Abstract
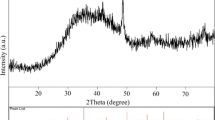
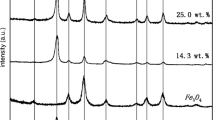
A composite material (Fe3O4/Coke) using coke supported Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles was successfully prepared via an in-situ chemical oxidation precipitation method and characterized by SEM, XRD, Raman, and FTIR. The results showed that the Fe3O4 nanoparticles existed steadily on the surface of coke, with better dispersing and smaller particle size. The catalytic ability of Fe3O4/Coke were investigatied by degrading p-nitrophenol (P-NP). The results showed that the apparent rate constant for the P-NP at 1.0 g·L−1 catalyst, 30 mmol·L−1 H2O2, pH=3.0, 30 °C and the best ratio of Coke/Fe3O4 0.6, was evaluated to be 0.027 min–1, the removal rate of CODCr was 75.47%, and the dissolubility of Fe was 2.42 mg·L–1. Compared with pure Fe3O4, the catalytic ability of Fe3O4/Coke in the presence of H2O2 was greatly enhanced. And Fe3O4/Coke was a green and environmental catalyst with high catalytic activity, showing a good chemical stability and reusability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Neuberger T, Schöpf B, Hofmann H, et al. Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications: Possibilities and Limitations of A New Drug Delivery System[J]. J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2005, 293: 483–496
Portet D, Rump E, Lejeune JJ, et al. Nonpolymeric Coatings of Iron Oxide Colloids for Biological Use as Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agents[J]. J. Colloid Inter. Sci., 2001, 238: 37–42
Ito A, Shinkai M, Honda H, et al. Augmentation of MHC Class I Antigen Presentation Via Heat Shock Protein Expression by Hyperthermia[J]. J. Biosci. Bioeng., 2005, 50: 515–522
Zhang Y, Chen YS, Westerhoff P, et al. Stability of Commercial Metal Oxide Nanoparticles in Water[J]. Water Res., 2008, 42(8-9): 2204–2212
Pickrodt RV, Fuentesa MC, Carolina P, et al. Influence of Stirring Velocity on the Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles (Fe3O4) by the Co-precipitation Method[J]. J. Alloy. Compd., 2009, 488: 227–231
Bruce IJ, Taylor J, Todd M, et al. Synthesis, Characterisation and Application of Silica-magnetite Nanocomposites[J]. J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2004, 284(1): 145–160
Asuha S, Suyala B, Siqintana X, et al. Direct Synthesis of Fe3O4 Nanopowder by Thermal Decomposition of Fe-urea Complex and its Properties[J]. J. Alloy. Compd., 2011, 509(6): 2870–2873
Hasanpour A, Niyaifar M, Asan M, et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Fe3O4 and ZnO Nanocomposites by the Sol-gel Method[J]. J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2013, 334: 43–44
Zubir NA, Yacou C, Motuzas J, et al. Structural and Functional Investigation of Graphene Oxide-Fe3O4 Nanocomposites for the Heterogeneous Fenton-like Reaction[J]. Sci. Rep-UK., 2014, 4: 4594
Shahamat YD, Farzadkia M, Nasseri S, et al. Magnetic Heterogeneous Catalytic Ozonation: A New Removal Method for Phenol in Industrial Wastewater[J]. J. Environ. Healt., 2014, 12: 50–61
Li SZ, Gong YB, Yang YC, et al. Bisphenol A from Water and their Regeneration[J]. Chem. Eng. J., 2015, 260: 231–239
Wauters S, Marin GB. Computer Generation of a Network of Elementary Steps for Coke Formation during the Thermal Cracking of Hydrocarbons[J]. Chem. Eng. J., 2001, 82(1-3): 267–279
Catak S, Hemelsoet IK, Hermosilla L, et al. Competitive Reactions of Organophosphorus Radicals on Coke Surfaces[J]. Chem-Eur. J., 2011, 17(43): 12027–12036
Wan D, Li WB, Wang GH, et al. Adsorption and Heterogeneous Degradation of Rhodamine B on the Surface of Magnetic Bentonite Material[J]. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2015, 349: 988–996
