Abstract
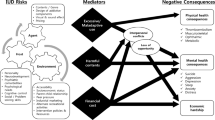
The objective of this study was to examine the risk factor of addictive Internet use from a cumulative risk perspective among rural Chinese adolescents. This was a cross-sectional study. A total of 1489 adolescents from three high schools in Henan Province participated in this study. The results showed that (1) the prevalence of addictive Internet use among rural Chinese adolescents was 11.8%; (2) male, depression, disharmonious family climate, parents’ divorce, poor teacher-student relationship, and poor neighborhood sanitation were risk factors; and (3) the prevalence of addictive Internet use increased from 3.4 to 45.8% as the number of risk factors increased from 0 to 5. Regression analysis indicated that experiencing ≥ 2 risk factors predicted addictive Internet use significantly. And the result of trend analysis with addictive Internet use as the dichotomous dependent variable shows that the increasing trend was statistically significant (p < 0.001). There is a cumulative risk effect of these factors on addictive Internet use. We hope our findings will contribute to identifying high-risk adolescents and multilevel preventions and interventions on addictive Internet use among rural Chinese adolescents, thus promoting their development.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ak, C. S. E., Koruklu, N., & Lmaz, Y. I. (2013). A study on Turkish adolescent’s Internet use: Possible predictors of Internet addiction. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 16(3), 205–209.
Alimoradi, Z., Lin, C., Brostrom, A., Bulow, P. H., Bajalan, Z., Griffiths, M. D., Ohayon, M. M., & Pakpour, A. H. (2019). Internet addiction and sleep problems: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 47, 51–61.
Andresen, E. M., Malmgren, J. A., Carter, W. B., & Patrick, D. L. (1994). Screening for depression in well older adults: Evaluation of a short form of the CES-D. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 10(2), 77–84.
Asyriati, R. (2020). Parent Attachment and Adolescent’s Problematic Internet Use: A Literature Review. In 5th ASEAN Conference on Psychology, Counselling, and Humanities (ACPCH 2019) (pp. 124–128). Atlantis Press.
Atkinson, L., Beitchman, J., Gonzalez, A., Young, A., Wilson, B., Escobar, M., Chisholm, V., Brownlie, E., Khoury, J. E., Ludmer, J., Others. (2015). Cumulative risk, cumulative outcome: A 20-year longitudinal study. PLoS One, 10(6), e127650.
Balhara, Y. P. S., Mahapatra, A., Sharma, P., Bhargava, R., Others. (2018). Problematic internet use among students in South-East Asia: Current state of evidence. Indian journal of public health, 62(3), 197.
Batigun, A. D., & Kilic, N. (2011). The relationships between internet addiction, social support, psychological symptoms and some socio-demographical variables. Turk Psikoloji Dergisi, 26(67), 1–13.
Bener, A., Yildirim, E., Torun, P., Atan, F. C. C., Bolat, E., Alicc, S. U. M., Akyel, S., & Griffiths, M. D. (2019). Internet addiction, fatigue, and sleep problems among adolescent students: A large-scale study. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 17(4), 959–969.
Bronfenbrenner, U., & Morris, P. A. (1998). The ecology of developmental processes.
Cao, H., Sun, Y., Wan, Y., Hao, J., & Tao, F. (2011). Problematic Internet use in Chinese adolescents and its relation to psychosomatic symptoms and life satisfaction. BMC Public Health, 11(1), 1–8.
Chen, Z. Y., Yang, X. D., & Li, X. Y. (2009). Psychometric features of CES-D in Chinese adolescents. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 17(4), 443–445.
Cheng, C., & Li, A. Y. (2014). Internet addiction prevalence and quality of (real) life: A meta-analysis of 31 nations across seven world regions. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 17(12), 755–760.
Evans, G. W., & Cassells, R. C. (2014). Childhood poverty, cumulative risk exposure, and mental health in emerging adults. Clinical Psychological Science, 2(3), 287–296.
