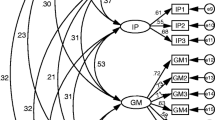
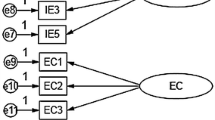
Abstract
The present study investigated the profiles of motivational regulation strategies for writing (MRSW) and examined the relationship between learners’ use of MRSW and their English writing performance across different profiles. L2 Writing Strategies for Motivational Regulation Questionnaire (L2WSMRQ) was administered to examine the potential profiles with a total of 604 senior high school students. Latent profile analysis yielded three subgroups of motivational regulation strategies for writing: limited, modest and competent regulators. The results of multi-group structural equation modeling revealed the significant effects of motivational regulation strategies on English writing in all three profiles. More importantly, the present study found that the relation between motivational regulation strategies and English writing performance varied across the three profiles. The most salient effect that motivational regulation strategies had was on the learners in the modest MRSW profiles, followed by the competent and limited MRSW profile, displaying a low-high-low pattern. These findings may provide pedagogical implications for EFL teachers.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike, H. (1974). A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 19, 716–723.
Bai, R., Hu, G., & Gu, P. Y. (2014). The relationship between use of writing strategies and English proficiency in Singapore primary schools. The Asia-Pacific Education Researcher, 23(3), 355–365.
Bai, B., Guo, W., & Wang, C. (2024). Relationships between struggling EFL writers’ motivation, self-regulated learning (SRL), and writing competence in Hong Kong primary schools. Applied Linguistics Review, 15(1), 135–159.
Baker, W., & Boonkit, K. (2004). Learning strategies in reading and writing: EAP contexts. RELC Journal, 35(3), 299–328.
Bäulke, L., Daumiller, M., & Dresel, M. (2021). The role of state and trait motivational regulation for procrastinatory behavior in academic contexts: Insights from two diary studies. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 65, 101951.
Boekaerts, M. (1996). Self-regulated learning at the junction of cognition and motivation. European Psychologist, 1(2), 100–112.
Byrne, B. M. (2016). Structural Equation Modeling with AMOS: Basic Concepts, Applications, and Programming (3rd Edition). New York: Routledge.
Cai, Y. (2022). Island Ridge Curve: An invisible hand behind self-regulated learning. In, 41. SSRL SIG Newsletter (Spring 2022) (pp. 10–11). https://ssrlsite.files.wordpress.com/2022/05/ssrl_spring_2022_newsletter_final.pdf
Cai, Y. (2024). Metacognitive strategy use in foreign language learning fluctuates from both ends towards the middle: Longitudinal evidence for the Island Ridge curve. System, 123, 103324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.system.2024.103324
Cai, Y., & Cheung, H. T. (2021). A dynamic language ability system framework for diagnosing EMI students’ readiness of English language ability. In L. I. W. Su, H. Cheung, & J. R. W. Wu (Eds.), Rethinking EMI: Rethinking EMI multidisciplinary perspectives from chinese-speaking regions (pp. 141–160). Taylor & Francis.
Cai, Y., & Kunnan, A. J. (2019). Detecting the language thresholds of the effect of background knowledge on a language for specific purposes reading performance: A case of the island ridge curve. Journal of English for Academic Purposes, 42, 100795.
Cai, Y., & Kunnan, A. J. (2020). Map** the fluctuating effect of strategic competence on nursing students’ English reading performance: An approach of multilayered moderation analysis. Language Testing, 37(2), 280–304.
Cai, Y., & Lei, C. (2021). Profiling the efficiency of strategy use across different levels of L2 readers. Educational Studies, 47(1), 117–122.
Cai, Y., & Yang, Y. (2022). The fluid relation between reading strategies and mathematics learning: A perspective of the Island Ridge curve. Learning and Individual Differences, 98., Article 102180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2022.102180
Cai, Y., Yang, M., & Yao, J. (2022). More is not always better: The nonlinear relationship between formative assessment strategies and reading achievement. Assessment in Education: Principles Policy & Practice, 29(6), 711–728.
