Abstract
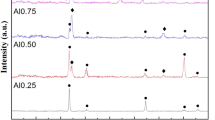
FeAlCrNiMo x high-entropy alloys were prepared. The effect of Mo content on the microstructure and the properties of the alloys were investigated. When the Mo content was 0.1, the alloys were composed of single BCC solid solution; when Mo content reaches 0.25, the alloys were composed of BCC solid solution and ordered B2 solid solution. When Mo content is more than 0.75, some σ phases emerged. The volume fraction of the second phase increases with the increasing Mo content, and the crystal grains became coarsening. The yield strength, fracture strength, and hardness increase with the increasing Mo content and reach 2252, 2612 MPa, and 1006 Hv, respectively. The magnetic transformation undergoes from the ferromagnetism to paramagnetism with the increasing Mo content. The saturation intensity and remnant magnetism are decreased with the increasing Mo content.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, S.J. Lin, J.Y. Gan, T.S. Chin, T.T. Shun, C.H. Tsau, and S.Y. Chang, Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2004, 6, p 299–303
J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, and J.Y. Gan, Formation of Simple Crystal Structures in Cu-Co-Ni-Cr-Al-Fe-Ti-V Alloys with Multiprincipal Metallic Elements, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2004, 35, p 2533–2536
Z. Tang, T. Yuan, C.W. Tsai, J.W. Yeh, C.D. Lundin, and P.K. Liaw, Fatigue Behavior of a Wrought Al0.5CoCrCuFeNi Two-Phase High-Entropy Alloy, Acta Mater., 2015, 99, p 247–258
J.Y. He, W.H. Liu, H. Wang, Y. Wu, X.J. Liu, T.G. Nieh, and Z.P. Lu, Effects of Al Addition on Structural Evolution and Tensile Properties of the FeCoNiCrMn high-Entropy Alloy System, Acta Mater., 2014, 62, p 105–113
B. Gludovatz, A. Hohenwarter, D. Catoor, E.H. Chang, E.P. George, and R.O. Ritchie, A Fracture-Resistant High-Entropy Alloy for Cryogenic Applications, Science, 2014, 345, p 1153–1158
Y. Zhang, T.T. Zuo, Z. Tang, M.C. Gao, K.A. Dahmen, P.K. Liaw, and Z.P. Lu, Microstructures and Properties of High-Entropy Alloys, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2014, 61, p 1–93
A. Gali and E.P. George, Tensile Properties of High- and Medium-Entropy Alloys, Intermetallics, 2013, 39, p 74–78
H.M. Daoud, A.M. Manzoni, N. Waderka, and U. Glatzel, High-Temperature Tensile Strength of Al10Co25Cr8Fe15Ni36Ti6 Compositionally Complex Alloy (High-Entropy Alloy), JOM, 2015, 67, p 2271–2277
M.H. Chuang, M.H. Tsai, W.R. Wang, S.J. Lin, and J.W. Yeh, Microstructure and Wear Behavior of AlxCo1.5CrFeNi1.5Tiy High-Entropy Alloys, Acta Mater., 2011, 59, p 6308–6317
Y. Zhang, J.W. Qiao, and P.K. Liaw, A Brief Review of High Entropy Alloys and Serration Behavior and Flow Units, J Iron Steel Res. Int., 2016, 23, p 2–6
M.H. Tsai, C.W. Wang, C.W. Tsai, W.J. Shen, J.W. Yeh, and J.Y. Gan, Thermal Stability and Performance of NbSiTaTiZr High Entropy Alloy Barrier for Copper Metallization, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2011, 158, p 1161–1165
S.Y. Chang, M.K. Chen, and D.S. Chen, Multiprincipal-Element AlCrTaTiZr-Nitride Nanocomposite Film of Extremely High Thermal Stability as Diffusion Barrier for Cu Metallization, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2009, 156, p 37–42
O.N. Senkov, G.B. Wilks, D.B. Miracle, C.P. Chuang, and P.K. Liaw, Refractory High-Entropy Alloys, Intermetallics, 2010, 18, p 1758–1765
J.M. Wu, S.J. Lin, J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, and Y.S. Huang, A Dhesive Wear Behavior of AlxCoCrCuFeNi High-Entropy Alloys as a Function of Aluminum Content, Wear, 2006, 261, p 513–519
C.Y. Hsu, T.S. Sheu, J.W. Yeh, and S.K. Chen, Effect of Iron Content on Wear Behavior of AlCoCrFexMo0.5Ni High-Entropy Alloys, Wear, 2010, 268, p 653–659
Y.P. Wang, D.Y. Li, L. Parent, and H. Tian, Improving the Wear Resistance of White Cast Iron Using a New Concept—High-Entropy Microstructure, Wear, 2011, 271, p 1623–1628
C.P. Lee, Y.Y. Chen, C.Y. Hsu, J.W. Yeh, and H.C. Shih, The Effect of Boron on the Corrosion resistance of the High Entropy Alloys Al0.5CoCrCuFeNiBx, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2007, 154, p 424–430
Y.Y. Chen, T. Duval, U.D. Hung, J.W. Yeh, and H.C. Shih, Microstructure and Electrochemical Properties of High Entropy Alloys—A Comparison with type-304 Stainless Steel, Corros. Sci., 2005, 47, p 2257–2279
