Abstract
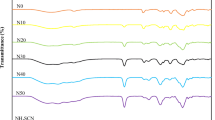
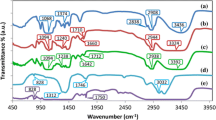
A polymer electrolyte system comprising methylcellulose (MC) as the host polymer and lithium bis(oxalato) borate (LiBOB) as the lithium ion source has been prepared via the solution cast technique. The electrolyte with the highest conductivity of 2.79 μS cm−1 has a composition of 75 wt% MC–25 wt% LiBOB. The mobile ion concentration (n) in this sample was estimated to be 5.70 × 1020 cm−3. A good correlation between ionic conductivity, dielectric constant, and free ion concentration has been observed. The ratio of mobile ion number density (n) at a particular temperature to the concentration n 0 of free ions at T = ∞ (n/n 0) and the power law exponents (s) exhibit opposite trends when varied with salt concentration.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramanarayanan TA, Singhal SC, Wachsman ED (2001) High temperature ion conducting ceramics. The Electrochemical Society Interface. Summer 1:22–27
Bebelis S, Bouzek K, Cornell A, Ferreira MGS, Kelsall GH, Lapicque F, Ponce de Leon C, Rodrigo MA, Wash FC (2013) Highlights during the development of electrochemical engineering. IChemE Journal 10:1998–2020
Yang J, Ghobadian S, Goodrich PJ, Montazami R, Hashemi N (2013) Miniaturized biological and electrochemical fuel cells: challenges and applications. Phys Chem Chem Phys 15:14147
De Souza FL, Leite ER (2010) Hybrid polymer electrolytes for electrochemical devices. In: Santos D, Sequeira S (eds) Polymer electrolytes: fundamentals and applications. Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge, pp 583–602
Zapata VH, Castro WA, Vargas RA (2012) Electrical conductivity relaxation in PVOH+LiH2PO4+Al2O3 polymer composites. Ionics 19:83–89
Winter M, Brodd RJ (2004) What are batteries, fuel cells and supercapacitors? Chem Rev 104:4245–4269
Ahmad MM (2015) Lithium ionic conduction and relaxation dynamics of spark plasma sintered Li5La3Ta2O12 garnet nanoceramics. Nano Res Lett 10:58
Jonscher AK (1977) The ‘universal’ dielectric response. Nature 267:673–679
Almond DP, West AR (1983) Mobile ion concentrations in solid electrolytes from an analysis of AC conductivity. Solid State Ionics 9–10:277–282
Almond DP, West AR (1983) Impedance and modulus spectroscopy of “real” dispersive conductors. Solid State Ionics 11:57–64
Almond DP, Duncan GK, West AR (1983) The determination of hop** rates and carrier concentrations in ionic conductors by a new analysis of ac conductivity. Solid State Ionics 8:159–163
Almond DP, Hunter CC, West AR (1984) The extraction of ionic conductivities and hop** rates from a.c. conductivity data. J Mater Sci 19:3236–3248
Nowick AS, Lim BS, Vaysleyb AV (1994) Nature of the ac conductivity of ionically conducting crystals and glasses. J Non-Cryst Solids 1243:172–174
Lunkenheimer P, Loidl A (2003) Response of disorder matter to electromagnetic fields. Phys Rev Lett 91:207601
Zhbankov RG (1966) New types of cellulose derivatives. In: Infrared spectra of cellulose and its derivatives. Consultants Bureau, New York, pp 131–165. ISBN 978-1-4899-2732-3
Thakur VK, Thakur MK (2015) Handbook of sustainable polymers: processing and applications. CRC, Boca Raton. ISBN 9789814613538
Ye D, Farriol (2005) A facile method to prepare methylcellulose from annual plants and wood using iodomethane. E-Polymers 41:1–13
Nasatto PL, Pignon F, Silveira JLM, Duarte MER, Noseda MD, Rinaudo M (2015) Methylcellulose, a cellulose derivative with original physical properties and extended applications. Polymers 7:777–803
Shokri J, Adibkia K (2013) Application of cellulose and cellulose derivatives in pharmaceutical industries. Cellulose—medical, pharmaceutical and electronic applications. Intech 3:47–66
Pinotti A, Garci MA, Martino MN, Zaritzky NE (2007) Study on microstructure and physical properties of composite films based on chitosan and methylcellulose. Food Hydrocoll 21:66–72
