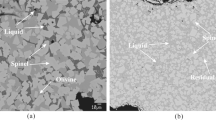
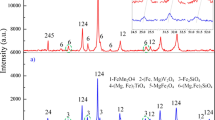
Abstract
The sodium roasting-water leaching technique is the major technique for vanadium extraction from vanadium slag in industry, which suffers from the low vanadium extraction efficiency and thus low sustainability. The lack of intrinsic evolution mechanism of vanadium-containing phases during sodium roasting hinders the improvement of vanadium extraction efficiency. Herein, the “atomic atmosphere” method is proposed to explore the phase evolution mechanism of vanadium slag during sodium roasting at the atomic scale. At the initial stage of roasting, FeV2O4 transformed into Fe2O3·V2O3. As roasting time increased to 5 min, V3+ in Fe2O3·V2O3 began to be oxidized to V4+. At 15 min, V5+-containing sodium vanadate of Na3VO4, NaV3O8, and NaVO3 began to appear. At 15 to 70 min, oxidization of vanadium occurred intensively, and the sodium vanadate nanowire crystals increased and grew into clusters. At 90 min, all the vanadium atoms were V5+, which are surrounded by O2- and Na+; the sodium vanadate nanowire bundles covered the whole slag surface. This work exemplifies the atomic atmosphere method to disclose the phase evolution mechanism of vanadium slag during sodium roasting at the atomic scale, which can not only promote the vanadium extraction efficiency of sodium roasting technique, but also provides insights for efficient and sustainable extraction of other valuable resources.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.-Y. Li, C.-J. Wang, Y.-H. Yuan, Y. Guo, J. Diao, and B. **e: J. Clean. Prod., 2020, vol. 260, p. 121091.
B. Satola: J. Electrochem. Soc., 2021, vol. 168, p. 060503.
J.C. Lee, E.Y. Kim, K.W. Chung, R. Kim, and H.S. Jeon: J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2021, vol. 12, pp. 343–64.
E. Del Carpio, L. Hernandez, C. Ciangherotti, V. Villalobos Coa, L. Jimenez, V. Lubes, and G. Lubes: Coord. Chem. Rev., 2018, vol. 372, pp. 117–40.
M. Li, H. Du, S. Zheng, S. Wang, Y. Zhang, B. Liu, D.B. Dreisinger, and Y. Zhang: JOM, 2017, vol. 69, pp. 1970–75.
F. Gao, A.U. Olayiwola, B. Liu, S. Wang, H. Du, J. Li, X. Wang, D. Chen, and Y. Zhang: Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev., 2022, vol. 43, pp. 466–88.
J. Wen, T. Jiang, J. Wang, L. Lu, and H. Sun: J. Clean. Prod., 2020, vol. 261, p. 121205.
L. Chen, Z. Wang, Z. Qin, G. Zhang, H. Yue, B. Liang, and D. Luo: J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2021, vol. 12, pp. 1391–1402.
H.-Y. Li, J. Cheng, C.-J. Wang, S. Shen, J. Diao, and B. **e: Metall. Trans. B, 2022, vol. 53, pp. 604–16.
W.-C. Song, K. Li, Q. Zheng, and H. Li: Waste Biomass Valori., 2013, vol. 5, pp. 327–32.
H.-Y. Li, C. Wang, M. Lin, Y. Guo, and B. **e: Powder Technol., 2020, vol. 360, pp. 503–08.
H.-Y. Li, H.-X. Fang, K. Wang, W. Zhou, Z. Yang, X.-M. Yan, W.-S. Ge, Q.-W. Li, and B. **e: Hydrometallurgy, 2015, vol. 156, pp. 124–35.
X.-S. Li, B. **e, G.-E. Wang, and X.-J. Li: T. Nonferr. Metal. Soc., 2011, vol. 21, pp. 1860–67.
Y. Ji, S. Shen, J. Liu, and Y. Xue: J. Clean. Prod., 2017, vol. 149, pp. 1068–78.
C.P.J. Van Vuuren and P.P. Stander: Miner. Eng., 2001, vol. 14, pp. 803–08.
H.-Y. Li, K. Wang, C. Wang, M. Lin, and B. **e: Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B, 2019, vol. 75, pp. 927–32.
G. Silversmit, D. Depla, H. Poelman, G.B. Marin, and R. De Gryse: J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom., 2004, vol. 135, pp. 167–75.
J. Mendialdua, R. Casanova, and Y. Barbaux: J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom., 1995, vol. 71, pp. 249–61.
M. Demeter, M. Neumann, and W. Reichel: Surf. Sci., 2000, vol. 454, pp. 41–44.
Z. Wang, L. Chen, T. Aldahrib, C. Li, W. Liu, G. Zhang, Y. Yang, and D. Luo: Hydrometallurgy, 2020, vol. 191, p. 105156.
S. Petnikota, R. Chua, K.M. Boopathi, R. Satish, F. Bonaccorso, V. Pellegrini, and M. Srinivasan: J. Electrochem. Soc., 2020, vol. 167, p. 100514.
W. Kou, J. Wu, Q. Zhang, Y. Shen, R. Bi, Y. Li, X. Miao, T. Yang, and G. Yang: J. Alloys Compd., 2022, vol. 924, p. 166414.
C. Ji, Z. Wu, L. Lu, X. Wu, J. Wang, X. Liu, H. Zhou, Z. Huang, J. Gou, and Y. Jiang: J. Mater. Chem. C, 2018, vol. 6, pp. 6502–09.
L. Chen, Z. Wang, Z. Qin, G. Zhang, H. Yue, B. Liang, and D. Luo: Powder Technol., 2021, vol. 387, pp. 434–43.
H. Yang, Y. Liu, T. Zhang, S. Lin, and K. Wang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2024, vol. 1, p. 1.
G.A. Sawatzky and D. Post: PRB, 1979, vol. 20, pp. 1546–55.
N. Alov, D. Kutsko, I. Spirovova, and Z. Bastl: Surf. Sci., 2006, vol. 600, pp. 1628–31.
T. Jiang, J. Wen, M. Zhou, and X. Xue: J. Alloys Compd., 2018, vol. 742, pp. 402–12.
Q. Zhang, Y. Wu, and T. Zuo: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2019, vol. 50B, pp. 471–79.
J. Pantic, A. Kremenovic, A. Dosen, M. Prekajski, N. Stankovic, Z. Bascarevic, and B. Matovic: Ceram. Int., 2013, vol. 39, pp. 483–88.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant Nos. 52074050, 52222407] and the Large Instrument Foundation of Chongqing University [No. 202303150188].
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, J., Li, HY., Zhong, Q. et al. Phase Evolution Mechanism of Vanadium Slag During Sodium Roasting via the Atomic Atmosphere Method Exploration. Metall Mater Trans B (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-024-03137-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-024-03137-8