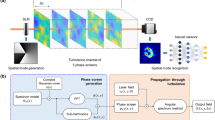
Abstract
Vortex beam with fractional orbital angular momentum (FOAM) is the excellent candidate for improving the capacity of free-space optical (FSO) communication system due to its infinite modes. Therefore, the recognition of FOAM modes with higher resolution is always of great concern. In this work, through an improved EfficientNetV2 based convolutional neural network (CNN), we experimentally achieve the implementation of the recognition of FOAM modes with a resolution as high as 0.001. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first time this high resolution has been achieved. Under the strong atmospheric turbulence (AT) \((C_n^2 = {10^{ - 15}}\,{{\rm{m}}^{ - 2/3}})\), the recognition accuracy of FOAM modes at 0.1 and 0.01 resolution with our model is up to 99.12% and 92.24% for a long transmission distance of 2000 m. Even for the resolution at 0.001, the recognition accuracy can still remain at 78.77%. This work provides an effective method for the recognition of FOAM modes, which may largely improve the channel capacity of the free-space optical communication.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Allen, M. W. Beijersbergen, R. J. C. Spreeuw, and J. P. Woerdman, Orbital angular momentum of light and the transformation of Laguerre–Gaussian laser modes, Phys. Rev. A 45(11), 8185 (1992)
G. C. G. Berkhout, M. P. J. Lavery, J. Courtial, M. W. Beijersbergen, and M. J. Padgett, Efficient sorting of orbital angular momentum states of light, Phys. Rev. Lett. 105(15), 153601 (2010)
K. Liu, Y. Q. Cheng, X. Li, and Y. Gao, Microwave-sensing technology using orbital angular momentum: Overview of its advantages, IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 14(2), 112 (2019)
L. Yan, P. Kristensen, and S. Ramachandran, Vortex fibers for STED microscopy, APL Photonics 4(2), 022903 (2019)
X. W. Zhuang, Unraveling DNA condensation with optical tweezers, Science 305(5681), 188 (2004)
Z. Y. Zhou, D. S. Ding, Y. K. Jiang, Y. Li, S. Shi, X. S. Wang, and B. S. Shi, Orbital angular momentum light frequency conversion and interference with quasi-phase matching crystals, Opt. Express 22(17), 20298 (2014)
S. J. Li, Z. Y. Li, G. S. Huang, X. B. Liu, R. Q. Li, and X. Y. Cao, Digital coding transmissive metasurface for multi-OAM-beam, Front. Phys. 17(6), 62501 (2022)
L. Zou, L. Wang, and S. M. Zhao, Turbulence mitigation scheme based on spatial diversity in orbital-angular-momentum multiplexed system, Opt. Commun. 400, 123 (2017)
E. M. Amhoud, M. Chafii, A. Nimr, and G. Fettweis, OFDM with index modulation in orbital angular momentum multiplexed free space optical links, in: IEEE 93rd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC-Spring), Electr Network, 2021
A. E. Willner, K. Pang, H. Song, K. H. Zou, and H. B. Zhou, Orbital angular momentum of light for communications, Appl. Phys. Rev. 8(4), 041312 (2021)
X. H. Zhang, T. **a, S. B. Cheng, and S. H. Tao, Freespace information transfer using the elliptic vortex beam with fractional topological charge, Opt. Commun. 431, 238 (2019)
V. V. Kotlyar, A. A. Kovalev, A. G. Nalimov, and A. P. Porfirev, Evolution of an optical vortex with an initial fractional topological charge, Phys. Rev. A 102(2), 023516 (2020)
S. S. Li, B. F. Shen, W. P. Wang, Z. G. Bu, H. Zhang, H. Zhang, and S. H. Zhai, Diffraction of relativistic vortex harmonics with fractional average orbital angular momentum, Chin. Opt. Lett. 17(5), 050501 (2019)
