Abstract
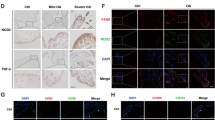
Macrophages and fibroblasts are the main effector cells in synovial tissue in the knee joint. Our previous studies showed that there was synovial macrophage pyroptosis in knee osteoarthritis (KOA) and that inhibiting this pyroptosis could alleviate synovial fibrosis. In the present study, we aimed to elucidate the mechanism by which macrophage pyroptosis affects synovial fibrosis. We established an LPS/ATP-induced model in macrophages that mimicked the inflammatory environment of KOA and induced macrophage pyroptosis. The TGF-β1, SMAD3, and P-SMAD3, and the synovial fibrosis markers (Collagen I, TIMP1, Vimentin, and TGF-β1) were significantly decreased after fibroblasts were cultured with RAGE inhibitors and SMAD3 inhibitors. Moreover, ELISA and immunofluorescence analysis showed that macrophage pyroptosis induced the release of IL-1β, IL-18, and HMGB1 and caused the translocation of HMGB1 from the fibroblast nucleus to the cell membrane, where it could bind with RAGE. Subsequently, in the synovial tissue of KOA model rats, we observed that inhibiting HMGB1, RAGE, and SMAD3 could alleviate the expression of synovial fibrosis markers (Collagen I, TIMP1, Vimentin, and TGF-β1) at both the mRNA and protein levels. Besides, HE and Sirius Red staining were used to observe the transverse diameter of the right knee. In conclusion, macrophage pyroptosis induced IL-1β, IL-18, and HMGB1, which could be caused HMGB1 to translocate from the fibroblast nucleus and bind with RAGE, activating the TGF-β1/SMAD3 signaling pathway and affecting synovial fibrosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All results and data are kept in the section for Departments of Orthopedics, the Affiliated Hospital of the Nan**g University of Chinese Medicine, Nan**g, China. These will be made available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bai LK, Su YZ, Wang XX, Bai B, Zhang CQ, Zhang LY, Zhang GL (2022) Synovial macrophages: past life, current situation, and application in inflammatory arthritis. Front Immunol 13:905356
Cheng L, Wang Y, Wu R, Ding T, Xue H, Gao C, Li X, Wang C (2021) New insights from single-cell sequencing data: synovial fibroblasts and synovial macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol 12:709178
Clavijo-Cornejo D, Martinez-Flores K, Silva-Luna K, Martinez-Nava GA, Fernandez-Torres J, Zamudio-Cuevas Y, Guadalupe SM, Granados-Montiel J, Pineda C, Lopez-Reyes A (2016) The overexpression of NALP3 inflammasome in knee osteoarthritis is associated with synovial membrane prolidase and NADPH oxidase 2. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016:1472567
Friedman SG, Czura CJ, Tracey KJ (2003) The gesture life of high mobility group box 1. Curr Opin Clin Nutr 6:283–287
Gao J, Peng S, Shan X, Deng G, Shen L, Sun J, Jiang C, Yang X, Chang Z, Sun X, Feng F, Kong L, Gu Y, Guo W, Xu Q, Sun Y (2019) Inhibition of AIM2 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis by andrographolide contributes to amelioration of radiation-induced lung inflammation and fibrosis. Cell Death Dis 10:957
Gardella S, Andrei C, Ferrera D, Lotti LV, Torrisi MR, Bianchi ME, Rubartelli A (2002) The nuclear protein HMGB1 is secreted by monocytes via a non-classical, vesicle-mediated secretory pathway. Embo Rep 3:995–1001