Chen, F. F. (2007). Sensitivity of goodness of fit indexes to lack of measurement invariance. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 14(3), 464–504.
Chen, G., & Dörnyei, Z. (2014). Motivation and self-regulated learning in second language writing. In B. Kroll, & M. Hallet (Eds.), Second language writing: Research insights for the classroom (pp. 33–50). Cambridge University Press.
Cohen, A. D. (2014). Strategies in learning and using a second language. Routledge.
Cohen, A. D., & Macaro, E. (Eds.). (2017). Language learner strategies: Thirty years of research and practice. Oxford University Press.
Csizér, K., & Tankó, G. (2017). English Majors’ Self-Regulatory Control Strategy Use in Academic writing and its relation to L2 motivation. Applied Linguistics, 38(3), 386–404.
Dörnyei, Z. (2003). Attitudes, orientations, and motivations in language learning: Advances in theory, research, and applications. Language Learning, 53(1), 3–32.
Dörnyei, Z. (2005). The psychology of the Language Learner: Individual Differences in Second Language Acquisition. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Garn, A. C., & Morin, A. J. S. (2021). University students’ use of motivational regulation during one semester. Learning and Instruction, 74, 101436.
Han, C. W. (2016). Change and Stability in Achievement Goals based on instructional tasks of a College Classroom. American Journal of Educational Research, 4(14), 999–1007.
Han, Y., & Hyland, F. (2019). Academic emotions in written corrective feedback situations. Journal of English for Academic Purposes, 38, 1–13.
Han, C. W., Farruggia, S. P., & Solomon, B. J. (2018). Latent profiling university students’ learning strategies use and effects on academic performance and retention. Higher Education Research and Development, 37, 1409–1423.
Hattie, J. (2009). Visible learning: A synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses relating to achievement. Routledge.
Hickendorff, M., Edelsbrunner, P. A., McMullen, J., Schneider, M., & Trezise, K. (2018). Informative tools for characterizing individual differences in learning: Latent class, latent profile, and latent transition analysis. Learning and Individual Differences, 66, 4–15.
Hong-Nam, K., & Page, L. (2014). Investigating metacognitive awareness and reading strategy use of EFL Korean university students. Reading Psychology, 35(3), 195–220.
Hu, X., Huang, Z., & Yang, M. (2022). Profiles of EFL Learners’ online self-regulation and their relationship with dimensions of self-determination motivation in Mainland China. The Asia-Pacific Education Researcher. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-022-00686-x
Icy, L., Yu, S., & Liu, Y. (2018). Hong Kong secondary students’ motivation in EFL writing: A survey study. TESOL Quarterly, 52(1), 176–187.
Jiang, L., Zhou, N., Gu, M. M., & Li, X. (2024). Exploring student motivation and engagement in EMI: A latent profile analysis. Language and Education. https://doi.org/10.1080/09500782.2024.2311146
Jiménez, R. T., García, G. E., & Pearson, P. D. (1996). The reading strategies of bilingual Latina/o students who are successful English readers: Opportunities and obstacles. Reading Research Quarterly, 31(1), 90–112.
Jung, T., & Wickrama, K. A. S. (2008). An introduction to latent class growth analysis and growth mixture modeling. Social and Personality Psychology Campass, 2, 302–317.
Kryshko, O., Fleischer, J., Waldeyer, J., Wirth, J., & Leutner, D. (2020). Do motivational regulation strategies contribute to university students’ academic success? Learning and Individual Differences, 82, 101912.
Kryshko, O., Fleischer, J., Grunschel, C., & Leutner, D. (2022). Self-efficacy for motivational regulation and satisfaction with academic studies in STEM undergraduates: The mediating role of study motivation. Learning and Individual Differences, 93, Article102096.
Kryshko, O., Fleischer, J., Grunschel, C., & Leutner, D. (2023). University students’ self-efficacy for motivational regulation, use of motivational regulation strategies, and satisfaction with academic studies: Exploring between-person and within-person associations. Journal of Educational Psychology, 115(4), 571–588.