Evans, G. W., Li, D., & Whipple, S. S. (2013). Cumulative risk and child development. Psychological Bulletin, 139(6), 1342.
Fan, X. H., & Fang, X. Y. (2010). A comparison of problem behaviors between parent-present children and parent-absent children in different care-taking modes. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 18(2), 232-234.
Flouri, E., & Kallis, C. (2007). Adverse life events and psychopathology and prosocial behavior in late adolescence: Testing the timing, specificity, accumulation, gradient, and moderation of contextual risk. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 46(12), 1651–1659.
Fumero, A. O. N., Marrero, R. J., Voltes, D., & Penate, W. (2018). Personal and social factors involved in internet addiction among adolescents: A meta-analysis. Computers in Human Behavior, 86, 387–400.
Gao, W., & Chen, Z. (2006). A study on psychopathology and psychotherapy of Internet addiction. Advances in Psychological Science, 14(4), 596–603.
Gonz A Lez-Cabrera, J. I. N., Machimbarrena, J. M., Fern A Ndez-Gonz A Lez, L., Prieto-Fidalgo, A. N., Vergara-Moragues, E., & Calvete, E. (2019). Health-related quality of life and cumulative psychosocial risks in adolescents. Youth \& Society, 44118X-19879461X.
Guo, L., Luo, M., Wang, W., Huang, G., Xu, Y., Gao, X., Lu, C., & Zhang, W. (2018). Association between problematic Internet use, sleep disturbance, and suicidal behavior in Chinese adolescents. Journal of Behavioral Addictions, 7(4), 965–975.
Hebron, J., & Humphrey, N. (2014). Exposure to bullying among students with autism spectrum conditions: A multi-informant analysis of risk and protective factors. Autism, 18(6), 618–630.
Hebron, J., Oldfield, J., & Humphrey, N. (2017). Cumulative risk effects in the bullying of children and young people with autism spectrum conditions. Autism, 21(3), 291–300.
Ho, V., Li, H., Yu, C., & Nguyen, B. (2012). The current situation and influencing factors of Internet addiction among Vietnamese adolescents. Journal of South China Normal University (Social Science Edition), 5.
Hou, K., Zhang, Y., Luo, F., & Ren, P. (2017). Effects of neighborhood, parental monitoring and deviant peers on adolescent problem behaviors. Psychological Development and Education, 33, 85–94.
Huang, S., Hu, Y., Ni, Q., Qin, Y., & Lu, W. (2021). Parent-children relationship and internet addiction of adolescents: The mediating role of self-concept. Current Psychology, 40(5), 2510–2517.
Jia, J., Li, D., Li, X., Zhou, Y., Wang, Y., & Sun, W. (2017). Psychological security and deviant peer affiliation as mediators between teacher-student relationship and adolescent Internet addiction. Computers in Human Behavior, 73, 345–352.
Jiang, Y., Ming, H., Tian, Y., Huang, S., Sun, L., Li, H. J., & Zhang, H. (2020). Cumulative Risk and subjective well-being among rural-to-urban migrant adolescents in China: Differential moderating roles of stress mindset and resilience. Journal of Happiness Studies, 21
Karriker-Jaffe, K. J., Foshee, V. A., & Ennett, S. T. (2011). Examining how neighborhood disadvantage influences trajectories of adolescent violence: A look at social bonding and psychological distress. Journal of School Health 81(12), 764–773.
Kokka, I., Mourikis, I., Nicolaides, N. C., Darviri, C., Chrousos, G. P., Kanaka-Gantenbein, C., & Bacopoulou, F. (2021). Exploring the effects of problematic internet use on adolescent sleep: A systematic review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(2), 760.
Lei, H., Zhang, Q., Li, X., Yang, H., Du, W., & Shao, J. (2019). Cumulative risk and problem behaviors among Chinese left-behind children: A moderated mediation model. School Psychology International, 40(3), 309–328.