Ge X, Arriazu E, Magdaleno F, Antoine DJ, Dela CR, Theise N, Nieto N (2018) High Mobility Group Box-1 drives fibrosis progression signaling via the receptor for advanced glycation end products in mice. Hepatology 68:2380–2404
Guo H, **e M, Zhou C, Zheng M (2019a) The relevance of pyroptosis in the pathogenesis of liver diseases. LIFE SCI 223:69–73
Guo J, Fang Y, Jiang F, Li L, Zhou H, Xu X, Ning W (2019b) Neohesperidin inhibits TGF-beta1/Smad3 signaling and alleviates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 864:172712
Haleagrahara N, Varkkey J, Chakravarthi S (2011) Cardioprotective effects of glycyrrhizic acid against isoproterenol-induced myocardial ischemia in rats. Int J Mol Sci 12:7100–7113
Hashimoto D, Chow A, Noizat C, Teo P, Beasley MB, Leboeuf M, Becker CD, See P, Price J, Lucas D, Greter M, Mortha A, Boyer SW, Forsberg EC, Tanaka M, van Rooijen N, Garcia-Sastre A, Stanley ER, Ginhoux F, Frenette PS, Merad M (2013) Tissue-resident macrophages self-maintain locally throughout adult life with minimal contribution from circulating monocytes. Immunity 38:792–804
He M, Kubo H, Ishizawa K, Hegab AE, Yamamoto Y, Yamamoto H, Yamaya M (2007) The role of the receptor for advanced glycation end-products in lung fibrosis. Am J Physiol-Lung C 293:L1427–L1436
Hu Z, Zhao TV, Huang T, Ohtsuki S, ** K, Goronzy IN, Wu B, Abdel MP, Bettencourt JW, Berry GJ, Goronzy JJ, Weyand CM (2022) The transcription factor RFX5 coordinates antigen-presenting function and resistance to nutrient stress in synovial macrophages. Nat Metab 4:759–774
**nin M, Ihn H, Tamaki K (2006) Characterization of SIS3, a novel specific inhibitor of Smad3, and its effect on transforming growth factor-beta1-induced extracellular matrix expression. Mol Pharmacol 69:597–607
Kim JH, Kim SJ, Lee IS, Lee MS, Uematsu S, Akira S, Oh KI (2009) Bacterial endotoxin induces the release of high mobility group box 1 via the IFN-beta signaling pathway. J Immunol 182:2458–2466
Lan Z, Chen L, Feng J, **e Z, Liu Z, Wang F, Liu P, Yue X, Du L, Zhao Y, Yang P, Luo J, Zhu Z, Hu X, Cao L, Lu P, Sah R, Lavine K, Kim B, Hu H (2021) Mechanosensitive TRPV4 is required for crystal-induced inflammation. Ann Rheum Dis 80:1604–1614
Lei H, Wen Q, Li H, Du S, Wu JJ, Chen J, Huang H, Chen D, Li Y, Zhang S, Zhou J, Deng R, Yang Q (2016) Paeonol inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced HMGB1 translocation from the nucleus to the cytoplasm in RAW264.7 cells. Inflammation 39:1177–1187
Li LF, Lee CS, Liu YY, Chang CH, Lin CW, Chiu LC, Kao KC, Chen NH, Yang CT (2015) Activation of Src-dependent Smad3 signaling mediates the neutrophilic inflammation and oxidative stress in hyperoxia-augmented ventilator-induced lung injury. Resp Res 16:112
Li N, Feng F, Wu K, Zhang H, Zhang W, Wang W (2019) Inhibitory effects of astragaloside IV on silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis via inactivating TGF-beta1/Smad3 signaling. Biomed Pharmacother 119:109387
Liao T, Ding L, Wu P, Zhang L, Li X, Xu B, Zhang H, Ma Z, **ao Y, Wang P (2020) Chrysin attenuates the NLRP3 inflammasome cascade to reduce synovitis and pain in KOA rats. Drug Des Devel Ther 14:3015–3027
Liu Y, Shen W, Chen Q, Cao Q, Di W, Lan R, Chen Z, Bai J, Han Z, Xu W (2020) Inhibition of RAGE by FPS-ZM1 alleviates renal injury in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Eur J Pharmacol 882:173228
