Abstract
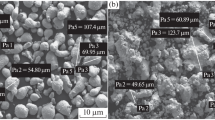
The objective of this work is to prepare porous Ni-Sn alloys by low temperature activation reaction sintering method. The phase composition, volume expansion ratio, pore structures and pore morphology of the sintered samples were studied by x-ray diffraction (XRD), vernier caliper measurement, aperture tester, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The results indicate that the phase composition is related to Sn content, pore size and porosity. The volume expansion rate of porous Ni-Sn alloys decreases first and then increases with the Sn amount. For Ni-Sn alloy with 50 wt.% of Sn content, the main phases are found to be Ni3Sn and Ni3Sn2. The average pore size is measured to be 2.78μm, which leads to an open porosity of 45.01% and a total porosity of 47.51%. Meanwhile, the volume expansion rate and permeability are determined to be – 0.99% and 105.1 m3 m–2 kpa–1 h–1, respectively. The high porosity of Ni-Sn alloy is attributed to the interconnected pores in the green compacts and the Kirkendall effect due to the difference in diffusion rates of Ni and Sn atoms.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Dong, Y. Jiang, Y. He, M. Song, J. Zou, N. Xu, B. Huang, C. Liu and P. Liaw, Formation of Porous Ni–Al Intermetallics Through Pressureless Reaction Synthesis, J. Alloy. Com., 2009, 48(4), p 907–913.
K. Zhuo, M.-G. Jeong and C.-H. Chung, Highly Porous Dendritic Ni–Sn Anodes For Lithium-Ion Batteries, J Power Sour, 2013, 24(4), p 601–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.01.055
Y.F. **ao, Y. Liu, Z. Tang, L. Wu and Y.H. He, High Temperature Oxidation Resistance of Porous Ni–Cr–Fe Materials, Inter J Mater Res, 2020, 11(1), p 356–359. https://doi.org/10.3139/146.111885
Z. Wang, Y. Jiang and Y. He, Oxidation Behavior Of Reactively Synthesized Porous Ti3(Si, Al)C2 Compound at 800 °C in Ambient Air, Ceram Inter, 2019, 45(3), p 15482–15487.
C. Ding, J. Zhang, Y. Liu, J. Guo and J. Luan, Effects of Pore-Forming Agent on Characterization of NiO/YSZ Porous Anode for SOFC, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2016, 848, p 389–395. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.848.389
X.T. Luo, Y.J. Li and C.J. Li, A Comparison of Cold Spray Deposition Behavior Between Gas Atomized and Dendritic Porous Electrolytic Ni Powders Under the Same Spray Conditions, Mater Lett, 2016, 16(3), p 58–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.10.048
Q. Zhen, Z. Zhang and H. Jia, Alloy composition dependence of formation of porous Ni prepared by rapid solidification and chemical dealloying, J Alloys Compd, 2009, 47(2), p 71–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.04.017
V.Y. Filimonov, M.A. Korchagin and I.A. Dietenberg, High Temperature Synthesis of Single-Phase Ti3al Intermetallic Compound in Mechanically Activated Powder Mixture, Powder Technol, 2013, 23(5), p 606–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2012.11.022
T. Aydoğmuş and Ş Bor, Processing of Porous TiNi Alloys Using Magnesium as Space Holder, J Alloys compd, 2009, 47(8), p 705–710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.11.141
M. Gao, C. Yang, Q. Zhang, Y. Yu, Y. Hua, Y. Li and P. Dong, Electrochemical fabrication of porous Ni-Cu alloy nanosheets with high catalytic activity for hydrogen evolution, Electrochim. Acta, 2016, 21(5), p 609–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.08.145
C. Baldizzone, L. Gan, N. Hodnik, G.P. Keeley, A. Kostka, M. Heggen, P. Strasser and K.J.J. Mayrhofer, Stability of Dealloyed Porous Pt/Ni Nanoparticles, ACS Catal., 2015, 5(4), p 5000–5007. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.5b01151
H. Cui, L. Cao, Y. Chen and J. Wu, Unique Microstructure of Porous Nial Intermetallic Compound Prepared by Combustion Synthesis, J Porous Mater, 2012, 19(2), p 415–422.
C. Yeh and W. Sun, Use of TiH2 as a reactant in combustion synthesis of porous Ti5Si3 and Ti5Si3/TiAl intermetallics, J Alloys Compd, 2016, 66(9), p 66–71.