Kraines S, Akatsuka T, Crissman LW, et al. Pollution and Cost in the Coke-Making Supply Chain in Shanxi Province, China[J]. J. Ind. Ecol., 2002, 6(3-4): 161–184
Yang SJ, He HP, Wu DQ, et al. Decolorization of Methylene Blue by Heterogeneous Fenton Reaction Using Fe3-xTixO4 (0 x 0. 78) at Neutral pH Values[J]. Appl. Catal. B-Environ., 2009, 89(3-4): 527–535
Wang NN, Zhen T, Jiang JP, et al. Pilot-scale Treatment of p-Nitrophenol Wastewater by Microwave-enhanced Fenton Oxidation Process: Effects of System Parameters and Kinetics Study[J]. Chem. Eng. J., 2014, 239: 351–359
Feng JY, Hu XJ, Yue PL. Discoloration and Mineralization of Orange II by Using a Bentonite Clay-based Fe Nanocomposite Film as a Heterogeneous Photo-Fenton Catalyst[J]. Water Res., 2005, 39(1): 89–96
Paipa C, Mateo M, Godoy I, et al. Comparative Study of Alternative Methods for the Simultaneous Determination of Fe3+ and Fe2+ in Leaching Solutions and in Acid Mine Drainages[J]. Miner. Eng., 2005, 18(11): 1116–1119
Zhang Z, Kong J. Novel Magnetic Fe3O4@C Nanoparticles as Adsorbents for Removal of Organic dyes from Aqueous Solution[J]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2011, 193: 325–329
Ilgeun Oh, Myeong** Kim, Jooheon Kim. Deposition of Fe3O4 on Oxidized Activated Carbon by Hydrazine Reducing Method for High Performance Supercapacitor[J]. Microelectron. Reliab., 2014, 55: 114–122
Hu XB, Liu BZ, Deng YH, et al. Adsorption and Heterogeneous Fenton Degradation of 17a-methyltestosterone on Nano Fe3O4/MWCNTs in Aqueous Solution[J]. Appl. Catal. B-Environ., 2011, 107(3/4): 274–283
Li Y, Leng T, Lin H, et al. Preparation of Fe3O4@ZrO2 Core-shell Microspheres as Affinity Probes for Selective Enrichment and Direct Determination of Phosphopeptides Using Matrix-assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Mass Spectrometry[J]. J. Proteome Res., 2007, 6: 4498–4510
Zhang S, Niu H, Hu Z, et al. Preparation of Carbon Coated Fe3O4 Nanoparticles and Their Application for Solid-phase Extraction of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from Environmental Water Samples[J]. J. Chromatogr. A, 2010, 1217: 4757–4764
Eklund PC, Holden JM, Jishi RA. Vibrational Modes of Carbon Nanotubes; Spectroscopy and Theory[J]. Carbon, 1995, 33: 959–972
Brown TL, LeMay HE, Bursten BE, et al. Chemistry-The Central Science[M]. 11th ed., Pearson Education, London, 2009.
Oliveira LCA, Riosa RVRA, Fabris JD, et al. Clay-iron Oxide Magnetic Compositesfor the Adsorption of Contaminants in Water[J]. Appl. Clay Sci., 2003, 22(4): 169–177
Xu LL, Wang J, Zhang XH. Development of a Novel Integrated Membrane System Incorporated with an Activated Coke Adsorption unit for Advanced Coal Gasication Wastewater Treatment[J]. Colloid. Surface. A., 2015, 484: 99–107
Sun SP, Lemley AT. p-Nitrophenol Degradation by a Heterogeneous Fenton-like Reaction on Nano-magnetite: Process Optimization, Kinetics, and Degradation Pathways[J]. J. Mol. Catal. A-Chem., 2011, 349: 71–79
Zhou L, Zhou MH, Hu ZX, et al. Chemically Modified Graphite Felt as an Efficient Cathode in Electro-Fenton for p-nitrophenol Degradation[J]. Electrochimica Acta., 2014, 140: 376–383
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the Specialized Research Fund for Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (No. 20114219110002), the Educational Department of Hubei Province of China (No. D20131107) and the Natural Science Fundation of Hubei Provice (No. 2014CFB810)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, L., Li, W., Wang, G. et al. Synthesis and characterization of biomimetic Fe3O4/coke magnetic nanoparticles composite material. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 31, 254–259 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-016-1361-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-016-1361-4