Leung, L., & Lee, P. S. (2012). Impact of internet literacy, internet addiction symptoms, and internet activities on academic performance. Social Science Computer Review, 30(4), 403–418.
Li, W., Garland, E. L., & Howard, M. O. (2014). Family factors in Internet addiction among Chinese youth: A review of English-and Chinese-language studies. Computers in Human Behavior, 31, 393–411.
Li, D., Zhou, Y., Zhao, L., Wang, Y., & Sun, W. (2016). Cumulative ecological risk and adolescent internet addiction: The mediating role of basic psychological need satisfaction and positive outcome expectancy. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 48(12), 1519–1537.
Li, X. (2017). Cumulative risk and Chinese adolescent problematic Internet use: The mediating role of self-esteem. State University of New York at Albany.
Liang, H. (2019). Impact of Residential Community on Adolescent Health. Contemporary Youth Research
Lima, J., Caughy, M., Nettles, S. M., & O Campo, P. J. (2010). Effects of cumulative risk on behavioral and psychological well-being in first grade: Moderation by neighborhood context. Social Science & Medicine, 71(8), 1447–1454.
Liu, Y., Li, D., Jia, J., Zhou, Y., Zhao, L., Wang, Y., & Sun, W. (2021). Perceived school climate and problematic internet use among Chinese adolescents: Psychological insecurity and negative peer affiliation as mediators. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 35(1), 113–123.
Luo, J., Dong, H., Ding, Q., & Li, D. (2017). Cumulative ecological risk and adolescent internet addiction: A moderating role of effortful control. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 5.
Mcewen, B. S., & Stellar, E. (1993). Stress and the individual: Mechanisms leading to disease. Archives of Internal Medicine, 153(18), 2093–2101.
Moreno, M. A., Jelenchick, L., Cox, E., Young, H., & Christakis, D. A. (2011). Problematic internet use among US youth: A systematic review. Archives of pediatrics & adolescent medicine, 165(9), 797–805.
O Ztekin, C. C. S. K., & O Ztekin, A. (2020). The association of depression, loneliness and internet addiction levels in patients with acne vulgaris. BioPsychoSocial Medicine, 14(1), 1–7.
Okwaraji, F. E., Aguwa, E. N., Onyebueke, G. C., Arinze-Onyia, S. U., & Shiweobi-Eze, C. (2015). Gender, age and class in school differences in internet addiction and psychological distress among adolescents in a Nigerian Urban City. International Neuropsychiatric Disease Journal, 4(3)
Pan, Y. C., Chiu, Y. C., & Lin, Y. H. (2020). Systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiology of internet addiction. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 118, 612-622.
Przepiorka, A., Blachnio, A., & Cudo, A. (2019). The role of depression, personality, and future time perspective in internet addiction in adolescents and emerging adults. Psychiatry Research, 272, 340–348.
Ren, C. (2014). The relationship between Internet addiction and social support and mental health among left-behind middle school students in Henan Province. Chinese Journal of School Health, 35(7)
Rios, R., Aiken, L. S., & Zautra, A. J. (2012). Neighborhood contexts and the mediating role of neighborhood social cohesion on health and psychological distress among Hispanic and non-Hispanic residents. Annals of Behavioral Medicine, 43(1), 50–61.
Rutter, M. (1979). Protective factors in children’s responses to stress and disadvantage. Annals of the Academy of Medicine, Singapore, 8(3), 324–338.
Sela, Y., Zach, M., Amichay-Hamburger, Y., Mishali, M., & Omer, H. (2020). Family environment and problematic internet use among adolescents: The mediating roles of depression and fear of missing out. Computers in Human Behavior, 106, 106226.
Sheibani, S. A. (2015). Internet addiction: A structured literature review and future research directions.
