Abstract
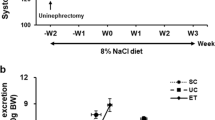
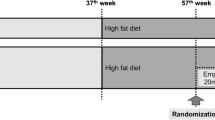
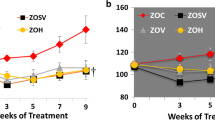
Diabetes, hypertension, and aging are major contributors to cardiovascular and chronic kidney disease (CKD). Sodium/glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors have become a preferred treatment for type II diabetic patients since they have cardiorenal protective effects. However, most elderly diabetic patients also have hypertension, and the effects of SGLT2 inhibitors have not been studied in hypertensive diabetic patients or animal models. The present study examined if controlling hyperglycemia with empagliflozin, or given in combination with lisinopril, slows the progression of renal injury in hypertensive diabetic rats. Studies were performed using hypertensive streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetic Dahl salt-sensitive (STZ-SS) rats and in deoxycorticosterone-salt hypertensive type 2 diabetic nephropathy (T2DN) rats. Administration of empagliflozin alone or in combination with lisinopril reduced blood glucose, proteinuria, glomerular injury, and renal fibrosis in STZ-SS rats without altering renal blood flow (RBF) or glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Blood pressure and renal hypertrophy were also reduced in rats treated with empagliflozin and lisinopril. Administration of empagliflozin alone or in combination with lisinopril lowered blood glucose, glomerulosclerosis, and renal fibrosis but had no effect on blood pressure, kidney weight, or proteinuria in hypertensive T2DN rats. RBF was not altered in any of the treatment groups, and GFR was elevated in empagliflozin-treated hypertensive T2DN rats. These results indicate that empagliflozin is highly effective in controlling blood glucose levels and slows the progression of renal injury in both hypertensive type 1 and type 2 diabetic rats, especially when given in combination with lisinopril to lower blood pressure.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Copies of data files, images presented in this manuscript, and breeding pairs of the animal strains used will be made available upon written request and after a Material Transfer Agreement is completed by both institutions.
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National diabetes statistics report (2020), in: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics-report/index.html (Ed.) 2022.
Agarwal R. Pathogenesis of Diabetic Nephropathy, Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes, American Diabetes Association 2021, pp. 2–7.
Tuttle KR, Brosius FC 3rd, Cavender MA, Fioretto P, Fowler KJ, Heerspink HJL, Manley T, McGuire DK, Molitch ME, Mottl AK, Perreault L, Rosas SE, Rossing P, Sola L, Vallon V, Wanner C, Perkovic V. SGLT2 inhibition for CKD and cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes: report of a scientific workshop sponsored by the National Kidney Foundation. Am J Kidney Dis. 2021;77:94–109.
Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, von Eynatten M, Mattheus M, Johansen OE, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC, Zinman B. Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:323–34.
CDC, Chronic kidney disease in the United States, 2021, Centers for disease control and prevention, US Department of Health and Human Services; 2021 2021.
Naha S, Gardner MJ, Khangura D, Kurukulasuriya LR, Sowers JR. Hypertension in diabetes, in: Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Boyce A, Chrousos G, de Herder WW, Dhatariya K, Dungan K, Hershman JM, Hofland J, Kalra S, Kaltsas G, Koch C, Kopp P, Korbonits M, Kovacs CS, Kuohung W, Laferrère B, Levy M, McGee EA, McLachlan R, Morley JE, New M, Purnell J, Sahay R, Singer F, Sperling MA, Stratakis CA, Trence DL, Wilson DP (Eds.), Endotext, MDText.com, Inc. Copyright © 2000–2022, MDText.com, Inc., South Dartmouth (MA), 2000.
Virani SS, Alonso A, Aparicio HJ, Benjamin EJ, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, Chamberlain AM, Cheng S, Delling FN, Elkind MSV, Evenson KR, Ferguson JF, Gupta DK, Khan SS, Kissela BM, Knutson KL, Lee CD, Lewis TT, Liu J, Loop MS, Lutsey PL, Ma J, Mackey J, Martin SS, Matchar DB, Mussolino ME, Navaneethan SD, Perak AM, Roth GA, Samad Z, Satou GM, Schroeder EB, Shah SH, Shay CM, Stokes A, VanWagner LB, Wang NY, Tsao CW. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2021 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021;143:e254–743.
Nespoux J, Vallon V. SGLT2 inhibition and kidney protection. Clin Sci (Lond). 2018;132:1329–39.
Ferrannini E. Sodium-glucose co-transporters and their inhibition: clinical physiology. Cell Metab. 2017;26:27–38.
