Abstract
Objective
Apatinib is a novel inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2. The goal of this study was to evaluate overall survival (OS) after a combination of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and apatinib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and to identify the factors affecting patient survival.
Methods
Fifty-one patients with advanced HCC who received TACE in combination with apatinib in our hospital from June 2015 to May 2017 were enrolled. The OS and progression-free survival (PFS) were calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method. The log-rank test and Cox regression model were used to determine the factors affecting OS.
Results
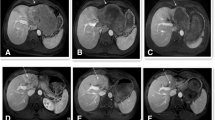
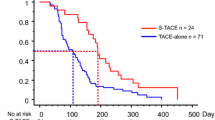
The median OS and PFS of the patients were 15 months and 10 months, respectively. The 1-, 2-, and 3-year survival rates were 64.7%, 23.5%, and 1.8%, respectively. Univariate survival analysis showed that patients with Child-Pugh A (P=0.006), reduction rate of proper hepatic artery (P=0.016), hand-foot syndrome (P=0.005), secondary hypertension (P=0.050), and without ascites (P=0.010) had a better OS. Multivariate analysis showed that hand-foot syndrome (P=0.014), secondary hypertension (P=0.017), and reduction rate of proper hepatic artery (P=0.025) were independent predictors of better OS.
Conclusion
TACE combined with apatinib is a promising treatment for advanced HCC. Hand-foot syndrome, secondary hypertension, and the reduction rate of proper hepatic artery were associated with a better OS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet, 2018,391(10127):1301–1314
Park JW, Chen M, Colombo M, et al. Global patterns of hepatocellular carcinoma management from diagnosis to death: the BRIDGE Study. Liver Int, 2015,35(9):2155, 2166
Bargellini I, Florio F, Golfieri R, et al. Trends in utilization of transarterial treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma: results of a survey by the Italian Society of Interventional Radiology. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol, 2017,37(4):438–444
Gaba, RC, Lokken RP, Hickey RM, et al. Quality Improvement Guidelines for Transarterial Chemoembolization and Embolization of Hepatic Malignancy. J Vasc Interv Radiol, 2017,28(9):1210–1223.e3
Liang B, Zheng CS, Feng GS, et al. Correlation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha with angiogenesis in liver tumors after transcatheter arterial embolization in an animal model. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol, 2010,33(4):806–812
Park JW, Kim YJ, Kim, DY, et al. Sorafenib with or without concurrent transarterial chemoembolization in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: The phase III STAH trial. J Hepatol, 2019,70(4):684–691
Ding J, Chen X, Gao Z, et al. Metabolism and pharmacokinetics of novel selective vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 inhibitor apatinib in humans. Drug Metab Dispos, 2013,41(6):1195–1210
Liang Q, Kong L, Du Y, et al. Antitumorigenic and antiangiogenic efficacy of apatinib in liver cancer evaluated by multimodality molecular imaging. Exp Mol Med, 2019,51(76):1–11
Yang C, Qin S. Apatinib targets both tumor and endothelial cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Med, 2018,7(9):4570–4583
Yang Z, Chen G, Cui Y, et al. The safety and efficacy of TACE combined with apatinib on patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study. Cancer Biol Ther, 2019,20(3):321–327
Lu W, ** XL, Yang C, et al. Comparison of efficacy between TACE combined with apatinib and TACE alone in the treatment of intermediate and advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A single-center randomized controlled trial. Cancer Biol Ther, 2017,18(6):433–438
Chen S, Yu W, Zhang K. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of transarterial chemoembolization with and without apatinib for the treatment of BCLC stage C hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer, 2018,18(1):1131
Zhu Y, Feng B, Mei L, et al. Clinical efficacy of TACE combined with Apatinib in the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J BUON, 2019,24(2):608–614
Fan W, Yuan G, Fan H, et al. Apatinib combined with transarterial chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein tumor thrombus: a multicenter retrospective study. Clin Ther, 2019,41(8):1463–1476
Kan X, Liang B, Zhou G, et al. Transarterial Chemoembolization Combined with Apatinib for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis. Front Oncol, 2020,7(10):970
European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol, 2018,69(1):182–236
Zhou J, Sun HC, Wang Z, et al. Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Primary Liver Cancer in China (2017 Edition). Liver Cancer, 2018,7(3):235–260
Scott LJ. Apatinib: A Review in Advanced Gastric Cancer and Other Advance Cancers. Drugs, 2018,78:747–758
Qiu L, Shukui Q, Shanzhi G. Apatinib as second-line therapy in Chinese patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomized, placebo-controlled, doubleblind, phase 3 study. 2020, ASCO Annual Meeting Symposium: 303249
Kok, VC, Chen Y, Chen Y, et al. Sorafenib with Transarterial Chemoembolization Achieves Improved Survival vs. Sorafenib Alone in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. Cancers (Basel), 2019,11(7):985
Chien SC, Chen CY, Cheng PN, et al. Combined Transarterial Embolization/Chemoembolization-Based Locoregional Treatment with Sorafenib Prolongs the Survival in Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Preserved Liver Function: A Propensity Score Matching Study. Liver Cancer, 2019,8(3):186–202
Sato Y, Nishiofuku H, Yasumoto T, et al. Multicenter Phase II Clinical Trial of Sorafenib Combined with Transarterial Chemoembolization for Advanced Stage Hepatocellular Carcinomas (Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Stage C): STAB Study. J Vasc Interv Radiol, 2018,29(8):1061–1067
Liu J, **e S, Duan X, et al. Assessment of efficacy and safety of the transcatheter arterial chemoembolization with or without apatinib in the treatment of large hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol, 2020,85(1):69–76
Zhou C, Yao Q, Zhang H, et al. Combining transcatheter arterial embolization with iodized oil containing Apatinib inhibits HCC growth and metastasis. Sci Rep, 2020,10(1):2964
Ni JY, Kong J, Sun HL, et al. Prognostic Factors for Survival After Transarterial Chemoembolization Combined with Sorafenib in the Treatment of BCLC Stage B and C Hepatocellular Carcinomas. Acad Radiol, 2018,25(4):423–429
Liu C, **ng W, Si T, et al. Efficacy and safety of apatinib combined with transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal venous tumor thrombus: a retrospective study. Oncotarget, 2017,8(59):100734–100735
Liu J, Xu J, Zhang W, et al. Safety and Efficacy of Drug-Eluting Bead Transarterial Chemoembolization Combined with Apatinib in Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Acad. Radiol, 2019,27(5): 704–709
Liao Z, Li F, Zhang C, et al. Phase II trial of VEGFR2 inhibitor apatinib for metastatic sarcoma: focus on efficacy and safety. Exp Mol Med, 2019,51(3):1–11
Pawlik TM, Reyes DK, Cosgrove D, et al. Phase II trial of sorafenib combined with concurrent transarterial chemoembolization with drug-eluting beads for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol, 2011,29(30):3960–3967
Pandey AK, Singhi EK, Arroyo JP, et al. Mechanisms of VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) Inhibitor-Associated Hypertension and Vascular Disease. Hypertension, 2018,71(2):e1–e8
Siegel AB, Cohen EI, Ocean A, et al. Phase II trial evaluating the clinical and biologic effects of bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol, 2008,26(18):2992–2998
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81771950, No. 81471765 and No. 81601578).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Zy., Kan, Xf., Zhang, Lj. et al. Transarterial Chemoembolization Combined with Apatinib for Treatment of Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Analysis of Survival and Prognostic Factors. CURR MED SCI 42, 1015–1021 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-022-2620-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-022-2620-6