Li, S. (2017). The role of self-regulation in second language writing. System, 65, 105–116.
Li, C., Wei, L., & Lu, X. (2023). Contributions of foreign language writing emotions to writing achievement. System, 116, 103074.
Liu, G. X. Y., & Helwig, C. C. (2020). Autonomy, social inequality, and support in Chinese urban and rural adolescents’ reasoning about the Chinese college entrance examination (Gaokao). Journal of Adolescent Research. https://doi.org/10.1177/0743558420914082
Luo, S., & Gan, Z. (2023). Use of motivational regulation strategies and its relations to motivational beliefs in a college English course context. Language Teaching Research. https://doi.org/10.1177/13621688231217095
Ma, L., Li, B., Jiao, Y., & Liu, J. (2023). Motivation profiles of Chinese rural foreign language learners: Link with learning strategy and achievement. Applied Linguistics Review. https://doi.org/10.1515/applirev-2022-0198
Manchón, R. M. (2009). Introduction: Broadening the perspective of L2 writing scholarship: The contribution of research on foreign language writing. In R. Manchón (Ed.), Writing in foreign language contexts: Learning, teaching, and research (pp. 1–19). Multilingual Matters.
Manchón, R. M., Roca de Larios, J., & Murphy, L. (2007). A review of writing strategies: Focus on conceptualization and impact of first language. In A. D. Cohen, & E. M. Macaro (Eds.), Language learner strategies: Thirty years of research and practice (pp. 229–250). Oxford University Press.
Muthén, B., & Muthén, L. K. (2000). Integrating person-centered and variable‐centered analyses: Growth mixture modeling with latent trajectory classes. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 24(6), 882–891.
Oxford, R. L. (1990). Language learning strategies: What every teacher should know. Heinle & Heinle.
Oxford, R. (2017). Teaching and researching language learning strategies: Self-regulation in context (2nd ed.). Routledge.
Pallant, J. (2010). SPSS survival manual: A step by step guide to data analysis using SPSS for Windows (3rd ed.). McGraw-Hill Education.
Pintrich, P. R., & Schrauben, B. (1992). Students’ motivational beliefs and their cognitive engagement in classroom academic tasks. In D. H. Schunk, & J. L. Meece (Eds.), Student perceptions in the Classroom (pp. 149–183). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.
Pintrich, P. R., & Schunk, D. H. (1996). Motivation in education: Theory, Research, and applications. Prentice Hall.
Qin, L., & Zhang, L. J. (2019). English as a foreign language writers’ metacognitive strategy knowledge of writing and their writing performance in multimedia environments. Journal of Writing Research, 12(2), 393–413.
Raoofi, S., & Maroofi, Y. (2017). Relationships among motivation (self-efficacy and task value), strategy use and performance in L2 writing. Southern African Linguistics and Applied Language Studies, 35(3), 299–310.
Schwarz, G. (1978). Estimating the dimension of a model. Annals of Statistics, 6, 461–464.
Schwinger, M., & Stiensmeier-Pelster, J. (2012). Effects of motivational regulation on effort and achievement: A mediation model. International Journal of Educational Research, 56, 35–47.
Schwinger, M., Steinmayr, R., & Spinath, B. (2009). How do motivational regulation strategies affect achievement: Mediated by effort management and moderated by intelligence. Learning and Individual Differences, 19(4), 621–627.
Shen, B., & Bai, B. (2022). Chinese university students’ self-regulated writing strategy use and EFL writing performance: Influences of self-efficacy, gender, and major. Applied Linguistics Review. https://doi.org/10.1515/applirev-2020-0103
Smit, K., de Brabander, C. J., Boekaerts, M., & Martens, R. L. (2017). The self-regulation of motivation: Motivational strategies as mediator between motivational beliefs and engagement for learning. International Journal of Educational Research, 82, 124–134.
