Abstract
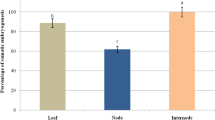
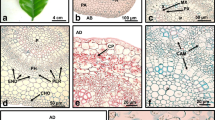
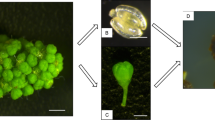
We examined the somatic embryogenesis from and histological studies of zygotic embryos of seeds in European Grape ‘Moldova’ (Vitis vinifera L. ‘Moldova’). Primary calli were initiated on Nitsch and Nitsch (NN) medium supplemented with 1.0 mg·L−1 2,4-D and 0.5 mg·L−1 6-BA. Embryogenic calli were produced upon transfer to a NN medium with 0.5 mg·L−1 6-BA and 2 mg·L−1 NAA and somatic embryos were obtained on a half strength MS medium without plant growth regulators. During the somatic embryo germination, an addition of 1.0 mg·L−1 6-BA in the medium could accelerate somatic embryos to develop into normal plants and increase the conversion rate from 0 to 43.3%. Histological studies of embryogenic calli and somatic embryos demonstrated dynamic changes of proteins and starch grains. The developmental processes of somatic embryos were similar to those of zygotic embryos, including typical epiderma, cotyledon primordium and vascular tissue.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben A A, Cobanov P, Boonrod K, Krczal G, Bouzid S, Ghorbel A, Reustle G M. 2007. Efficient procedure for grapevine embryogenic suspension establishment and plant regeneration: role of conditioned medium for cell proliferation. Plant Cell Rep, 26(9): 1439–1447
Carimi F, Barizza E, Gardiman M, Schiavo F L. 2005. Somatic embryogenesis from stigmas and styles of grapevine. In Vitro Cell Dev-Pl, 41(3): 249–252
Das D, Reddy M, Upadhyaya K, Sopory S. 2002. An efficient leaf-disc culture method for the regeneration via somatic embryogenesis and transformation of grape (Vitis vinifera L.). Plant Cell Rep, 20(11): 999–1005
Faure O. 1990. Somatic embryos of Vitis rupestris and zygotic embryos of Vitis species: morphology, histology, histochemistry and development. Can J Bot, 68(3): 2305–2315
Faure O, Aarrouf J, Nougarede A. 1996. Ontogenesis, differentiation and precocious germination in anther-derived somatic embryos of grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.): Embryonic organogenesis. Ann Bot, 78(1): 29–37
Franks T, Gang H D, Thomas M. 1998. Regeneration of transgenic shape Vitis vinifera L. Sultana plants: genotypic and phenotypic analysis. Mol Breed, 4(4): 321–333
Gambino G, Bondaz J, Gribaudo I. 2006. Detection and elimination of viruses in callus, somatic embryos and regenerated plantlets of grapevine. Eur J Plant Pathol, 114(4): 397–404
Gambino G, Ruffa P, Vallania R, Gribaudo I. 2007. Somatic embryogenesis from whole flowers, anthers and ovaries of grapevine (Vitis spp.). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult, 90(1): 79–83
Goebel-Tourand I, Mauro M C, Sossountzov L, Miginiac E, Deloire A. 1993. Arrest of somatic embryo development in grapevine: histological characterization and the effect of ABA, BAP and zeatin in stimulating plantlet development. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult, 33(1): 91–103
Gray D J. 1987. Quiescence in monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous somatic embryos induced by dehydration. HortScience, 22(5): 810–814
Gray D J. 1989. Effects of dehydration and exogenous growth regulators on dormancy, quiescence and germination of grape somatic embryos. In Vitro Cell Dev-Pl, 25(12): 1173–1178
Gray D J. 1992. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from immature zygotic embryos of muscadine grape (Vitis rotundifolia) cultivars. Am J Bot, 79(5): 542–546
Gray D J. 1995. Somatic embryogenesis in grape. In: Jain S, Gupta P, Newton R (eds.). Somatic Embryogenesis in Woody Plants, Vol. 2. Dordrecht: Kluwer, 191–217
Gray D J, Compton M E, Harrel R C, Cantliffe D J, Bajaj Y P. 1995. Somatic embryogenesis and the technology of synthetic seed. In: Bajaj Y P S (ed.). Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry (Alemania). Berlin: Spring-Verlag, 126–151
Gray D J, Mortensen J A. 1987. Initiation and maintenance of long term somatic embryogenesis from anthers and ovaries of Vitis longii ‘Microsperma’. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult, 9(1): 73–80
Iocco P, Franks T, Thomas M R. 2001. Genetic transformation of major wine grape cultivars of Vitis vinifera L. Transgen Res, 10(2): 105–112
Jayasankar S, Bondada B, Li Z, Gray D. 2002. A unique morphotype of grapevine somatic embryos exhibits accelerated germination and early plant development. Plant Cell Rep, 20(10): 907–911
Jayasankar S, Gray D J, Litz R E. 1999. High-efficiency somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from suspension cultures of grapevine. Plant Cell Rep, 18(7): 533–537
Murashige T, Skoog F. 1962. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco cultures. Physiol Plant, 15(3): 473–497
Nitsch J P, Nitsch C. 1969. Haploid plants from pollen grains. Science, 163(3862): 85–87
Perl A, Saad S, Sahar N, Holland D. 1995. Establishment of long-term embryogenic cultures of seedless Vitis vinifera cultivars—a synergistic effect of auxins and the role of abscisic acid. Plant Sci, 104(2): 193–200
Pinto-Sintra A L. 2007. Establishment of embryogenic cultures and plant regeneration in the Portuguese cultivar ‘Touriga Nacional’ of Vitis vinifera L. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult, 88(3): 253–265
Rajasekaran K, Vine J, Mullins M G. 1982. Dormancy in somatic embryos and seeds of Vitis: changes in endogenous abscisic acid during embryogeny and germination. Planta, 154(2): 139–144
Rodriguez A P, Wetzstein H Y. 1998. A morphological and histological comparison of the initiation and development of pecan (Carya illinoinensis) somatic embryogenic cultures induced with naphthaleneacetic acid or 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Protoplasma, 204(1): 71–83
Sass J E. 1958. Botanical Microtechnique. Ames: Iowa State University Press
Takeno K, Koshioka M, Pharis R P, Rajasekaran K, Mullins M G. 1983. Endogenous gibberellin-like substances in somatic embryos of grape (Vitis vinifera×Vitis rupestris) in relation to embryogenesis and the chilling requirement for subsequent development of mature embryos. Plant Physiol, 73(3): 803–808
Vilaplana M, Mullins M G. 1989. Regeneration of grapevines (Vitis spp.) in vitro: formation of adventitious buds on hypocotyls and cotyledons of somatic embryos. J Plant Physiol, 134(4): 413–419
Zhao S, Guo Z, Ma A. 2006. A late-maturing grape cultivar with characteristic of strong resistance to diseases — Moldva. China Fruits, 33(3): 60–61 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Li, Fl., Du, Jc. et al. Somatic embryogenesis and histological analysis from zygotic embryos in Vitis vinifera L. ‘Moldova’. For. Stud. China 10, 253–258 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11632-008-0040-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11632-008-0040-8