Abstract
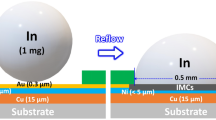
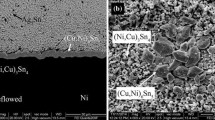
In electronic packaging technology, intermetallic compounds (IMCs) formed during a reflow process significantly affect the mechanical properties of the devices. In this study, In solder and Ni under-bump metallization (UBM) were chosen to investigate the solid–liquid interfacial reaction under an isothermal reflow process. Two types of IMCs, uniform and scallop-type, were formed in turn after being reflowed at three different temperatures, 220°C, 250°C, and 280°C. Elemental analysis has revealed that the compositions of both types of IMCs are nearly the same and were eventually identified as Ni3In7. By the growth rate of IMC formation, the mechanism of the growing process was proposed to be a diffusion-controlled process. The activation energy (Q) of the IMC formation was calculated to be 83.8 \(\frac{{ {\text{kJ}}}}{{{\text{mol}}}}\).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Haasen, G.E.R. Schulze: Metallphysik. Akademie-Verlag, Berlin 1967. 458 Seiten, 30 Tabellen, 227 Abbildungen. Preis: DM 48,–Berichte der Bunsengesellschaft für physikalische Chemie 72(2), 359 (1968).
T. An, and F. Qin, Effects of the Intermetallic Compound Microstructure on the Tensile Behavior of Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu/Cu Solder Joint Under Various Strain Rates Microelectron. Reliab. 54, 932 (2014).
Y.-F. Lin, Y.-C. Hao, and F.-Y. Ouyang, Improvement of Thermomigration Resistance in Lead-Free Sn3.5Ag Alloys by Ag Interlayer J. Alloys Compd. 847, 156429 (2020).
F.-Y. Ouyang, G.-L. Hong, Y.-R. Hsu, S.-Y. Mao, and W.-J. Liu, Thermomigration in Co/SnAg/Co and Cu/SnAg/Co Sandwich Structure Microelectron. Reliab. 97, 16 (2019).
C. Chen, H.-Y. Hsiao, Y.-W. Chang, F. Ouyang, and K.N. Tu, Thermomigration in Solder Joints Mater. Sci. Eng., R 73, 85 (2012).
X. Gu, and Y.C. Chan, Thermomigration and Electromigration in Sn58Bi Solder Joints J. Appl. Phys. 105, 093537 (2009).
Y.-H. Liao, C.-H. Chen, C.-L. Liang, K.-L. Lin, and A.T. Wu, A Comprehensive Study of Electromigration in Pure Sn: Effects on Crystallinity, Microstructure, and Electrical Property Acta Mater. 200, 200 (2020).
Z. Zhang, X. Hu, X. Jiang, and Y. Li, Influences of Mono-Ni(P) and Dual-Cu/Ni(P) Plating on the Interfacial Microstructure Evolution of Solder Joints Metall. Mater. Trans. A 50, 480 (2019).
P. Zhang, S. Xue, and J. Wang, New Challenges of Miniaturization of Electronic Devices: Electromigration and Thermomigration in Lead-Free Solder Joints Mater. Des. 192, 108726 (2020).
M. AbdelAziz, D.E. Xu, G. Wang, and M. Mayer, Electromigration in Solder Joints: A Cross-Sectioned Model System for Real-time Observation Microelectron. Reliab. 119, 114068 (2021).
A. Kunwar, Y.A. Coutinho, J. Hektor, H. Ma, and N. Moelans, Integration of Machine Learning with Phase Field Method to Model the Electromigration Induced Cu6Sn5 IMC Growth at Anode side Cu/Sn Interface J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 59, 203 (2020).
H. Saeki, J. Ikeda, and H. Ishimaru, Optical Window Sealed with Indium for Ultrahigh Vacuum Vac. 39, 563 (1989).
T. Wang, S. Li, B. He, X. Zhu, Y. Luo, Q. Liu, T. Li, S. Lu, C. Ye, A.M. Asiri, and X. Sun, Commercial Indium-tin Oxide Glass: A Catalyst Electrode for Efficient N2 Reduction at Ambient Conditions Chin. J. Catal. 42, 1024 (2021).
