Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to evaluate the technical success, complications, and effectiveness of re-radiofrequency (re-RF) ablation for recurrent lung tumors previously treated with RF ablation.
Materials and methods
Reenlargement at the site of ablation seen on follow-up computed tomography (CT) is defined as local progression. CT-guided re-RF ablation was performed during 11 treatment sessions (mean tumor size 2.6 cm diameter) in 10 patients. The treated lesions consisted of five recurrences of primary lung cancer and six metastatic lung tumors from the esophagus (n = 2), bladder (n = 2), kidney (n = 1), and colon (n = 1).
Results
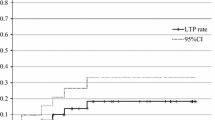
At 3 of the 11 treatment sessions there were no relapses; at 8 of the 11 sessions local progression was seen at a median of 7 months (range 3–17 months). The local progression rate was significantly higher for tumors >2.5 cm (P < 0.05). Minor complications included pneumothorax not requiring drainage (n = 3), subcutaneous emphysema (n = 1), and self-limited hemoptysis (n = 2).
Conclusion
Re-RF ablation for lung tumors was feasible without any major complications. Although our study comprised only a few cases with a short follow-up period, patients with re-RF ablation were at higher risk of local progression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dupuy DE, Zagoria RJ, Akerley W, Mayo-Smith WW, Kavanagh PV, Safran H. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of malignancies in the lung. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2000;174:57–59.
Rose SC, Thistlethwaite PA, Sewell PE, Vance RB. Lung cancer and radiofrequency ablation. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2006;17:927–951.
Matsuoka T, Okuma T. CT-guided radiofrequency ablation for lung cancer. Int J Clin Oncol 2007;12:71–78.
Okuma T, Matsuoka T, Yamamoto A, Oyama Y, Inoue K, Nakamura K, et al. Factors contributing to cavitation after CT-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for lung tumors. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2007;18:399–404.
Yamakado K, Hase S, Matsuoka T, Tanigawa N, Nakatsuka A, Takaki H, et al. Radiofrequency ablation for the treatment unresectable lung metastases in patients with colorectal cancer: a multicenter study in Japan. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2007;18:393–398.
Goldberg SN, Grassi CJ, Cardell JF, Charboneau JW, Dodd GD, Dupuy DE, et al. Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2006;16:765–778.
De Baere T, Palussiere J, Auperin A, Hakime A, Abdel-Rehim M, Kind M, et al. Midterm local efficacy and survival after radiofrequency ablation of lung tumors with minimum follow-up of 1 year: prospective evaluation. Radiology 2006;240:587–596.
Simon CJ, Dupuy DE, DiPetrillo TA, Safran HP, Grieco CA, Ng T, et al. Pulmonary radiofrequency ablation: long-term safety and efficacy in 153 patients. Radiology 2007;243:268–275.
Hiraki T, Sakurai J, Tsuda T, Gobara H, Sano Y, Mukai T, et al. Risk factors for local progression after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of lung tumors: evaluation based on a preliminary review of 342 tumors. Cancer 2006;107:2873–2880.
Okuma T, Matsuoka T, Yamamoto A, Oyama Y, Toyoshima M, Nakamura K, et al. Frequency and risk factors of various complications after computed tomography-guided radiofrequency ablation of lung tumors. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 2008;1:122–130.
Iguchi T, Hiraki T, Gobara H, Mimura H, Fujiwara H, Tajiri N, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of lung tumors close to the heart or aorta: evaluation of safety and effectiveness. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2007;18:733–740.
Akeboshi M, Yamakado K, Nakatsuka A, Hataji O, Taguchi O, Takao M, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of lung neoplasms: initial therapeutic response. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2004;15:463–470.
Herrera LJ, Fernando HC, Perry Y, Gooding WE, Buenaventura PO, Christie NA, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of pulmonary malignant tumors in nonsurgical candidates. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2003;125:929–937.
Okuma T, Okamura T, Matsuoka T, Yamamoto A, Oyama Y, Toyoshima M, et al. Fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography for assessment of patients with unresectable recurrent or metastatic lung cancers after CT-guided radiofrequency ablation: preliminary results. Ann Nucl Med 2006;20:115–121.
Yasui K, Kanazawa S, Sano Y, Kagawa S, Miura H, Dendo S, et al. Thoracic tumors treated with CT-guided radiofrequency ablation: initial experience. Radiology 2004;231:850–857.
Grieco CA, Simon CJ, Mayo-Smith WW, DiPetrillo TA, Ready NE, Dupuy DE. Percutaneous image-guided thermal ablation and radiation therapy: outcomes of combined treatment for 41 patients with inoperable stage I/II non-small-cell lung cancer. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2006;17:1117–1124.
Hiraki T, Gobara H, Takemoto M, Mimura H, Mukai T, Himei K, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation combined with previous bronchial arterial chemoembolization and followed by radiation therapy for pulmonary metastasis from hepatocellular carcinoma. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2006;17:1189–1193.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Okuma, T., Matsuoka, T., Yamamoto, A. et al. Computed tomography-guided re-radiofrequency ablation for unresectable lung tumor with local progression previously treated with the same procedure. Radiat Med 26, 519–525 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-008-0267-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-008-0267-2