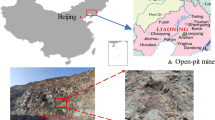
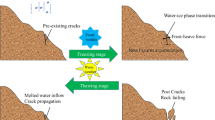
Abstract
To study the damage mechanisms of anhydrite rock under freeze-thaw cycles, the physical-mechanical properties and the microcracking activities of anhydrite rock were investigated through mass variation, nuclear magnetic resonance, scanning electron microscope tests, and uniaxial compression combined with acoustic emission (AE) tests. Results show that with the increase of freeze-thaw processes, the mass, uniaxial compression strength, and elastic modulus of the anhydrite specimens decrease while the porosity and plasticity characteristics increase. For example, after 120 cycles, the uniaxial compression strength and elastic modulus decrease by 46.54% and 60.16%, and the porosity increase by 75%. Combined with the evolution trend of stressstrain curves and the detected events, three stages were labeled to investigate the AE characteristics in freeze-thaw weathered anhydrite rock. It is found that with the increase of freeze-thaw cycles, the proportions of AE counts in stage I and stage II show a decaying exponential trend. Contrarily, the proportion of AE counts in stage III displays an exponential ascending trend. Meanwhile, as the freeze-thaw cycles increase, the low-frequency AE signals increase while the intermediate-frequency AE signals decrease. After 120 cycles, the proportion of low-frequency AE signals increases by 168.95%, and the proportion of intermediate-frequency AE signals reduces by 81.14%. It is concluded that the micro-tensile cracking events occupy a dominant position during the loading process. With the increase of freeze-thaw cycles, the b value of samples decreases. After 120 cycles, b value decreases by 27.2%, which means that the proportion of cracking events in rocks with small amplitude decreases. Finally, it is proposed that the freeze-thaw damage mechanism of anhydrite is also characterized by the water chemical softening effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdolghanizadeh K, Hosseini M, Saghafiyazdi M (2020) Effect of freezing temperature and number of freeze-thaw cycles on mode I and mode II fracture toughness of sandstone. Theor Appl Fract Mec 105: 102428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tafmec.2019.102428
Bieniawski ZT (1967) Mechanism of brittle fracture of rock: part II-experimental studies. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 4 (4): 407–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(67)90031-9
Codeglia D, Dixon N, Fowmes G J, et al. (2016) Analysis of acoustic emission patterns for monitoring of rock slope deformation mechanisms. Eng Geol 219: 21–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.11.021
DL/T 5368–2007 (2007) Code for rock tests of hydroelectric and water conservancy engineering. China Electric Power Press, Bei**g, China. (In Chinese).
Eslami J, Walbert C, Beaucour AL, et al. (2018) Influence of physical and mechanical properties on the durability of limestone subjected to freeze-thaw cycles. Constr Build Mater 162: 420–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.12.031
Fan LF, Xu C, Wu ZJ (2019) Effects of cyclic freezing and thawing on the mechanical behavior of dried and saturated sandstone. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79(2): 755–765. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01586-z
Feng Q, Jiang BS, Zhang Q, et al. (2014) Analytical elastoplastic solution for stress and deformation of surrounding rock in cold region tunnels. Cold Reg Sci Technol 108: 59–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2014.08.001
Gao F, **ong X, Xu CS, et al. (2021) Mechanical property deterioration characteristics and a new constitutive model for rocks subjected to freeze-thaw weathering process. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 140: 104642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2021.104642
Gutenberg B, Richter CF (1944) Frequency of earthquakes in California. Bull Seismol Soc Am 34: 185–188. https://doi.org/10.1038/156371a0
Hall K (1986) Rock moisture-content in the field and the laboratory and its relationship to mechanical-weathering studies. Earth Surf Proc Land 11(2): 131–142. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.3290110204
Huang SB, Lu ZX, Ye ZY, et al. (2020) An elastoplastic model of frost deformation for the porous rock under freeze-thaw. Eng Geol 278: 105820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105820.