B. Ren, Z.X. Liu, D.M. Li, L. Shi, B. Cai, and M.X. Wang, Corrosion Behavior of CuCrFeNiMn High Entropy Alloy System in 1M Sulfuric Acid Solution, Mater. Corros., 2012, 63, p 828–834
Y.L. Chou, J.W. Yeh, and H.C. Shih, The Effect of Molybdenum on the Corrosion Behaviour of the High-Entropy Alloys Co1.5CrFeNi1.5Ti0.5Mo x in Aqueous Environments, Corros. Sci., 2010, 52, p 2571–2581
H.P. Chou, Y.S. Chang, S.K. Chen, and J.W. Yeh, Microstructure, Thermophysical and Electrical Properties in AlxCoCrFeNi (0 6 × 6 2) High-Entropy Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. B, 2009, 163, p 184–189
Y. Zhang, T.T. Zuo, Y.Q. Cheng, and P.K. Liaw, High-Entropy Alloys with High Saturation Magnetization, Electrical Resistivity, and Malleability, Sci. Rep., 2013, 3, p 1455
Y.F. Kao, S.K. Chen, T.J. Chen, P.C. Chu, J.W. Yeh, and S.J. Lin, Electrical, Magnetic, and Hall Properties of Al x CoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloys, J. Alloy Compd., 2011, 509, p 1607–1614
M.S. Lucas, L. Mauger, J.A. Munoz, Y. **ao, A.O. Sheets, S.L. Semiatin et al., Magnetic and Vibrational Properties of High-Entropy Alloys, J. Appl. Phys., 2011, 109, p 07E307
C. Li, J.C. Li, M. Zhao, and Q. Jiang, Effect of Alloying Elements on Microstructure and Properties of Multiprincipal Elements High Entropy Alloys, J. Alloy Compd., 2009, 475, p 752–757
Y.J. Zhou, Y. Zhang, Y.L. Wang, and G.L. Chen, Solid Solution Alloys of AlCoCrFeNiTix with Excellent Room-Temperature Mechanical Properties, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2007, 90, p 181904
X.F. Wang, Y. Zhang, Y. Qiao, and G.L. Chen, Novel Microstructure and Properties of Multicomponent CoCrCuFeNiTix alloys, Intermetallics, 2007, 15, p 357–362
C. Li, J.C. Li, L. Zhang, and Q. Jiang, Microstructure and Properties of AlTiNiMnBx Multicomponent High Entropy Alloys, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2008, 24, p 376–379
L. Liu, J.B. Zhu, C. Zhang, J.C. Li, and Q. Jiang, Microstructure and the Properties of FeCoCuNiSnx High Entropy Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 548, p 64–68
W.R. Wang, W.L. Wang, S.C. Wang, Y.C. Tsai, C.H. Lai, and J.W. Yeh, Effects of Al Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Property of AlxCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloys, Intermetallics, 2012, 26, p 44–51
W.H. Liu, J.Y. He, H.L. Huang, H. Wang, Z.P. Lu, and C.T. Liu, Effects of Nb Additions on the Microstructure and Mechanical Property of CoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloys, Intermetallics, 2015, 62, p 76–83
Y. Dong, Y.P. Lu, J.R. Kong, J.J. Zhang, and T.J. Li, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Multi-Component AlCrFeNiMox High-Entropy Alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 2013, 573, p 96–101
C.D. Gómez-Esparza, J.C. Cisneros, I.E. Guel, J.G. Cabañas-Moreno, J.M. Herrera-Ramírez, and R. Martínez-Sánchez, Effect of Cr, Mo and Ti on the Microstructure and Vickers Hardness of Multi-Component Systems, J. Alloys Compd., 2014, 615, p S638–S644
L. Jiang, Z.Q. Cao, J.C. Jie, J.J. Zhang, Y.P. Lu, T.M. Wang, and T.J. Li, Effect of Mo and Ni Elements on Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of the CoFeNixVMoy High Entropy Alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 649, p 585–590
Z.Q. Fu, W.P. Chen, H.M. Wen, Z. Chen, and E.J. Lavernia, Effects of Co and Sintering Method on Microstructure and Mechanical Behavior of a High-Entropy Al0.6NiFeCrCo Alloy Prepared by Powder Metallurgy, J. Alloys Compd., 2014, 646, p 175–182
J.T. Guo, Materials Science and Engineering for Superalloys, Science Press, Bei**g, 2008
C. Miclea, C. Tanasoiu, and C.F. Miclea, Soft Ferrite Materials for Magnetic Temperature Transducers and Applications, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2005, 290, p 1506–1509
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial supports from NNSFC (Grant No. 50571040), Key Basic Research and Development Program (Grant No. 2014CB643303) and the National Foundation of Doctoral Station (Grant No. 20100061110019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X.C., Dou, D., Zheng, Z.Y. et al. Microstructure and Properties of FeAlCrNiMo x High-Entropy Alloys. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 25, 2164–2169 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2060-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2060-1