Wang S, Jiao F, Border JJ, Fang X, Crumpler RF, Liu Y, Zhang H, Jefferson J, Guo Y, Elliott PS, Thomas KN, Strong LB, Urvina AH, Zheng B, Rijal A, Smith SV, Yu H, Roman RJ, Fan F. Luseogliflozin, a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor, reverses cerebrovascular dysfunction and cognitive impairments in 18-mo-old diabetic animals. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022;322:H246-259.
Vallon V, Thomson SC. Targeting renal glucose reabsorption to treat hyperglycaemia: the pleiotropic effects of SGLT2 inhibition. Diabetologia. 2017;60:215–25.
Wright EM. Renal Na(+)-glucose cotransporters. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2001;280:F10–8.
Wang XX, Levi J, Luo Y, Myakala K, Herman-Edelstein M, Qiu L, Wang D, Peng Y, Grenz A, Lucia S, Dobrinskikh E, D’Agati VD, Koepsell H, Kopp JB, Rosenberg AZ, Levi M. SGLT2 protein expression is increased in human diabetic nephropathy: SGLT2 protein inhibition decreases renal lipid accumulation, inflammation, and the development of nephropathy in diabetic mice. J Biol Chem. 2017;292:5335–48.
Vallon V, Thomson SC. Renal function in diabetic disease models: the tubular system in the pathophysiology of the diabetic kidney. Annu Rev Physiol. 2012;74:351–75.
Nespoux J, Vallon V. Renal effects of SGLT2 inhibitors: an update. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2020;29:190–8.
Zelniker TA, Bonaca MP, Furtado RHM, Mosenzon O, Kuder JF, Murphy SA, Bhatt DL, Leiter LA, McGuire DK, Wilding JPH, Budaj A, Kiss RG, Padilla F, Gause-Nilsson I, Langkilde AM, Raz I, Sabatine MS, Wiviott SD. Effect of dapagliflozin on atrial fibrillation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: insights from the DECLARE-TIMI 58 trial. Circulation. 2020;141:1227–34.
Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E, Hantel S, Mattheus M, Devins T, Johansen OE, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC, Inzucchi SE. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:2117–28.
Bhatt DL, Szarek M, Pitt B, Cannon CP, Leiter LA, McGuire DK, Lewis JB, Riddle MC, Inzucchi SE, Kosiborod MN, Cherney DZI, Dwyer JP, Scirica BM, Bailey CJ, Díaz R, Ray KK, Udell JA, Lopes RD, Lapuerta P, Steg PG. Sotagliflozin in patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:129–39.
Neal B, Perkovic V, Matthews DR. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:2099. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc1712572.
McMurray JJV, DeMets DL, Inzucchi SE, Køber L, Kosiborod MN, Langkilde AM, Martinez FA, Bengtsson O, Ponikowski P, Sabatine MS, Sjöstrand M, Solomon SD. A trial to evaluate the effect of the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor dapagliflozin on morbidity and mortality in patients with heart failure and reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (DAPA-HF). Eur J Heart Fail. 2019;21:665–75.
Perkovic V, Jardine MJ, Neal B, Bompoint S, Heerspink HJL, Charytan DM, Edwards R, Agarwal R, Bakris G, Bull S, Cannon CP, Capuano G, Chu PL, de Zeeuw D, Greene T, Levin A, Pollock C, Wheeler DC, Yavin Y, Zhang H, Zinman B, Meininger G, Brenner BM, Mahaffey KW. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:2295–306.
Ye N, Jardine MJ, Oshima M, Hockham C, Heerspink HJL, Agarwal R, Bakris G, Schutte AE, Arnott C, Chang TI, Górriz JL, Cannon CP, Charytan DM, de Zeeuw D, Levin A, Mahaffey KW, Neal B, Pollock C, Wheeler DC, Luca Di Tanna G, Cheng H, Perkovic V, Neuen BL. Blood pressure effects of canagliflozin and clinical outcomes in type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease: insights from the CREDENCE trial. Circulation. 2021;143:1735–49.
Rieg T, Vallon V. Development of SGLT1 and SGLT2 inhibitors. Diabetologia. 2018;61:2079–86.
Vallon V, Verma S. Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on kidney and cardiovascular function. Annu Rev Physiol. 2021;83:503–28.
Kojima N, Williams JM, Slaughter TN, Kato S, Takahashi T, Miyata N, Roman R.J. Renoprotective effects of combined SGLT2 and ACE inhibitor therapy in diabetic Dahl S rats, Physiol Rep 2015;3. https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.12436
Kojima N, Williams JM, Takahashi T, Miyata N, Roman RJ. Effects of a new SGLT2 inhibitor, luseogliflozin, on diabetic nephropathy in T2DN rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013;345:464–72.