Jamshidi A, Nikudel MR, Khamehchiyan M (2013) Predicting the long-term durability of building stones against freeze-thaw using a decay function model. Cold Reg Sci Technol 92: 29–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2013.03.007
Jamshidi A. Nikudel MR, Khamehchiyan M (2016) Evaluation of the durability of Gerdoee travertine after freeze-thaw cycles in fresh water and sodium sulfate solution by decay function models. Eng Geol 202: 36–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.01.004
Jia HL, **ang W, Tan L, et al. (2016) Theoretical analysis and experimental verifications of frost damage mechanism of sandstone. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 35(5): 879–895. https://doi.org/10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2015.1300 (in Chinese).
Jumassultan A, Sagidullina N, Kim J, et al. (2021) Performance of cement-stabilized sand subjected to freeze-thaw cycles. Geomech Eng 25(1): 41–48. https://doi.org/10.12989/gae.2021.25.1.000
Kou MM, Liu XR, Tang SD, et al. (2019) 3-D X-ray computed tomography on failure characteristics of rock-like materials under coupled hydro-mechanical loading. Theor Appl Fract Mec 104: 102396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tafmec.2019.102396
Lai JX, Qiu JL, Fan HB, et al. (2016) Freeze-proof method and test verification of a cold region tunnel employing electric heat tracing. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 60: 56–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2016.08.002
Li ZZ, Yang ZY, Fan JY, et al. (2022) Fatigue mechanical properties of salt rocks under high stress plateaus: the interaction between creep and fatigue. Rock Mech Rock Eng 55(11): 6627–6642. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-022-02983-9
Liu B, Ma YJ, Zhang G, et al. (2018) Acoustic emission investigation of hydraulic and mechanical characteristics of muddy sandstone experienced one freeze-thaw cycle. Cold Reg Sci Technol 151: 335–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2018.03.029
Liu HY, Yuan XP, **e TC (2019) A damage model for frost heaving pressure in circular rock tunnel under freezing-thawing cycles. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 83: 401–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2018.10.012
Luo XD, Nan J, Fan XY, et al. (2015) Effects of freeze-thaw on the determination and application of parameters of slope rock mass in cold regions. Cold Reg Sci Technol 110: 32–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2014.11.002
Meng FZ, Zhou H, Wang ZQ, et al. (2017) Influences of shear history and infilling on the mechanical characteristics and acoustic emissions of joints. Rock Mech Rock Eng 50(8): 2039–2057. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-017-1207-1
Miao ST, Pan PZ, Zhao XG, et al. (2020) Experimental study on damage and fracture characteristics of Beishan granite subjected to high-temperature treatment with DIC and AE techniques. Rock Mech Rock Eng 54: 721–743. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02271-4
Mimouni T, Dupray F, Laloui L (2014) Estimating the geothermal potential of heat exchanger anchors on a cut-and-cover tunnel. Geothermics 51: 380–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2014.02.007
Mousavi SZS, Tavakoli H, Moarefvand P, et al. (2019) Assessing the effect of freezing-thawing cycles on the results of the triaxial compressive strength test for calc-schist rock. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 123: 104090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2019.104090
Mu JQ, Pei XJ, Huang RQ, et al. Degradation characteristics of shear strength of joints in three rock types due to cyclic freezing and thawing. Cold Reg Sci Technol 138: 91–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2017.03.011
Ni X, Shen X, Zhu Z (2020) Mechanical and Acoustic Emission Characteristics of Sandstone through Triaxial Unloading Test after Cyclic Freezing-Thawing Treatment. Adv Civ Eng 2020(4): 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/7150536
Niu Y, Zhou XP, Zhou LC (2020) Fracture damage prediction in fissured red sandstone under uniaxial compression: acoustic emission b — value analysis. Fatigue Fract Eng M 43(1): 175–190. https://doi.org/10.1111/ffe.13113
Park J, Hyun CU, Park HD (2014) Changes in microstructure and physical properties of rocks caused by artificial freeze-thaw action. Bull Eng Geol Environ 74: 555–565. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-014-0630-8