L.F. Li, Y.K. Cheng, G.L. Xu, E.Z. Wang, Z.H. Zhang, and H. Wang, Effects of Indium Addition on Properties and Wettability of Sn–0.7Cu–0.2Ni Lead-Free Solders Mater. Des. 64, 15 (2014).
K. Kanlayasiri, M. Mongkolwongrojn, and T. Ariga, Influence of Indium Addition on Characteristics of Sn–0.3Ag–0.7Cu Solder Alloy J. Alloys Compd. 485, 225 (2009).
Y.-C. Tseng, H. Lee, S.-C. Tsai, Y.-W. Yen, and C.-M. Chen, Suppression Effect of Ni Grain Size on the Ni3Sn4 Growth at the Sn/Ni Interface Mater. Charact. 128, 232 (2017).
Y.-A. Shen, F.-Y. Ouyang, and C. Chen, Effect of Sn Grain Orientation on Growth of Cu-Sn Intermetallic Compounds During Thermomigration in Cu-Sn23Ag-Ni Microbumps Mater. Lett. 236, 190 (2019).
Y.-S. Yang, C.-J. Yang, and F.-Y. Ouyang, Interfacial Reaction of Ni3Sn4 Intermetallic Compound in Ni/SnAg Solder/Ni System Under Thermomigration J. Alloys Compd. 674, 331 (2016).
F.-Y. Ouyang, and Y.-P. Su, Growth Kinetic of Ag3Sn Intermetallic Compound in Micro-scale Pb-Free Solder Alloys Under a Temperature Gradient J. Alloys Compd. 655, 155 (2016).
A. Sharif, and Y.C. Chan, Effect of Indium Addition in Sn-rich Solder on the Dissolution of Cu metallization J. Alloys Compd. 390, 67 (2005).
K.D. Min, C.J. Lee, B.U. Hwang, J.H. Kim, J.H. Jang, and S.B. Jung, Hybrid Transient Liquid Phase Sintering Bonding of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu Solder with Added Cu and Ni for Cu-Ni Bonding Appl. Surf. Sci. 551, 149396 (2021).
Y.H. Tseng, M.S. Yeh, and T.H. Chuang, Interfacial Reactions Between Liquid Indium and Nickel Substrate J. Electron. Mater. 28, 105 (1999).
D. Liang, B. Unveroglu, and G. Zangari, Electrodeposition of Cu-In Alloys as Precursors of Chalcopyrite Absorber Layers J. Electrochem. Soc. 161, D613 (2014).
S.-W. Chen, T.-C. Yang, J.-M. Lin, and T.-Y. Huang, Interfacial Reactions in the Co/In/Cu and Ni/In/Cu Samples J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 97, 356 (2019).
S. Norainiza, S.I. Najib, M.A.A. Mohd Salleh, Low and High Temperature Isothermal Aging Effect on Morphology and Diffusion Kinetics of Intermetallic Compound (IMC) for Sn-Cu-Si3N4 Composite Solder. Key. Engz. Mater. 666, 594-595 (2014).
J.-W. Jang, L.N. Ramanathan, J.-K. Lin, and D.R. Frear, Spalling of Cu3Sn Intermetallics in High-lead 95Pb5Sn Solder Bumps on Cu Under Bump Metallization During Solid-State Annealing J. Appl. Phys. 95, 8286 (2004).
H. Chen, Y.-L. Tsai, Y.-T. Chang, and A.T. Wu, Effect of Massive Spalling on Mechanical Strength of Solder Joints in Pb-Free Solder Reflowed on Co-Based Surface Finishes J. Alloys Compd. 671, 100 (2016).
A.M. Huntz, Parabolic Laws During High Temperature Oxidation: Relations with the Grain Size and Thickness of the Oxide J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 18, 1981 (1999).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the funding support from the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan, R.O.C., under contract nos. 108-2221-E-007-055-MY3 and 110-2811-M-007-507. The authors would also like to thank the Instrumentation Center at National Tsing Hua University (NTHU) for their JEOL JSM-6500F Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, YJ., Lu, CH. & Ouyang, FY. Interfacial Solid–Liquid Reaction of Ni/In/Ni Structure During Isothermal Reflow Process. J. Electron. Mater. 50, 6575–6583 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-021-09253-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-021-09253-4