M. I. Dedo, Z. Wang, K. Guo, Y. Sun, F. Shen, H. Zhou, J. Gao, R. Sun, Z. Ding, and Z. Guo, Retrieving performances of vortex beams with GS algorithm after transmitting in different types of turbulences, Appl. Sci. (Basel) 9(11), 2269 (2019)
X. Yan, P. F. Zhang, J. H. Zhang, X. X. Feng, C. H. Qiao, and C. Y. Fan, Effect of atmospheric turbulence on entangled orbital angular momentum three-qubit state, Chin. Phys. B 26(6), 064202 (2017)
Y. J. Yang, Q. Zhao, L. L. Liu, Y. D. Liu, C. Rosales-Guzman, and C. W. Qiu, Manipulation of orbital-angular-momentum spectrum using pinhole plates, Phys. Rev. Appl. 12(6), 064007 (2019)
Z. C. Zhang, J. C. Pei, Y. P. Wang, and X. G. Wang, Measuring orbital angular momentum of vortex beams in optomechanics, Front. Phys. 16(3), 32503 (2021)
A. Forbes, A. Dudley, and M. McLaren, Creation and detection of optical modes with spatial light modulators, Adv. Opt. Photonics 8(2), 200 (2016)
J. Yu and Z. F. Wang, 3D facial motion tracking by combining online appearance model and cylinder head model in particle filtering, Sci. China Inf. Sci. 57(7), 029101 (2014)
N. Uribe-Patarroyo, A. Fraine, D. S. Simon, O. Minaeva, and A. V. Sergienko, Object identification using correlated orbital angular momentum states, Phys. Rev. Lett. 110(4), 043601 (2013)
J. Zhu, P. Zhang, D. Z. Fu, D. X. Chen, R. F. Liu, Y. N. Zhou, H. Gao, and F. L. Li, Probing the fractional topological charge of a vortex light beam by using dynamic angular double slits, Photon. Res. 4(5), 187 (2016)
D. Deng, M. C. Lin, Y. Li, and H. Zhao, Precision measurement of fractional orbital angular momentum, Phys. Rev. Appl. 12(1), 014048 (2019)
S. Zheng and J. Wang, Measuring orbital angular momentum (OAM) states of vortex beams with annular gratings, Sci. Rep. 7(1), 40781 (2017)
K. Bayoudh, R. Knani, F. Hamdaoui, and A. Mtibaa, A survey on deep multimodal learning for computer vision: Advances, trends, applications, and datasets, Vis. Comput. 38(8), 2939 (2022)
N. O’Mahony, S. Campbell, A. Carvalho, S. Harapana-halli, G. V. Hernandez, L. Krpalkova, D. Riordan, and J. Walsh, Deep learning vs. traditional computer vision, in: Computer Vision Conference (CVC), Springer International Publishing Ag, Las Vegas, NV, 2019, pp 128–144
J. Long, E. Shelhamer, and T. Darrell, Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation, in: IEEE Conference on Computer, Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, Boston, MA, 2015, pp 3431–3440
N. Le, V. S. Rathour, K. Yamazaki, K. Luu, and M. Savvides, Deep reinforcement learning in computer vision: a comprehensive survey, Artif. Intell. Rev. 55(4), 2733 (2022)
R. Yamashita, M. Nishio, R. K. G. Do, and K. Togashi, Convolutional neural networks: An overview and application in radiology, Insights Imaging 9(4), 611 (2018)
P. Michalski, B. Ruszczak, and M. Tomaszewski, Convolutional neural networks implementations for computer vision, in: 3rd International Scientific Conference on Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI), Springer International Publishing Ag, Opole Univ Technol, Opole, POLAND, 2018, pp 98–110
Z. W. Liu, S. Yan, H. G. Liu, and X. F. Chen, Super-high-resolution recognition of optical vortex modes assisted by a deep-learning method, Phys. Rev. Lett. 123(18), 183902 (2019)
M. Cao, Y. L. Yin, J. W. Zhou, J. H. Tang, L. P. Cao, Y. **a, and J. P. Yin, Machine learning based accurate recognition of fractional optical vortex modes in atmospheric environment, Appl. Phys. Lett. 119(14), 141103 (2021)