Lorenz G, Darisipudi MN, Anders HJ (2014) Canonical and non-canonical effects of the NLRP3 inflammasome in kidney inflammation and fibrosis. Nephrol Dial Transpl 29:41–48
Magna M, Pisetsky DS (2015) The role of cell death in the pathogenesis of SLE: is pyroptosis the missing link? Scand J Immunol 82:218–224
McKenzie BA, Mamik MK, Saito LB, Boghozian R, Monaco MC, Major EO, Lu JQ, Branton WG, Power C (2018) Caspase-1 inhibition prevents glial inflammasome activation and pyroptosis in models of multiple sclerosis. P Natl Acad Sci USA 115:E6065–E6074
Mollica L, De Marchis F, Spitaleri A, Dallacosta C, Pennacchini D, Zamai M, Agresti A, Trisciuoglio L, Musco G, Bianchi ME (2007) Glycyrrhizin binds to high-mobility group box 1 protein and inhibits its cytokine activities. Chem Biol 14:431–441
Remst DF, Blaney DE, van der Kraan PM (2015) Unravelling osteoarthritis-related synovial fibrosis: a step closer to solving joint stiffness. Rheumatology 54:1954–1963
Sanajou D, Ghorbani HA, Argani H, Roshangar L, Rashtchizadeh N, Ahmad S, Ashrafi-Jigheh Z, Bahrambeigi S, Asiaee F, Rashedi J, Aslani S (2019) Reduction of renal tubular injury with a RAGE inhibitor FPS-ZM1, valsartan and their combination in streptozotocin-induced diabetes in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 842:40–48
Shen C, Ma Y, Zeng Z, Yin Q, Hong Y, Hou X, Liu X (2017) RAGE-specific inhibitor FPS-ZM1 attenuates AGEs-induced neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in rat primary microglia. Neurochem Res 42:2902–2911
Shi J, Gao W, Shao F (2017) Pyroptosis: gasdermin-mediated programmed necrotic cell death. Trends Biochem Sci 42:245–254
Simmons DP, Nguyen HN, Gomez-Rivas E, Jeong Y, Jonsson AH, Chen AF, Lange JK, Dyer GS, Blazar P, Earp BE, Coblyn JS, Massarotti EM, Sparks JA, Todd DJ, Rao DA, Kim EY, Brenner MB (2022) SLAMF7 engagement superactivates macrophages in acute and chronic inflammation. Sci Immunol 7:eabf2846
Stewart AG, Thomas B, Koff J (2018) TGF-beta: master regulator of inflammation and fibrosis. Respirology 23:1096–1097
Tan MS, Tan L, Jiang T, Zhu XC, Wang HF, Jia CD, Yu JT (2014) Amyloid-beta induces NLRP1-dependent neuronal pyroptosis in models of Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Death Dis 5:e1382
Tu J, Hong W, Guo Y, Zhang P, Fang Y, Wang X, Chen X, Lu S, Wei W (2019) Ontogeny of synovial macrophages and the roles of synovial macrophages from different origins in arthritis. Front Immunol 10:1146
Wu CP, Murakami M, Hsiao SH, Liu TC, Yeh N, Li YQ, Hung TH, Wu YS, Ambudkar SV (2018) SIS3, a specific inhibitor of Smad3 reverses ABCB1- and ABCG2-mediated multidrug resistance in cancer cell lines. Cancer Lett 433:259–272
**ao Y, Ding L, Yin S, Huang Z, Zhang L, Mei W, Wu P, Wang P, Pan K (2021) Relationship between the pyroptosis of fibroblastlike synoviocytes and HMGB1 secretion in knee osteoarthritis. Mol Med Rep 23(2):97
Xue M, Gong S, Dai J, Chen G, Hu J (2016) The treatment of fibrosis of joint synovium and frozen shoulder by Smad4 gene silencing in rats. PLoS ONE 11:e0158093
Yan Y, Lu A, Dou Y, Zhang Z, Wang XY, Zhai L, Ai LY, Du MZ, Jiang LX, Zhu YJ, Shi YJ, Liu XY, Jiang D, Wang JC (2023) Nanomedicines reprogram synovial macrophages by scavenging nitric oxide and silencing CA9 in progressive osteoarthritis. Adv Sci 10(11):e2207490
Zajd CM, Ziemba AM, Miralles GM, Nguyen T, Feustel PJ, Dunn SM, Gilbert RJ, Lennartz MR (2020) Bone marrow-derived and elicited peritoneal macrophages are not created equal: the questions asked dictate the cell type used. Front Immunol 11:269