Nik Aziz NA, Idris NK, Isa MIN (2010) Solid polymer electrolytes based on methylcellulose: FTIR and ionic conductivity studies. Int J Polym Anal Charact 15:319–327
Chiappone A, Gerbaldi C, Roppolo I, Garino N, Bongiovanni R (2015) Degradable photopolymerized thiol-based solid polymer electrolytes towards greener Li-ion batteries. Polymer 75:64–72
Wu X-L, **n S, Seo H-H, Kim J, Guo Y-G, Lee J-S (2011) Enhanced Li+ conductivity in PEO–LiBOB polymer electrolytes by using succinonitrile as a plasticizer. Solid State Ionics 186:1–6
Tominaga Y, Yamazaki K, Nanthana V (2015) Effect of anions on lithium ion conduction in poly(ethylene carbonate)-based polymer electrolytes. J Electrochem Soc 162:A3133–A3136
Ye L, Feng Z (2010) . Polymer electrolytes as solid solvents and their applications, chapter 14. In: Santos D, Sequeira S (eds) Polymer electrolytes: fundamentals and applications. Bei**g Institute of Technology, China, pp 550–581
Holomb R, Xu W, Markusson H, Johansson P, Jacobsson P (2006) Vibrational spectroscopy and ab initio studies of lithium bis(oxalato) borate (LiBOB) in different solvents. J Phys Chem A 110:11467–11472
Zhang SS (2006) An unique lithium salt for the improved electrolyte of Li-ion battery. Electrochem Commun 8:1423–1428
Yang L-J, Yang X-Q, Huang K-M, G-Zhu J, Shang H (2009) Dielectric properties of binary solvent mixtures of dimethyl sulfoxide with water. Int J Mol Sci 10(3):1261–1270
Garusinghe GSP, Bessey SM, Boyd C, Aghamoosa M, Frederick BG, Bruce MRM, Bruce AE (2015) Identification of dimethyl sulfide in dimethyl sulfoxide and implications for metal–thiolate disulfide exchange reactions. RSC Adv 5:40603–40606
Arof AK, Amiruddin S, Yusof SZ, Noor IM (2013) A method based on impedance spectroscopy to determine transport properties of polymer electrolytes. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:1856–1867
Lee TK, Afiqah S, Ahmad A, Dahlan HM, Rahman MYA (2012) Temperature dependence of the conductivity of plasticized poly(vinyl chloride)–low molecular weight liquid 50% epoxidized natural rubber solid polymer electrolyte. J Solid State Electrochem 16:2251–2260
Kumar M, Tiwari T, Srivastava N (2012) Electrical transport behavior of bio-polymer electrolyte system: potato starch + ammonium iodide. Carbohydr Polym 88:54–60
Kumar M, Srivastava N (2014) Investigation of electrical and dielectric properties of NaI doped synthesized systems. J Non-Cryst Solids 389:28–34
Vieira DF, Avellaneda CO, Pawlicka A (2007) Conductivity study of a gelatin-based polymer electrolyte. Electrochim Acta 53:1404–1408
Ravi M, Bhavani S, Pavani Y, Narasimha Rao VVR (2013) Investigation on electrical and dielectric properties of PVP:KCLO4 polymer electrolyte films. Indian J Pure Appl Phys 51:362–366
Shukla N, Thakur AK, Shukla A, Marx DT (2014) Ion conduction mechanism in solid polymer electrolyte: an applicability of Almond–West formalism. Int J Electrochem Sci 9:7644–7659
Funke K (1993) Jump relaxation in solid electrolytes. Prog Solid State Chem 22:111–195
Shukur MF, Ithnin R, Sonsudin F, Yahya R, Ahmad Z, Kadir MFZ (2013) Conduction mechanism and dielectric properties of solid biopolymer electrolyte incorporated with silver nitrate. Adv Mater Res 701:115–119
Tiwari T, Srivastava N, Srivastava PC (2013) Ion dynamics study of potato starch + sodium salts electrolyte system. Int J Electrochem 2013:Article ID 670914, 8 pp
Srivastava N, Kumar M (2014) Ion dynamic behavior in solid polymer electrolyte. Solid State Ionics 262:806–810
Acknowledgments
Financial supports from the University of Malaya (IPPP no. PG112-2013A) and from the Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia (FRGS no. FP053-2014A) are greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yusof, S.Z., Woo, H.J. & Arof, A.K. Ion dynamics in methylcellulose–LiBOB solid polymer electrolytes. Ionics 22, 2113–2121 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1733-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1733-y