, and F. Mücklich, Microstructural Analysis of Selective Laser Melted Ti6Al4V Modified by Laser Peening and Shot Peening for Enhanced Fatigue Characteristics, Mater. Charact., 2020, 2021, p 173.
B. Jose, T. Patil, S.S. Rajan, K. Praveenkumar, G. Manivasagam, and S. Swaroop, Effect of laser Shock Peening Without Coating (LPwC) on a Surface and Sub-Surface Characteristics of Aged Ti 15 V-3Al-3Cr-3Sn Alloy, Mater. Today. Proceed., 2021, 46, p 578–582.
J. Vishnu, A.R. Ansheed, P. Hameed, K. Praveenkumar, S. Pilz, L.A. Alberta, S. Swaroop, M. Calin, A. Gebert, and G. Manivasagam, Insights into the Surface and Biocompatibility Aspects of Laser Shock Peened Ti-22Nb Alloy for Orthopedic Implant Applications, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2022, 586, p 152816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.152816
P. Delgado, I.I. Cuesta, J.M. Alegre, and A. Díaz, State of the Art of Deep Rolling, Precis. Eng., 2016, 46, p 1.
R.K. Nalla, I. Altenberger, U. Noster, G.Y. Liu, B. Scholtes, and R.O. Ritchie, On the Influence of Mechanical Surface Treatments-Deep Rolling and Laser Shock Peening-on the Fatigue Behavior of Ti-6Al-4V at Ambient and Elevated Temperatures, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, 355(1–2), p 216–230.
I. Altenberger, R.K. Nalla, Y. Sano, L. Wagner, and R.O. Ritchie, On the Effect of Deep-Rolling and Laser-Peening on the Stress-Controlled Low- and High-Cycle Fatigue Behavior of Ti-6Al-4V at Elevated Temperatures up to 550 °c, Int. J. Fatigue, 2012, 44, p 292–302.
H. Park, J. Kim, Y. Pyun, A. Auezhan, and Y.S. Choi, Numerical and Experimental Studies on Subscale Behaviors of Ultrasonic Surface Peening, Met. Mater. Int., 2019, 25(3), p 606–616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-018-00234-7
S. Kumar, K. Chattopadhyay, and V. Singh, Effect of Ultrasonic Shot Peening on LCF Behavior of the Ti-6Al-4V Alloy, J. Alloys. Compd., 2017, 724, p 187–197.
S. Kumar, K. Chattopadhyay, G.S. Mahobia, and V. Singh, Hot Corrosion Behaviour of Ti-6Al-4V Modified by Ultrasonic Shot Peening, Mater Des., 2016, 110, p 196–206.
J.A. Travieso-Rodríguez, R. Jerez-Mesa, G. Gómez-Gras, J. Llumà-Fuentes, O. Casadesús-Farràs, and M. Madueño-Guerrero, Hardening Effect and Fatigue Behavior Enhancement through Ball Burnishing on AISI 1038, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2019, 8(6), p 5639–5646.
M. Srivastava, S. Hloch, N. Gubeljak, M. Milkovic, S. Chattopadhyaya, and J. Klich, Surface Integrity and Residual Stress Analysis of Pulsed Water Jet Peened Stainless Steel Surfaces, Measurement, 2019, 143, p 81–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2019.04.082
A.S. Grinspan and R. Gnanamoorthy, Surface Modification by Oil Jet Peening in Al Alloys, AA6063-T6 and AA6061-T4: Part 2: Surface Morphology, Erosion, and Mass Loss, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2006, 253(2), p 997–1005.
P.S. Prevey, D.J. Hornbach, and P.W. Mason, Thermal Residual Stress Relaxation and Distortion in Surface Enhanced Gas Turbine Engine Components, 17th ASM Heat Treat. Soc. Conf. 1998 p 3–12.
O. Hatamleh, J. Lyons, and R. Forman, Laser Peening and Shot Peening Effects on Fatigue Life and Surface Roughness of Friction Stir Welded 7075-T7351 Aluminum, Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct., 2007, 30(2), p 115–130.
J.Z. Zhou, S. Huang, L.D. Zuo, X.K. Meng, J. Sheng, Q. Tian, Y.H. Han, and W.L. Zhu, Effects of Laser Peening on Residual Stresses and Fatigue Crack Growth Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Titanium Alloy, Opt. Lasers Eng., 2014, 52(1), p 189–194.