L. Yu, Y. Jiang, Y. He, X. Liu and H. Zhang, Fabrication Of Porous Nickel–Copper Alloy With Controlled Micro-Sized Pore Structure Through The Kirkendall Effect, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2015, 163, p 355–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2015.07.050
L. Wu, Y. He, T. Lei, B. Nan, N. Xu, J. Zou, B. Huang and C. Liu, Characterization of the Porous Ni3al–Mo Electrodes During Hydrogen Generation From Alkaline Water Electrolysis, Energy, 2013, 63(4), p 216–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2013.10.029
B.M. Jovic, U.C. Lacnjevac, N.V. Krstajic and V.D. Jovic, Service Life Test of the Nisn Coatings as Cathodes for Hydrogen Evolution in Industrial Chlor-Alkali Electrolysis, Inter J Hydro Energy, 2014, 39(2), p 8947–8958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.04.015
M.B.F. Santos, E.P.D. Silva, R.J. Andrade and J.A.F. Dias, NiSn and Porous NiZn Coatings for Water Electrolysis, Electrochim. Acta, 2010 https://doi.org/10.1002/chin.199210014
C. Kong, Z. Li and G. Lu, Noble-Metal-Free Nisnxoy Decorated Graphene Cocatalyst For Highly Efficient Reduction of Water to Hydrogen, Inter J Hydro Energy, 2015, 40(3), p 9634–9641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.05.144
H. Dong, Q. Liu, Y. He and C.T. Liud, Formation of Porous Two-Phase Ni–Al Alloys Through Reactive Synthesis, J Com Theore Nanoence, 2012, 12, p 272–275. https://doi.org/10.1166/asl.2012.2746
L. Wu, Y.H. He, Y. Jiang, Y. Zeng and B. Nan, Effect of Pore Structures on Corrosion Resistance of Porous Ni3al Intermetallics, Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(2), p 3509–3516. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63495-6
Y. He, C.T. Liu, Y. Jiang and L. Yu, The Corrosion Behavior of Sintering Micro-Porous Ni-Cu Alloy in Hydrofluoric Acid Solution, J All Com: An Inter J Mater Sci Solid-state Chem Phys, 2015, 638, p 7–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.01.281
L. Yu, T. Lei and B. Nan, Characteristics of a Sintered Porous Ni–Cu Alloy Cathode for Hydrogen Production in a Potassium Hydroxide Solution, Energy, 2016, 2016(97), p 498–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2015.12.138
I. Standards, Permeable Sintered Metal Materials - Determination of Bubble Test Pore Size.
H. Gao, Y. He, P. Shen, J. Zou, N. Xu, Y. Jiang, B. Huang and C.T. Liu, Porous FeAl Intermetallics Fabricated by Elemental Powder Reactive Synthesis, Intermetallics, 2009, 17, p 1041–1046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2009.05.007
Y. Jiang, Y. He, C.T. Liu, Review Of Porous Intermetallic Compounds By Reactive Synthesis Of Elemental Powders, Intermetallics, S0966979517300262, (2017) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2017.06.003
J. Yang, C. Liao, J. Wang, Y. Jiang and Y. He, Reactive Synthesis for Porous Ti3AlC2 Ceramics Through TiH2, Al Graph Powders, Ceram Inter, 2014, 40(5), p 6739–6745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.11.136
J. Yang, C. Liao, J. Wang, Y. Jiang and Y. He, Effects of the Al Content on Pore Structures of Porous Ti3alc2 Ceramics by Reactive Synthesis, Ceram Inter, 2014, 40(8), p 4643–4648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.09.004
V. Tallapally, T.A. Nakagawara, D.O. Demchenko, U. Ozgur and I.U. Arachchige, Ge1xSnx Alloy Quantum Dots with Composition-Tunable Energy Gaps and Near-Infrared Photoluminescence, Nanoscale, 2018, 10(4), p 20296–20305. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NR04399J
Y. Gu, Q. Zhang, Y. Li, H. Wang and R.J. ** with Y3+ Ions, Mater Lett, 2009, 63(5), p 1448–1450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2009.03.045
L. Zhao, J.S. Zhang, G. Ahmed, X. Liao and J.M. Greneche, Understanding the Element Segregation and Phase Separation in the Ce-Substituted Nd-(Fe, Co)-B Based Alloys, Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1), p 68–26. https://doi.org/10.1038/41598-018-25230-0
X. Li, J. Yang, X. Feng and C. Zhang, Electrochemical Performance of Porous Ni–Cr–Mo–Cu Alloys for Hydrogen Evolution Reactions in Alkali Solution, Mater Res Ex, 2020, 9(2), p 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/abb562
X.H. Wang and Y.C. Zhou, Microstructure and Properties of Ti3alc2 Prepared by the Solid-Liquid Reaction Synthesis and Simultaneous in-Situ Hot Pressing Process, Acta Mater., 2002, 50, p 3143–3151. https://doi.org/10.1016/1359-6454(02)00117-9
R.A. Masumura, B.B. Rath and C.S. Pande, Analysis of Cu–Ni Diffusion in a Spherical Geometry for Excess Vacancy Production, Acta Mater, 2002, 50, p 4535–4544. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6454(02)00273
Acknowledgments
This project is financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (51974217, 51704221) and outstanding youth fund of Wuhan Polytechnic University (2018J05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X Li craft and writing, Y Fan literature research, Y Liu software, J Liu and J Yang funding and Review, Y Zhu and J Li language modification.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Conflict of interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Fan, Y., Liu, Y. et al. Effect of Sn Content on the Pore Structures of Porous Ni-Sn Alloys Produced by Reactive Synthesis Sintering Method. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 32, 135–143 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07088-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07088-6