J. Zhou, Y. Yin, J. Tang, C. Ling, M. Cao, L. Cao, G. Liu, J. Yin, and Y. **a, Recognition of high-resolution optical vortex modes with deep residual learning, Phys. Rev. A 106(1), 013519 (2022)
W. W. Song, S. T. Li, L. Y. Fang, and T. Lu, Hyperspectral image classification with deep feature fusion network, IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 56(6), 3173 (2018)
M. X. Tan and Q. V. Le, EfficientNetV2: Smaller models and faster training, in: International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Electr Network, 2021, pp 7102–7110
M. L. Huang and Y. C. Liao, A lightweight CNN-based network on COVID-19 detection using X-ray and CT images, Comput. Biol. Med. 146, 105604 (2022)
R. Karthik, T. S. Vaichole, S. K. Kulkarni, O. Yadav, and F. Khan, Eff2Net: An efficient channel attention-based convolutional neural network for skin disease classification, Biomed. Signal Process. Control 73, 103406 (2022)
H. Zhang, J. Zeng, X. Y. Lu, Z. Y. Wang, C. L. Zhao, and Y. J. Cai, Review on fractional vortex beam, Nanophotonics 11(2), 241 (2022)
A. Belafhal and L. Dalil-Essakali, Collins formula and propagation of Bessel-modulated Gaussian light beams through an ABCD optical system, Opt. Commun. 177(1–6), 181 (2000)
Y. J. Yang, Y. Dong, C. L. Zhao, and Y. J. Cai, Generation and propagation of an anomalous vortex beam, Opt. Lett. 38(24), 5418 (2013)
P. H. F. Mesquita, A. J. Jesus-Silva, E. J. S. Fonseca, and J. M. Hickmann, Engineering a square truncated lattice with light’s orbital angular momentum, Opt. Express 19(21), 20616 (2011)
B. Rodenburg, M. P. J. Lavery, M. Malik, M. N. O’Sullivan, M. Mirhosseini, D. J. Robertson, M. Padgett, and R. W. Boyd, Influence of atmospheric turbulence on states of light carrying orbital angular momentum, Opt. Lett. 37(17), 3735 (2012)
S. Y. Fu and C. Q. Gao, Influences of atmospheric turbulence effects on the orbital angular momentum spectra of vortex beams, Photon. Res. 4(5), B1 (2016)
L. C. Andrews, An analytical model for the refractive index power spectrum and its application to optical scintillations in the atmosphere, J. Mod. Opt. 39(9), 1849 (1992)
W. Cheng, J. W. Haus, and Q. W. Zhan, Propagation of vector vortex beams through a turbulent atmosphere, Opt. Express 17(20), 17829 (2009)
S. M. Zhao, J. Leach, L. Y. Gong, J. Ding, and B. Y. Zheng, Aberration corrections for free-space optical communications in atmosphere turbulence using orbital angular momentum states, Opt. Express 20(1), 452 (2012)
Y. Kim, I. Ohn, and D. Kim, Fast convergence rates of deep neural networks for classification, Neural Netw. 138, 179 (2021)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 62271332, 12374273, and 62275162), the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (No. 2023A1515030152), the Shenzhen Government’s Plan of Science and Technology (Nos. JCYJ20180305124927623 and JCYJ20190808150205481), and the Training Program for Excellent Young innovators of Changsha (No. kq2107013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Declarations The authors declare that they have no competing interests and there are no conflicts.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Y., Ma, Z., Chen, H. et al. High-resolution recognition of FOAM modes via an improved EfficientNet V2 based convolutional neural network. Front. Phys. 19, 32205 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-023-1373-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-023-1373-4