Zhang H, Lin C, Zeng C, Wang Z, Wang H, Lu J, Liu X, Shao Y, Zhao C, Pan J, Xu S, Zhang Y, **e D, Cai D, Bai X (2018) Synovial macrophage M1 polarisation exacerbates experimental osteoarthritis partially through R-spondin-2. Ann Rheum Dis 77:1524–1534
Zhang L, Chen X, Cai P, Sun H, Shen S, Guo B, Jiang Q (2022b) Reprogramming mitochondrial metabolism in synovial macrophages of early osteoarthritis by a camouflaged meta-defensome. Adv Mater 34:e2202715
Zhang L, Li M, Li X, Liao T, Ma Z, Zhang L, **ng R, Wang P, Mao J (2022a) Characteristics of sensory innervation in synovium of rats within different knee osteoarthritis models and the correlation between synovial fibrosis and hyperalgesia. J Adv Res 35:141–151
Zhang L, **ng R, Huang Z, Zhang N, Zhang L, Li X, Wang P (2019b) Inhibition of synovial macrophage pyroptosis alleviates synovitis and fibrosis in knee osteoarthritis. Mediat Inflamm 2019:2165918
Zhang L, Zhang L, Huang Z, **ng R, Li X, Yin S, Mao J, Zhang N, Mei W, Ding L, Wang P (2019a) Increased HIF-1alpha in knee osteoarthritis aggravate synovial fibrosis via fibroblast-like synoviocyte pyroptosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019:6326517
Zhang LL, Huang S, Ma XX, Zhang WY, Wang D, ** SY, Zhang YP, Li Y, Li X (2016) Angiotensin(1–7) attenuated Angiotensin II-induced hepatocyte EMT by inhibiting NOX-derived H2O2-activated NLRP3 inflammasome/IL-1beta/Smad circuit. Free Radical Bio Med 97:531–543
Zhao LR, **ng RL, Wang PM, Zhang NS, Yin SJ, Li XC, Zhang L (2018) NLRP1 and NLRP3 inflammasomes mediate LPS/ATP-induced pyroptosis in knee osteoarthritis. Mol Med Rep 17:5463–5469
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to express their gratitude to all staff in the Medical Research Center of the First College of Clinical Medicine, especially all the teachers in the Tang ZhongYing Science and Technology Building, Nan**g University of Chinese Medicine, Nan**g, China.
Funding
The current work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82004391 and 82205143), the third batch of Peak Academic Talents of Jiangsu Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine (y2021rc20), the Jiangsu Provincial Medical Key Discipline (Laboratory) Cultivation Unit (js2252), and the Excellent Young Doctor Program of Jiangsu Hospital of Chinese Medicine (2023QB0122).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Peng Wu, Zhengquan Huang, Taiyang Liao, and Jun Mao conceived the study and drafted the manuscript. Zhenyuan Ma, Songjiang Yin, and Yibao Wei designed and performed the animal experiments. Taiyang Liao and Peng Wu performed cell experiments. All the authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was permitted by the Animal Ethics Committee of Nan**g University of Chinese Medicine (Nan**g, China) on May 2019 (approval number 201905A002). All experiments were conducted in accordance with the National Institutes of Health guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, P., Liao, T., Ma, Z. et al. Macrophage pyroptosis promotes synovial fibrosis through the HMGB1/TGF- β1 axis: an in vivo and in vitro study. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 59, 289–299 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-023-00769-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-023-00769-z