Abstract
Purpose
To suppress hepatic pseudo-anisotropy, which is a specific artifact in diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) of the liver obtained under respiratory triggering, the authors developed a novel acquisition technique for DWI that we termed “diffusion-weighted imaging under split breath-hold acquisition and postprocessing” (DWI-SBAP). We evaluated its feasibility in this study.
Materials and methods
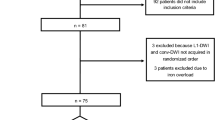
Of 113 patients whose hepatic DWI under respiratory triggering (RT-DWI) showed prominent hepatic pseudo-anisotropy, 35 were included in the study. DWI-SBAP was additionally performed in these patients. Two radiologists visually evaluated the RT-DWI and DWI-SBAP from the viewpoints of the degree of pseudo-anisotropy and the image quality of trace images of both sequences. During evaluation of the image quality of trace images, both pseudo-anisotropy and slice misregistration artifacts were taken into consideration.
Results
The pseudo-anisotropy seen was significantly lower in DWI-SBAP than that in RT-DWI. Regarding visual evaluation of the trace images, the image quality of DWI-SBAP was superior to that of RT-DWI, although misregistration artifacts were observed in DWI-SBAP trace images of two patients.
Conclusion
DWI-SBAP is a feasible technique for obtaining fine abdominal DWI and is effective in suppressing hepatic pseudo-anisotropy. To use this sequence in the clinical scenario, we believe it is necessary to develop a method of generating apparent diffusion coefficient maps and simultaneous use of slice tracking techniques.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rovira A, Rovira-Gols A, Pedraza S, Grive E, Molina C, Alvarez-Sobin J. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in the acute phase of transient ischemic attacks. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2002;23:77–83.
Kuroki Y, Nasu K, Kuroki K, Murakami K, Hayashi T, Sekiguchi R, et al. Diffusion weighted imaging of breast cancer with the apparent diffusion coefficient value. Magn Reson Med Sci 2004;3:79–85.
Shimofusa R, Fujimoto H, Akamata H, Motoori K, Yamamoto S, Ueda T, et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging of prostate cancer. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2005;29:149–153.
Nasu K, Kuroki Y, Kuroki S, Murakami K, Nawano S, Moriyama N. Diffusion-weighted single shot echo planar imaging of colorectal cancer using a sensitivity-encoding technique. Jpn J Clin Oncol 2004;34:620–626.
Nasu K, Kuroki Y, Nawano S, Kuroki S, Tsukamoto T, Yamamoto S, et al. Hepatic metastases: diffusion-weighted sensitivity-encoding versus SPIO-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 2006;239:122–130.
Kim T, Murakami T, Takahashi S, Hori M, Tsuda K, Nakamura H. Diffusion-weighted single-shot echoplanar MR imaging for liver disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1999;173:393–398.
Nasu K, Kuroki Y, Sekiguchi R, Nawano S. The effect of simultaneous use of respiratory triggering in diffusion weighted imaging of the liver. Magn Reson Med Sci 2006;5:129–136.
Nasu K, Kuroki Y, Sekiguchi R, Kazama T, Nakajima H. Measurement of the apparent diffusion coefficient in the liver: is it a reliable index for hepatic disease diagnosis? Radiat Med 2006;24:438–444.
Murz P, Flacke S, Traber F, van den Brink JS, Gieseke J, Schild HH. Abdomen: diffusion-weighted MR imaging with pulse-triggered single-shot sequence. Radiology 2002;224:258–264.
Bernstein MA, King KF, Zhou XJ. Advanced pulse sequence technique. In: Handbook of pulse sequence. San Diego: Elsevier; 2004. p. 802–896.
Bottomley PA, Hardy CJ, Argersinger RE, Allen-Moore G. A review article of 1H nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation in pathology: are T1 and T2 diagnostic? Med Phys 1987;14:1–37.
Farraher SW, Jara H, Chang KJ, Ozonoff A, Soto JA. Differentiation of hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatic metastasis from cysts and hemangiomas with calculated T2 relaxation times and the T1/T2 relaxation times ratio. J Magn Reson Imaging 2006;24:1333–1341.
Nasu K, Kuroki Y, Kazama T, Nawano S. Clinical features of diffusion weighted-imaging of the liver, rectum and breast: why should SENSE-DWI be indicated in these organs? Jpn J Magn Reson Med 2005;25:229–246.
Nasu K, Kuroki Y, Fujii H, Minami M. Hepatic pseudo-anisotropy: a specific artifact in hepatic diffusion-weighted imaging obtained with respiratory triggering. MAGMA 2007;20:205–211.
Le Bihan D, Poupon C, Amadon A, Lethimonnier F. Artifacts and pitfalls in diffusion DWI. J Magn Reson Imaging 2006;24:467–488.
Rohlifing T, Maurer CR Jr, O’Dell WG, Zhong J. Modeling liver motion and deformation during the respiratory cycle using intensity-based nonrigid registration of gated MR images. Med Phys 2004;31:427–432.
Shimizu S, Shirato H, Xo B, Kagei K, Nishioka T, Hashimoto S, et al. Three dimensional movement of a liver detected by high-speed magnetic resonance imaging. Radiother Oncol 1999;50:367–370.
Miller KL, Pauly JM. Nonlinear phase correction for navigated diffusion imaging. Magn Reson Med 2003;50:343–353.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Nasu, K., Kuroki, Y. & Minami, M. Feasibility of diffusion-weighted imaging under split breath-hold acquisition and postprocessing (DWI-SBAP): an attempt to suppress hepatic pseudo-anisotropy. Jap J Radiol 27, 78–85 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-008-0303-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-008-0303-2