Slaughter TN, Paige A, Spires D, Kojima N, Kyle PB, Garrett MR, Roman RJ, Williams JM. Characterization of the development of renal injury in type-1 diabetic Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2013;305:R727–34.
Gembardt F, Bartaun C, Jarzebska N, Mayoux E, Todorov VT, Hohenstein B, Hugo C. The SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin ameliorates early features of diabetic nephropathy in BTBR ob/ob type 2 diabetic mice with and without hypertension. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014;307:F317–25.
Kario K, Ferdinand KC, O’Keefe JH. Control of 24-hour blood pressure with SGLT2 inhibitors to prevent cardiovascular disease. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2020;63:249–62.
Vallon V, Gerasimova M, Rose MA, Masuda T, Satriano J, Mayoux E, Koepsell H, Thomson SC, Rieg T. SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin reduces renal growth and albuminuria in proportion to hyperglycemia and prevents glomerular hyperfiltration in diabetic Akita mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014;306:F194-204.
Kario K, Okada K, Kato M, Nishizawa M, Yoshida T, Asano T, Uchiyama K, Niijima Y, Katsuya T, Urata H, Osuga JI, Fujiwara T, Yamazaki S, Tomitani N, Kanegae H. 24-hour blood pressure-lowering effect of an sglt-2 inhibitor in patients with diabetes and uncontrolled nocturnal hypertension: results from the randomized, placebo-controlled SACRA study. Circulation. 2018;139:2089–97.
Fan L, Gao W, Liu Y, Jefferson JR, Fan F, Roman RJ. Knockout of gamma-adducin promotes N(G)-nitro-L-arginine-methyl-ester-induced hypertensive renal injury. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2021;377:189–98.
Fan F, Geurts AM, Pabbidi MR, Ge Y, Zhang C, Wang S, Liu Y, Gao W, Guo Y, Li L, He X, Lv W, Muroya Y, Hirata T, Prokop J, Booz GW, Jacob HJ, Roman RJ. A mutation in gamma-adducin impairs autoregulation of renal blood flow and promotes the development of kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020;31:687–700.
Zhang C, He X, Murphy SR, Zhang H, Wang S, Ge Y, Gao W, Williams JM, Geurts AM, Roman RJ, Fan F. Knockout of dual-specificity protein phosphatase 5 protects against hypertension-induced renal injury. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2019;370:206–17.
Guo Y, Wang S, Liu Y, Fan L, Booz GW, Roman RJ, Chen Z, Fan F. Accelerated cerebral vascular injury in diabetes is associated with vascular smooth muscle cell dysfunction. Geroscience. 2020;42:547–61.
Nobrega MA, Fleming S, Roman RJ, Shiozawa M, Schlick N, Lazar J, Jacob HJ. Initial characterization of a rat model of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 2004;53:735–42.
Wang S, Lv W, Zhang H, Liu Y, Li L, Jefferson JR, Guo Y, Li M, Gao W, Fang X, Paul IA, Rajkowska G, Shaffery JP, Mosley TH, Hu X, Liu R, Wang Y, Yu H, Roman RJ, Fan F. Aging exacerbates impairments of cerebral blood flow autoregulation and cognition in diabetic rats. Geroscience. 2020;42:1387–410.
Muroya Y, He X, Fan L, Wang S, Xu R, Fan F, Roman RJ. Enhanced renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in aging and diabetes. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018;315:F1843-1854.
Li C, Zhang J, Xue M, Li X, Han F, Liu X, Xu L, Lu Y, Cheng Y, Li T, Yu X, Sun B, Chen L. SGLT2 inhibition with empagliflozin attenuates myocardial oxidative stress and fibrosis in diabetic mice heart. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2019;18:15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-019-0816-2
Lin B, Koibuchi N, Hasegawa Y, Sueta D, Toyama K, Uekawa K, Ma M, Nakagawa T, Kusaka H, Kim-Mitsuyama S. Glycemic control with empagliflozin, a novel selective SGLT2 inhibitor, ameliorates cardiovascular injury and cognitive dysfunction in obese and type 2 diabetic mice. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014;13:148. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-014-0148-1.
Mui JV, Zhou J, Lee S, Leung KSK, Lee TTL, Chou OHI, Tsang SL, Wai AKC, Liu T, Wong WT, Chang C, Tse G, Zhang Q. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors vs. dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) inhibitors for new-onset dementia: a propensity score-matched population-based study with competing risk analysis, Front Cardiovasc Med 2021;8:747620. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2021.747620.
Zinman B, Lachin JM, Inzucchi SE. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:B1094.
