Abstract
The Chinese herbal medicine formula Tao Hong Si Wu decoction (THSWD) is traditionally used for the prevention and treatment of ischemic stroke. Transcription factor NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) regulates a battery of phase II enzymes and is known as the major mechanism of cellular defense against oxidative stress. The present study aimed to explore the potential effect of THSWD on the Nrf2 signaling pathway and the consequent effect during cerebral ischemia−reperfusion (I/R) injury. We found that THSWD reduced infarct volume and improved neurological function in a rat stroke model induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). Additionally, heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1), a key endogenous antioxidant enzyme regulated by Nrf2, was significantly further induced by THSWD in this in vivo model. In neuronal-like PC12 cells, THSWD remarkably up-regulated HO-1 expression and promoted Nrf2 nuclear translocation. Furthermore, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt kinase was found to be involved in the upstream of Nrf2 regulation. In an in vitro oxygen−glucose deprivation/reperfusion (OGD-Rep) model, THSWD treatment significantly reduced cell death induced by OGD-Rep insult. Importantly, the protective action was attenuated while PI3K activity was inhibited by a specific inhibitor, LY294002, and the Nrf2 signaling pathway was blocked by antioxidant response element (ARE) decoy oligonucleotides. Collectively, these results demonstrated that THSWD exhibited notable neuroprotective properties in vitro and in vivo and activation of PI3K/Akt and the Nrf2 signaling pathway may be, at least in part, responsible for the protection. This study provides a better understanding of the molecular mechanism underlying the traditional use of the Chinese herbal medicine formula THSWD.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rahman K (2007) Studies on free radicals, antioxidants, and co-factors. Clin Interv Aging 2:219–236
Allen C, Bayraktutan U (2009) Oxidative stress and its role in the pathogenesis of ischaemic stroke. Int J Stroke 4:461–470
Chan PH (2001) Reactive oxygen radicals in signaling and damage in the ischemic brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 21:2–14
Zhang Q, Pi J, Woods CG, Andersen ME (2010) A systems biology perspective on Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 244:84–97
Itoh K, Tong KI, Yamamoto M (2004) Molecular mechanism activating Nrf2-Keap1 pathway in regulation of adaptive response to electrophiles. Free Radic Biol Med 36:1208–1213
Li J, Calkins MJ, Johnson DA, Johnson JA (2007) Role of Nrf2-dependent ARE-driven antioxidant pathway in neuroprotection. Methods Mol Biol 399:67–78
Qi H, Han Y, Rong J (2012) Potential roles of PI3K/Akt and Nrf2-Keap1 pathways in regulating hormesis of Z-ligustilide in PC12 cells against oxygen and glucose deprivation. Neuropharmacology 62:1659–1670
Shih AY, Li P, Murphy TH (2005) A small-molecule-inducible Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response provides effective prophylaxis against cerebral ischemia in vivo. J Neurosci 25:10321–10335
van Muiswinkel FL, Kuiperij HB (2005) The Nrf2-ARE Signalling pathway: promising drug target to combat oxidative stress in neurodegenerative disorders. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord 4:267–281
Yeh LL, Liu JY, Lin KS, Liu YS, Chiou JM, Liang KY, Tsai TF, Wang LH, Chen CT, Huang CY (2007) A randomised placebo-controlled trial of a traditional Chinese herbal formula in the treatment of primary dysmenorrhoea. PLoS One 2:e719
Wang SM, Xu XY, Zhang WL, Hu YY, Chen WH (2005) Effects of Taohongsiwu Decoction and its separated prescriptions decoction on angiogenesis of chick chorioallantoic membrane. Chin J Chin Mater Med 27:4–7
Qi ZX, Du CB (2008) Local microcirculation changes in rabbits with glucocorticoid-induced avascular necrosis of femoral head following Taohong Siwu decoction treatment. J Clin Rehabil Tiss Eng Res 12:2104–2107
Wu CJ, Chen JT, Yen TL, Jayakumar T, Chou DS, Hsiao G, Sheu JR (2011) Neuroprotection by the traditional Chinese medicine, Tao-Hong-Si-Wu-Tang, against middle cerebral artery occlusion-induced cerebral ischemia in rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2011:803015