Slopen, N., Koenen, K. C., & Kubzansky, L. D. (2014). Cumulative adversity in childhood and emergent risk factors for long-term health. The Journal of Pediatrics, 164(3), 631–638.
T O Th-Kir A Ly, I. A. N., Morin, A. J., Hietaj A Rvi, L., & Salmela-Aro, K. (2021). Longitudinal trajectories, social and individual antecedents, and outcomes of problematic Internet use among late adolescents. Child Development
Wang, W., Zhou, D. D., Ai, M., Chen, X. R., Lv, Z., Huang, Y., & Kuang, L. (2019). Internet addiction and poor quality of life are significantly associated with suicidal ideation of senior high school students in Chongqing, China. Peerj, 7, e7357.
Wen, L., Garland, E. L., & Howard, M. O. (2014). Family factors in Internet addiction among Chinese youth: A review of English- and Chinese-language studies. Computers in Human Behavior, 31(feb), 393–411.
**ao-yi, D. L. F., **-tao, W. M. Z., & Qin-xue, L. (2013). Family environment, parent-child attachment and adolescent Internet addiction [J]. Psychological Development and Education, 3
**n, M., **ng, J., Wang, P., Li, H., & Hong, Z. (2018). Online activities, prevalence of Internet addiction and risk factors related to family and school among adolescents in China. Addictive Behaviors Reports, 7, 14–18.
**ong, G. (2015). The Validity of the Depression Scale in the Short-Term Flow Center in Chinese Adolescents, Hunan Normal University].
Xu, D., Lok, K., Liu, H., Cao, X., An, F., Hall, B. J., Ungvari, G. S., Lei, S., & **ang, Y. (2020). Internet addiction among adolescents in Macau and mainland China: prevalence, demographics and quality of life. Scientific Reports, 10
Yang, X., Guo, W., Tao, Y., Meng, Y., Wang, H., Li, X., Zhang, Y., Zeng, J., Tang, W., Wang, Q., Others. (2022). A bidirectional association between internet addiction and depression: A large-sample longitudinal study among Chinese university students. Journal of Affective Disorders, 299, 416–424.
Young, K. S. (1998). Internet addiction: The emergence of a new clinical disorder. Cyberpsychology & behavior, 1(3), 237–244.
Young, K. S. (1998b). Caught in the net: How to recognize the signs of internet addiction--and a winning strategy for recovery. John Wiley \& Sons.
Zhai, B., Li, D., Li, X., Liu, Y., Zhang, J., Sun, W., & Wang, Y. (2020). Perceived school climate and problematic internet use among adolescents: Mediating roles of school belonging and depressive symptoms. Addictive Behaviors, 110, 106501.
Zhang, Z., & Sun, Y. (2018). A meta-analysis on Internet addiction disorder in Chinese middle school students. Chinese Journal of School Health, 39(10)
Zhou, N., Cao, H., Li, X., Zhang, J., Yao, Y., Geng, X., Lin, X., Hou, S., Liu, F., Chen, X., Others. (2018). Internet addiction, problematic internet use, nonproblematic internet use among Chinese adolescents: Individual, parental, peer, and sociodemographic correlates. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 32(3), 365.
Acknowledgements
We thank Chun Ran and Jiadi Hou for their contributions to data collection.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Social Science Foundation [grant numbers 16BSH100].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yiqing Wang And Ling Jiang were responsible for the analysis and interpretation of data, drafted the first version of the manuscript, and critically revised the manuscript; **aohua Wang designed this study and conceived this paper; Shuang Ma, **g Guo, Tingting **g, and Qinian Chen provided critical revisions of the manuscript for important intellectual content and approved the final manuscript; and all authors approved the final manuscript as submitted and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Jiang, L., **g, T. et al. Risk Factors of Addictive Internet Use Among Rural Chinese Adolescents: from a Cumulative Risk Perspective. Int J Ment Health Addiction 22, 1357–1375 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-022-00930-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-022-00930-x