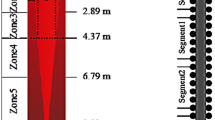
Abstract
Thin slab casting and rolling (TSCR) is a near-net-shape manufacturing process and a key development technology in China's iron and steel industry. This study uses cross-scale calculations to analyze the complete process of thin slab casting. The focus is on simulating and predicting the final solidification structure by adjusting process parameters. The aim is to enable further investigation into material performance and establish a foundation for researching deformation and phase transformation. To achieve this, a coupled model has been developed to simulate the entire thin slab casting process, using hot stam** steel as the research subject. The model encompasses fluid flow, heat transfer, and solidification. The study identifies the optimal combination for flow field, temperature distribution, and equiaxed grain ratio within the specified parameter range at a casting speed of 4.0 m/min and a superheat of 40 °C. The aim of the study is to establish an integrated computational materials engineering (ICME) research system for near-net-shape automotive steel casting processes.
Graphical Abstract
























Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Sun, W. Peng, J. Ding, X. Li, and D. Zhang: Metals, 2018, vol. 8, pp. 1–10. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8080597.
L. Wang, C. Deng, M. Dong, L. Shi, and J. Zhang: J. Iron. Steel Res. Int., 2012, vol. 19, pp. 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(12)60051-X.
X. **, Y. Gong, X. Han, H. Du, W. Ding, B. Zhu, Y. Zhang, Y. Feng, M. Ma, B. Liang, Y. Zhao, Y. Li, J. Zheng, and Z. Shi: Acta Metall. Sin., 2020, vol. 56, pp. 411–28. https://doi.org/10.11900/0412.1961.2019.00381.
J. Majta and A. Bator: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2002, vol. 125, pp. 77–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(02)00288-1.
D. Pan, H. Zhong, Q. Guo, Y. Li, Y. **ao, and K. Zhang: Mater. Lett., 2022, vol. 327, p. 133028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2022.133028.
Z. Niu, Z. Cai, and M. Zhu: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2020, vol. 47, pp. 1135–47. https://doi.org/10.1080/03019233.2019.1674590.
Y. Sheng, X. Meng, X. Liu, and Z. Zhou: Steel Res. Int., 2023, vol. 94, p. 2200874. https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.202200874.
A. Maurya, R. Kumar, and P. Jha: J. Manuf. Process., 2020, vol. 60, pp. 596–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.11.003.
J. Mahmoudi: J. Manuf. Process., 2022, vol. 77, pp. 561–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.03.035.
S. Yu, M. Long, D. Chen, H. Fan, H. Yu, H. Duan, X. **e, and T. Liu: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2019, vol. 270, pp. 157–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2019.02.009.
C. Dürr, I. Rapaport, and G. Theyssier: Theor. Comput. Sci., 2004, vol. 322, pp. 355–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcs.2004.03.017.
M. Zappulla, S. Cho, S. Koric, H. Lee, S. Kim, and B. Thomas: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2019, vol. 278, p. 116469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2019.116469.
S. Shahane, N. Aluru, P. Ferreira, S. Kapoor, and S. Vanka: J. Manuf. Process., 2020, vol. 51, pp. 130–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.01.016.
M. Long, D. Chen, Q. Wang, D. Luo, Z. Han, Q. Liu, and W. Gao: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2012, vol. 39, pp. 370–77. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743281211Y.0000000088.
H. Nakada, M. Susa, Y. Seko, M. Hayashi, and K. Nagata: ISIJ Int., 2008, vol. 48, pp. 446–53. https://doi.org/10.2355/isi**ternational.48.446.
R. Saraswat, D.M. Maijer, P.D. Lee, and K.C. Mills: ISIJ Int., 2007, vol. 47, pp. 95–104. https://doi.org/10.2355/isi**ternational.47.95.
W. Song, J. Zhang, Y. Liu, S. Wang, and B. Wang: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2015, vol. 42, pp. 656–63. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743281215Y.0000000011.
S. Mosayebidorcheh and M. Gorji-Bandpy: Appl. Therm. Eng., 2017, vol. 118, pp. 724–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.03.031.
R. Hardin, K. Liu, A. Kapoor, and C. Beckermann: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2003, vol. 34B, pp. 297–306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-003-0075-0.
T. Wang, S. Cai, J. Xu, Y. Du, J. Zhu, J. Xu, and T. Li: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2010, vol. 37, pp. 341–46. https://doi.org/10.1179/030192310X12683045806026.
B. Thomas and L. Zhang: ISIJ Int., 2001, vol. 41, pp. 1181–93. https://doi.org/10.2355/isi**ternational.41.1181.
A. Pourfathi and R. Tavakoli: Int. J. Therm. Sci., 2023, vol. 183, p. 107860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2022.107860.
M. Zhu and C. Hong: ISIJ Int., 2002, vol. 42, pp. 520–26. https://doi.org/10.2355/isi**ternational.42.520.
H. Rafii-Tabar and A. Chirazi: Phys. Rep. Rev. Sect. Phys. Lett., 2002, vol. 365, pp. 145–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0370-1573(02)00028-5.
Y. Tan and H. Wang: J. Mater. Sci., 2012, vol. 47, pp. 5308–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-6417-z.
Z. Zhang, M. Wu, H. Zhang, S. Hahn, F. Wimmer, A. Ludwig, and A. Kharicha: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2022, vol. 301, p. 117434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2021.117434.
Acknowledgments
The financial supports from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2021YFB3702401), the National Science Foundation of China (52304360) and the Open Foundation of the State Key Laboratory of Advanced Metallurgy, University of Science and Technology Bei**g, China (K22-07) and the Key Research and Development Program of **angjiang Laboratory (22XJ01002) are greatly acknowledged.
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, J., Pan, W., Wang, W. et al. Full-Process Numerical Simulation of Flow, Heat Transfer and Solidification for Hot Stam** Steel Manufactured via Thin Slab Continuous Casting Process. Metall Mater Trans B (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-024-03177-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-024-03177-0