Wen Z, Wang Z, Wang S, Ravula R, Yang L, Xu J, Wang C, Zuo Z, Chow MS, Shi L, Huang Y (2011) Discovery of molecular mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicinal formula Si-Wu-Tang using gene expression microarray and connectivity map. PLoS One 6:e18278
Wu XM, Qian ZM, Zhu L, Du F, Yung WH, Gong Q, Ke Y (2011) Neuroprotective effect of ligustilide against ischaemia-reperfusion injury via up-regulation of erythropoietin and down-regulation of RTP801. Br J Pharmacol 164:332–343
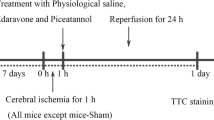
Joshi CN, Jain SK, Murthy PS (2004) An optimized triphenyltetrazolium chloride method for identification of cerebral infarcts. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc 13:11–17
Peng B, Zhao P, Lu YP, Chen MM, Sun H, Wu XM, Zhu L (2013) Z-ligustilide activates the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in vivo and in vitro. Brain Res 1520:168–177
Garcia JH, Wagner S, Liu KF, Hu XJ (1995) Neurological deficit and extent of neuronal necrosis attributable to middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats: statistical validation. Stroke 26:627–634 (discussion 635)
Ishiyama M, Miyazono Y, Sasamoto K, Ohkura Y, Ueno K (1997) A highly water-soluble disulfonated tetrazolium salt as a chromogenic indicator for NADH as well as cell viability. Talanta 44:1299–1305
Qi H, Siu SO, Chen Y, Han Y, Chu IK, Tong Y, Lau AS, Rong J (2010) Senkyunolides reduce hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage in human liver HepG2 cells via induction of heme oxygenase-1. Chem Biol Interact 183:380–389
Tsapenko MV, d’Uscio LV, Grande JP, Croatt AJ, Hernandez MC, Ackerman AW, Katusic ZS, Nath KA (2012) Increased production of superoxide anion contributes to dysfunction of the arteriovenous fistula. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 303:F1601–1607
Zhao J, Moore AN, Redell JB, Dash PK (2007) Enhancing expression of Nrf2-driven genes protects the blood brain barrier after brain injury. J Neurosci 27:10240–10248
Konishi T (2009) Brain oxidative stress as basic target of antioxidant traditional oriental medicines. Neurochem Res 34:711–716
Mattson MP, Cheng A (2006) Neurohormetic phytochemicals: low-dose toxins that induce adaptive neuronal stress responses. Trends Neurosci 29:632–639
Mattson MP, Son TG, Camandola S (2007) Viewpoint: mechanisms of action and therapeutic potential of neurohormetic phytochemicals. Dose Response 5:174–186
Mattson MP (2008) Hormesis defined. Ageing Res Rev 7:1–7
Huang HC, Nguyen T, Pickett CB (2000) Regulation of the antioxidant response element by protein kinase C-mediated phosphorylation of NF-E2-related factor 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:12475–12480
Brunet A, Datta SR, Greenberg ME (2001) Transcription-dependent and -independent control of neuronal survival by the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Curr Opin Neurobiol 11:297–305
Barrera-Ocampo AA, Cespedes-Rubio AE, Cardona-Gomez GP (2008) A potential neuroprotective and synaptic plasticity mechanism induced by estradiol through PI3K/GSK3beta in cerebral ischaemia. Rev Neurol 46:32–39
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the NSFC Projects (No. 81202946), TCM Scientific Program Grant (2012-2-87) from Chongqing Municipal Health Bureau Grant, Doctoral Fund Program grant (swu11107) from Southwest University and Basic Scientific Research Program of Scientific Research Institutes for Public Welfare (to Na Yang).
Conflict of interests
There is no conflict of interest to be declared by the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
L. Li and N. Yang contributed equally.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Yang, N., Nin, L. et al. Chinese herbal medicine formula Tao Hong Si Wu decoction protects against cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury via PI3K/Akt and the Nrf2 signaling pathway . J Nat Med 69, 76–85 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-014-0865-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-014-0865-5