Abstract
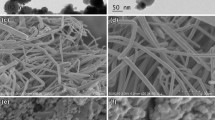
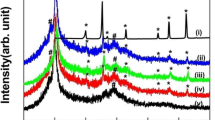
Light weight, flexible and easily processable polymeric nanocomposites possessing either high or low dielectric permittivity is in demand for high density capacitors and in microelectronics, respectively. The present study was designed to investigate the effect of separate zinc oxide (ZnO), copper oxide (CuO), graphene oxide (GO) and reduced graphene oxide (RGO) nanofillers on the electrical properties of poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) based composite strips. Herein, a simple solution casting technique has been adopted to fabricate composite strips at different nanofillers loadings. The electrical properties of composite strips were evaluated using a frequency response analyzer. There was observed a rise in dielectric constant (\( \varepsilon^{\prime } \)), dielectric loss (\( \varepsilon^{\prime \prime } \)) and AC conductivity (σac) of separate ZnO and GO nanofillers loaded PVA strips; whereas a decrease in the said parameters was observed on loading with separate CuO and RGO nanofillers in the PVA based composite strips. The frequency response analysis showed a prominent effect of applied frequency and nanofiller contents on the electrical properties of composite strips. There was observed a significant decrease in \( \varepsilon^{\prime } \) and \( \varepsilon^{\prime \prime } \) on just 0.004 wt.% RGO loading in the PVA based composite strips. Such efficient nanocomposites might be suitable for their use in microelectronics and microwave applications at above the 1 MHz range.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Barber, S. Balasubramanian, Y. Anguchamy, S. Gong, A. Wibowo, H. Gao, H.J. Ploehn, and H.C. Zur Loye, Materials 2, 1697 (2009).
Z.M. Dang, J.K. Yuan, J.W. Zha, T. Zhou, S.T. Li, and G.H. Hu, Prog. Mater. Sci. 57, 660 (2012).
T. Kuilla, S. Bhadra, D. Yao, N.H. Kim, S. Bose, and J.H. Lee, Prog. Polym. Sci. 35, 1350 (2010).
C.W. Nan, Y. Shen, and J. Ma, Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 40, 131 (2010).
M. Aslam, M.A. Kalyar, and Z.A. Raza, Polym. Eng. Sci. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.24855.
M. Aslam, M.A. Kalyar, and Z.A. Raza, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 13401 (2017).
M. Aslam, M.A. Kalyar, and Z.A. Raza, Polym. Bull. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-018-2367-1.
M. Aslam, M.A. Kalyar, and Z.A. Raza, Appl. Phys. A 123, 424 (2017).
M. Aslam, M.A. Kalyar, and Z.A. Raza, J. Electron. Mater. 47, 3912 (2018).
J.K. Rao, A. Raizada, D. Ganguly, M.M. Mankad, S.V. Satayanarayana, and G.M. Madhu, J. Mater. Sci. 50, 7064 (2015).
M. Aslam, M.A. Kalyar, and Z.A. Raza, Mater. Res. Express 3, 105036 (2016).
S.B. Aziz and Z.H. Abidin, Phys. Chem. Mater. 144, 280 (2014).
A.S. Ayesh, Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 28, 537 (2010).
C. Gavade, N.L. Singh, D. Singh, S. Shah, A. Tripathi, and D.K. Avasthi, Integr. Ferroelectr. 117, 76 (2010).
S.H. **e, B.K. Zhu, X.Z. Wei, Z.K. Xu, and Y.Y. Xu, Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 36, 1152 (2005).
R.F. Bhajantri, V. Ravindrachary, A. Harisha, C. Ranganathaiah, and G.N. Kumaraswamy, Appl. Phys. A 87, 797 (2007).
G.C. Psarras, E. Manolakaki, and G.M. Tsangaris, Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 34, 1187 (2003).
Y. Cao, P.C. Irwin, and K. Younsi, IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 11, 797 (2004).
T. Tanaka, IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 12, 914 (2005).
N. Ahad, E. Saion, and E. Gharibshahi, J Nanomater. 2012, 94 (2012).
S.G. Rathod, R.F. Bhajantri, V. Ravindrachary, P.K. Pujari, T. Sheela, and J. Naik, in AIP Conference Proceedings (2014), pp. 1769–1771.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aslam, M., Kalyar, M.A. & Raza, Z.A. Effect of Separate Zinc, Copper and Graphene Oxides Nanofillers on Electrical Properties of PVA Based Composite Strips. J. Electron. Mater. 48, 1116–1121 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6793-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6793-5