J.J. Ruschau, R. John, S.R. Thompson, and T. Nicholas, Fatigue Crack Nucleation and Growth Rate Behavior of Laser Shock Peened Titanium, Int. J. Fatigue, 1999 https://doi.org/10.1016/s0142-1123(99)00072-9
K. Praveenkumar, P. Mylavarapu, A. Sarkar, E.I. Samuel, A. Nagesha, and S. Swaroop, Residual Stress Distribution and Elevated Temperature Fatigue Behaviour of Laser Peened Ti-6Al-4V with a Curved Surface, Int. J. Fatigue., 2022, 156, p 106641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2021.106641
K. Praveenkumar, S. Swaroop, and G. Manivasagam, Effect of Multiple Laser Peening on Microstructural, Fatigue and Fretting-Wear Behaviour of Austenitic Stainless Steel, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2022, 443, p 128611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2022.128611
S.S. Rajan, G. Manivasagam, M. Ranganathan, and S. Swaroop, Influence of Laser Peening without Coating on Microstructure and Fatigue Limit of Ti-15V-3Al-3Cr-3Sn, Opt. Laser. Technol., 2018, 111, p 481–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2018.10.027
S.S. Rajan, S. Swaroop, G. Manivasagam, and M.N. Rao, Fatigue Life Enhancement of Titanium Alloy by the Development of Nano/Micron Surface Layer Using Laser Peening, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 2019, 19(11), p 7064–7073.
C.S. Montross, T. Wei, L. Ye, G. Clark, and Y.W. Mai, Laser Shock Processing and Its Effects on Microstructure and Properties of Metal Alloys: A Review, Int. J. Fatigue, 2002, 24(10), p 1021–1036.
A.K. Gujba and M. Medraj, Laser Peening Process and Its Impact on Materials Properties in Comparison with Shot Peening and Ultrasonic Impact Peening, Materials., 2014, 7(12), p 7925–7974.
B. Dhakal and S. Swaroop, Laser Shock Peening as Post Welding Treatment Technique, J. Manufact. Process., 2018, 32, p 721–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.04.006
P.P. Shukla, P.T. Swanson, and C.J. Page, Laser Shock Peening and Mechanical Shot Peening Processes Applicable for the Surface Treatment of Technical Grade Ceramics: A Review, Proceed. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manufact., 2014, 228(5), p 639–652.
P. Peyre, C. Carboni, P. Forget, G. Beranger, C. Lemaitre, and D. Stuart, Influence of Thermal and Mechanical Surface Modifications Induced by Laser Shock Processing on the Initiation of Corrosion Pits in 316L Stainless Steel, J. Mater. Sci., 2007, 42(16), p 6866–6877.
P. Ganesh, R. Sundar, H. Kumar, R. Kaul, K. Ranganathan, P. Hedaoo, P. Tiwari, L.M. Kukreja, S.M. Oak, S. Dasari and G. Raghavendra, Studies on Laser Peening of Spring Steel for Automotive Applications, Opt. Lasers. Eng., 2012, 50(5), p 678–686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlaseng.2011.11.013
P. Peyre, L. Berthe, X. Scherpereel, and R. Fabbro, Laser-Shock Processing of Aluminium-Coated 55C1 Steel in Water-Confinement Regime, Characterization and Application to High-Cycle Fatigue Behaviour, J. Mater. Sci., 1998, 33(6), p 1421–1429.
N. Mukai, N. Aoki, M. Obata, A. Ito, Y. Sano, and C. Konagai, “Laser Processing for Underwater Maintenance in Nuclear Plants,” 3rd JSME/ASME joint international conference on nuclear engineering, 1995, p 1489–1494, https://inis.iaea.org/search/search.aspx?orig_q=RN:38008928. Accessed 11 March 2020.
J. Zhu, X. Jiao, C. Zhou, and H. Gao, Applications of Underwater Laser Peening in Nuclear Power Plant Maintenance, Energy. Procedia, 2012, 16, p 153–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2012.01.026
K. Praveenkumar, G. Manivasagam, and S. Swaroop, Effect of Laser Peening on the Residual Stress Distribution and Wettability Characteristics of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy for Biomedical Applications, Trend. Biomater. Artif. Organs., 2022, 36(S1), p 18–25.
Z. Lu, F. Xu, C. Tang, Y. Cui, H. Xu, and J. Mao, Stress Corrosion Cracking Susceptibility of 304 Stainless Steel Subjected to Laser Shock Peening without Coating, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2021 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05898-8
A.H. Clauer, Laser Shock Peening, the Path to Production, Metals., 2019, 9(6), p 626.
D. Karthik and S. Swaroop, Laser Peening without Coating—an Advanced Surface Treatment: A Review, Mater. Manuf. Process., 2017, 32(14), p 1565–1572.