Heerspink HJL, Stefánsson BV, Correa-Rotter R, Chertow GM, Greene T, Hou FF, Mann JFE, McMurray JJV, Lindberg M, Rossing P, Sjöström CD, Toto RD, Langkilde AM, Wheeler DC. Dapagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:1436–46.
Lee YH, Kim SH, Kang JM, Heo JH, Kim DJ, Park SH, Sung M, Kim J, Oh J, Yang DH, Lee SH, Lee SY. Empagliflozin attenuates diabetic tubulopathy by improving mitochondrial fragmentation and autophagy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019;317:F767–80.
Layton AT, Vallon V. SGLT2 inhibition in a kidney with reduced nephron number: modeling and analysis of solute transport and metabolism. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018;314:F969–84.
Ge Y, Murphy SR, Fan F, Williams JM, Falck JR, Liu R, Roman RJ. Role of 20-HETE in the impaired myogenic and TGF responses of the Af-Art of Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014;307:F509–15.
Fan F, Muroya Y, Roman RJ. Cytochrome P450 eicosanoids in hypertension and renal disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2015;24:37–46.
Cassis P, Locatelli M, Cerullo D, Corna D, Buelli S, Zanchi C, Villa S, Morigi M, Remuzzi G, Benigni A, Zoja C. SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin limits podocyte damage in proteinuric nondiabetic nephropathy, JCI Insight 2018;3. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.98720.
Kidokoro K, Cherney DZI, Bozovic A, Nagasu H, Satoh M, Kanda E, Sasaki T, Kashihara N. Evaluation of glomerular hemodynamic function by empagliflozin in diabetic mice using in vivo imaging. Circulation. 2019;140:303–15.
Cherney DZ, Perkins BA, Soleymanlou N, Maione M, Lai V, Lee A, Fagan NM, Woerle HJ, Johansen OE, Broedl UC, von Eynatten M. Renal hemodynamic effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 2014;129:587–97.
Rajasekeran H, Lytvyn Y, Bozovic A, Lovshin JA, Diamandis E, Cattran D, Husain M, Perkins BA, Advani A, Reich HN, Kulasingam V, Cherney DZI. Urinary adenosine excretion in type 1 diabetes. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017;313:F184-191.
Ren Y, Garvin JL, Carretero OA. Efferent arteriole tubuloglomerular feedback in the renal nephron. Kidney Int. 2001;59:222–9.
van Bommel EJM, Muskiet MHA, van Baar MJB, Tonneijck L, Smits MM, Emanuel AL, Bozovic A, Danser AHJ, Geurts F, Hoorn EJ, Touw DJ, Larsen EL, Poulsen HE, Kramer MHH, Nieuwdorp M, Joles JA, van Raalte DH. The renal hemodynamic effects of the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin are caused by post-glomerular vasodilatation rather than pre-glomerular vasoconstriction in metformin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes in the randomized, double-blind RED trial. Kidney Int. 2020;97:202–12.
Roman RJ, Fan F. 20-HETE: hypertension and beyond. Hypertension. 2018;72:12–8.
Tikkanen I, Narko K, Zeller C, Green A, Salsali A, Broedl UC, Woerle HJ, Investigators E-RB. empagliflozin reduces blood pressure in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:420–8.
Tye SC, de Vries ST, Wanner C, Denig P, Heerspink HJL. Prediction of the effects of empagliflozin on cardiovascular and kidney outcomes based on short-term changes in multiple risk markers, Front Pharmacol 2022;12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.786706
Funding
This study was partially supported by grants DK109133, AG057842, P20GM104357, and HL138685 from the National Institutes of Health and a collaborative research agreement DE 811138149 from Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH. The views expressed in this manuscript are expressly those of the author(s) and were not influenced by the funding institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R.J.R conceived and designed research; S.R.M., J.M.W., and W.W. performed experiments; J.M.W., S.R.M., W.W., J.J.B., F.F., and R.J.R analyzed data; J.M.W., F.F., and R.J.R interpreted results of experiments; S.R.M., J.J.B., and F.F. prepared figures; J.M.W. and F.F. drafted the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study utilized Dahl salt-sensitive and type 2 diabetic nephropathy rats that were obtained from in-house colonies in the Laboratory Animal Facility at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, which is approved by the American Association for the Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care. All of the animal studies were performed in accordance with the US Public Health Service Policy on the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and were approved by the Animal Care Committee of the University of Mississippi Medical Center.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Williams, J.M., Murphy, S.R., Wu, W. et al. Renoprotective effects of empagliflozin in type 1 and type 2 models of diabetic nephropathy superimposed with hypertension. GeroScience 44, 2845–2861 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-022-00610-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-022-00610-7