Tein, J. Y., Coxe, S., & Cham, H. (2013). Statistical power to detect the correct number of classes in latent profile analysis. Structural Equation Modeling, 20(4), 640–657.
Teng, L. S. (2024). Individual differences in self-regulated learning: Exploring the nexus of motivational beliefs, self-efficacy, and SRL strategies in EFL writing. Language Teaching Research, 28(2), 366–388.
Teng, L. S., & Zhang, L. J. (2016). Fostering Strategic Learning: The Development and Validation of the writing strategies for motivational regulation questionnaire (WSMRQ). The Asia-Pacific Education Researcher, 25(1), 123–134.
Teng, L. S., & Zhang, L. J. (2018). Effects of motivational regulation strategies on writing performance: A mediation model of self-regulated learning of writing in English as a second/foreign language. Metacognition & Learning, 13(2), 213–240.
Teng, L. S., Yuan, R. E., & Sun, P. P. (2020). A mixed-methods approach to investigating motivational regulation strategies and writing proficiency in English as a foreign language context. System, 88, Article 102182.
Valle, A., Pieiro, I., Susana Rodríguez, Regueiro, B., & Pedro Rosário. (2019). Time spent and time management in homework in elementary school students: A person-centered approach. Psicothema, 31(4), 422–428.
Wang, Y., & Xu, J. (2023). A latent profile analysis of L2 writing emotions and their relations to writing buoyancy, motivation and proficiency. Applied Linguistics Review. https://doi.org/10.1515/applirev-2022-0080
Wang, C., Cai, Y., Zhao, M., & You, X. (2021). Disentangling the relation between motivation regulation strategy and writing performance: A perspective of the Island Ridge curve. Foreign Language World (Chinese), 3, 46–54.
Wolters, C. A. (1998). Self-regulated learning and college students’ regulation of motivation. Journal of Educational Psychology, 90, 224–235.
Wolters, C. A. (1999). The relation between high school students’ motivational regulation and their use of learning strategies, effort, and classroom performance. Learning and Individual Differences, 11(3), 281–299.
Wolters, C. A. (2003). Regulation of motivation: Evaluating an underemphasized aspect of self-regulated learning. Educational Psychologist, 38(4), 189–205.
Wolters, C. A. (2011). Regulation of motivation: Contextual and social aspects. Teachers College Record, 113(2), 265–283.
Wolters, C. A., & Benzon, M. B. (2013). Assessing and Predicting College Students’ use of strategies for the self-regulation of motivation. Journal of Experimental Education, 81(2), 199–221.
Xu, J. (2022). A profile analysis of online assignment motivation: Combining achievement goal and expectancy-value perspectives. Computers & Education, 177. Article 104367.
Yu, S., Jiang, L., Liu, C., & Zhou, N. (2022). Profiles of Chinese secondary students’ L2 writing motivation and engagement. Educational Psychology, 42(8), 972–990.
Zhang, L. J. (2013). Second language writing as and for second language learning. Journal of Second Language Writing, 22(4), 446–447.
Zhang, L. J. (2016). Reflections on the pedagogical imports of western practices for professionalizing ESL/EFL writing and writing-teacher education. Australian Review of Applied Linguistics, 39(3), 203–232.
Zimmerman, B. J. (1998). Academic studying and the development of personal skill: A self-regulatory perspective. Educational Psychologist, 33, 73–86.
Zimmerman, B. J., & Risemberg, R. (1997). Becoming a self-regulated writer: A social cognitive perspective. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 22, 73–101.
Zimmerman, B. J., & Schunk, D. H. (2008). Motivation: An essential dimension of self-regulated learning. In D. H. Schunk, & B. J. Zimmerman (Eds.), Motivation and self-regulated learning: Theory, research, and applications (pp. 1–30). Erlbaum.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Z., Hu, X., Yu, X. et al. Profiles of EFL Learners’ motivational regulation strategies and their nonlinear relationship to English writing performance in mainland China. Metacognition Learning (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11409-024-09386-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11409-024-09386-x