Y. Sano, Quarter Century Development of Laser Peening without Coating, Metals., 2020, 10(1), p 152.
P. Peyre, C. Carboni, A. Sollier, L. Berthe, C. Richard, E. de Los Rios, and R. Fabbro, New Trends in Laser Shock Wave Physics and Applications, High-Power Laser Ablation IV, 2002, 4760, p 654–666.
K. Praveenkumar, S. Swaroop, and G. Manivasagam, Residual Stress Distribution, Phase Transformation, and Wettability Characteristics of Laser Peened Austenitic Stainless Steel, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2022 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-06748-x
M.V. Nataraj and S. Swaroop, Deformation-Induced Phase Transition and Nanotwins in SS 304 Steel during Cryogenic Laser Shock Peening without Coating, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2022, 19, p 2611–2622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.06.005
A. Umapathi and S. Swaroop, Phase Gradient in a Laser Peened TC6 Titanium Alloy Analyzed Using Synchrotron Radiation, Mater. Charact., 2017, 131, p 431–439.
A. Umapathi and S. Swaroop, Residual Stress Distribution in a Laser Peened Ti-25 Cu Alloy, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2016, 307, p 38–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2016.08.053
Y. Sano, K. Akita, K. Masaki, Y. Ochi, I. Altenberger, and B. Scholtes, Laser Peening without Coating as a Surface Enhancement Technology, J. Laser. Micro. Nanoeng. Jpn. Laser. Process. Soc., 2006, 1(3), p 161–166.
D. Karthik, K.U. Yazar, A. Bisht, S. Swaroop, C. Srivastava, and S. Suwas, Gradient Plastic Strain Accommodation and Nanotwinning in Multi-Pass Laser Shock Peened 321 Steel, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2019, 487, p 426–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.05.130
I. Gurappa, Protection of Titanium Alloy Components against High Temperature Corrosion, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, 356(1–2), p 372–380.
M.J. Donachie, “Titanium - A Techincal Guide,” ASM International, II, ASM Internationa, 2000, http://www.intechopen.com/books/corrosion-resistance.
T. Dobrev, D.T. Pham, and S.S. Dimov, Laser Polishing, 4M 2006 - Second International Conference on Multi-Material Micro Manufacture, Elsevier, 2006, p 273–276.
C. Langlade, A.B. Vannes, J.M. Krafft, and J.R. Martin, Surface Modification and Tribological Behaviour of Titanium and Titanium Alloys after YAG-Laser Treatments, Surf. Coat. Technolgy., 1998, 100, p 383–387.
S. Kanou, O. Takakuwa, S.R. Mannava, D. Qian, V.K. Vasudevan, and H. Soyama, Effect of the Impact Energy of Various Peening Techniques on the Induced Plastic Deformation Region, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2012, 212(10), p 1998–2006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2012.05.003
G. Ranjith Kumar, G. Rajyalakshmi, and S. Swaroop, A Critical Appraisal of Laser Peening and Its Impact on Hydrogen Embrittlement of Titanium Alloys, Proceed. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part. B. J. Eng. Manufact., 2019, 233(13), p 2371–2398.
M.A. Meyers, Y.B. Xu, Q. Xue, M.T. Pérez-Prado, and T.R. McNelley, Microstructural Evolution in Adiabatic Shear Localization in Stainless Steel, Acta. Mater., 2003, 51(5), p 1307–1325.
A.S. Gill, A. Telang and V.K. Vasudevan, Characteristics of Surface Layers Formed on Inconel 718 by Laser Shock Peening with and without a Protective Coating, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2015, 225, p 463–472.
D. Karthik and S. Swaroop, Laser Shock Peening Enhanced Corrosion Properties in a Nickel Based Inconel 600 Superalloy, J. Alloys. Compd., 2017, 694, p 1309–1319.
S. Sathyajith, S. Kalainathan, and S. Swaroop, Laser peening without coating on aluminum alloy Al-6061-T6 using low energy Nd: YAG laser, Opt. Laser. Technol., 2013, 45, p 389–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2012.06.019
Acknowledgments
We thank Aeronautics R&D Board, India (Grant No. ARDB/GTMAP/01/2031839/M/I) for the financial support, VIT University for the infrastructure and constant support throughout the project, National Facility of OIM and Texture and Sophisticated Analytical Instrument Facility (SAIF) at IIT-Bombay for EBSD and SIMS measurements. One of us (SS) would like to thank Dr. Allan H. Clauer (LSP Technologies, OH, USA) for useful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Praveenkumar, K., Mylavarapu, P. & Swaroop, S. Surface Oxidation and Subsurface Deformation in a Laser-Peened Ti-6Al-4V. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 32, 7348–7362 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07639-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07639-x