Shen YJ, Yang GS, Rong TL, et al. (2016) Proposed scheme for freeze-thaw cycle tests on rock. Chinese J Geotech Eng 38(10): 1775–1782. https://doi.org/10.11779/CJGE201610005 (In Chinese)
Song ZY, Wang Y, Konietzky H, et al. (2021) Mechanical behavior of marble exposed to freeze-thaw-fatigue loading. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 138: 104648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2021.104648
Sun WB, Du HQ, Zhou F, et al. (2019) Experimental study of crack propagation of rock-like specimens containing conjugate fractures. Geomech Eng 17(4): 323–331. https://doi.org/10.12989/gae.2019.17.4.323
Takarli M, Prince W, Siddique R (2008) Damage in granite under heating/cooling cycles and water freeze-thaw condition. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 45 (7): 1164–1175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2008.01.002
Tan XJ, Chen WZ, Yang JP, et al. (2011) Laboratory investigations on the mechanical properties degradation of granite under freeze-thaw cycles. Cold Reg Sci Technol 68 (3): 130–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2011.05.007
Wang HX, Zhang B, Wang L, et al. (2019) Experimental investigation on the long-term interactions of anhydrite rock, crude oil, and water in a mine-out space for crude-oil storage. Eng Geol 265: 105414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105414
Wang SH, Wang QZ, Qi JL, et al. (2018) Experimental study on freezing point of saline soft clay after freeze-thaw cycling. Geomech Eng 15(4): 997–1004. https://doi.org/10.12989/gae.2018.15.4.997
Wang SH, Qi JL, Yu F, et al. (2016) A novel modeling of settlement of foundations in permafrost regions. Geomech Eng 10(2): 225–245. https://doi.org/10.12989/gae.2016.10.2.225
Wang Y, Feng WK, Wang HJ, et al. (2020a) Rock bridge fracturing characteristics in granite induced by freeze-thaw and uniaxial deformation revealed by AE monitoring and post-test CT scanning. Cold Reg Sci Technol 177: 103115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2020.103115
Wang Y, Han JQ, Li CH (2020b) Acoustic emission and CT investigation on fracture evolution of granite containing two flaws subjected to freeze-thaw and cyclic uniaxial increasing-amplitude loading conditions. Constr Build Mater 260: 119769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.119769
Weng L, Wu ZJ, Taheri A, et al. (2020) Deterioration of dynamic mechanical properties of granite due to freeze-thaw weathering: considering the effects of moisture conditions. Cold Reg Sci Technol 176: 103092. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2020.103092
Xu J, Wang Z, Ren J, et al. (2018) Mechanism of shear strength deterioration of loess during freeze-thaw cycling. Geomech Eng 14(4): 307–314. https://doi.org/10.12989/gae.2018.14.4.307
Xu P, Wu YM, Wang ZJ, et al. (2020) Distribution laws of freeze-thaw cycles and unsaturated concrete experiments in cold-region tunnels. Cold Reg Sci Technol 172: 102985.1–102985.9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2019.102985
Yang XR, Jiang AN, Li MX (2019) Experimental investigation of the time-dependent behavior of quartz sandstone and quartzite under the combined effects of chemical erosion and freeze-thaw cycles. Cold Reg Sci Technol 161: 51–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2019.03.008
Zhang JZ, Zhou XP (2020) Forecasting catastrophic rupture in brittle rocks using precursory AE time series. J Geophys Res-Sol EA 125(8): e2019JB019276. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JB019276
Zhang SJ, Lai YM, Zhang XF, et al. (2004) Study on the damage propagation of surrounding rock from a cold-region tunnel under freeze-thaw cycle condition. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 19(3): 295–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2003.11.011
Zhu TT, Chen JX, Huang D, et al. (2021) A DEM-based approach for modeling the damage of rock under freeze-thaw cycles. Rock Mech Rock Eng 54(6): 2843–2858. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-021-02465-4
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Project No. 2022CDJKYJH037) and the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2021YFB3901402). These supports are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., **, Xg., Hou, C. et al. Mechanical and acoustic emission characteristics of anhydrite rock under freeze-thaw cycles. J. Mt. Sci. 20, 227–241 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-022-7661-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-022-7661-6