Abstract
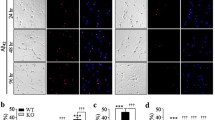
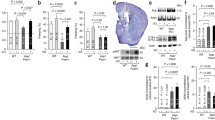
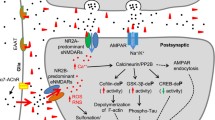
Aging is a crucial cause of cognitive decline and a major risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease (AD); however, AD’s underlying molecular mechanisms remain unclear. Recently, tetraspanins have emerged as important modulators of synaptic function and memory. We demonstrate that the level of tetraspanin CD82 is upregulated in the brains of AD patients and middle-aged mice. In young adult mice, injection of AAV-CD82 to the hippocampus induced AD-like cognitive deficits and impairments in neuronal spine density. CD82 overexpression increased TRPM7 α-kinase cleavage via caspase-3 activation and induced Numb phosphorylation at Thr346 and Ser348 residues. CD82 overexpression promoted beta-amyloid peptide (Aβ) secretion which could be reversed by Numb T346S348 mutants. Importantly, hippocampus-related memory functions were improved in Cd82−/− mice. Taken together, our findings provide the evidence that links the elevated CD82-TRPM7-Numb signaling to age-related cognitive impairment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarts M, Iihara K, Wei WL, **ong ZG, Arundine M, Cerwinski W, MacDonald J, Tymianski M (2003) A key role for TRPM7 channels in anoxic neuronal death. Cell 115(7):863–877
Bassani S, Cingolani LA, Valnegri P, Folci A, Zapata J, Gianfelice A, Sala C, Goda Y, Passafaro M (2012) The X-linked intellectual disability protein TSPAN7 regulates excitatory synapse development and AMPAR trafficking. Neuron 73(6):1143–1158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2012.01.021
Bassani S, Folci A, Zapata J, Passafaro M (2013) AMPAR trafficking in synapse maturation and plasticity. Cell Mol Life Sci 70(23):4411–4430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-013-1309-1
Belghali M, Chastan N, Cignetti F, Davenne D, Decker LM (2017) Loss of gait control assessed by cognitive-motor dual-tasks: pros and cons in detecting people at risk of develo** Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Geroscience 39(3):305–329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-017-9977-7
Callisaya ML, Launay CP, Srikanth VK, Verghese J, Allali G, Beauchet O (2017) Cognitive status, fast walking speed and walking speed reserve-the Gait and Alzheimer Interactions Tracking (GAIT) study. Geroscience 39(2):231–239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-017-9973-y
Chan SL, Pedersen WA, Zhu H, Mattson MP (2002) Numb modifies neuronal vulnerability to amyloid beta-peptide in an isoform-specific manner by a mechanism involving altered calcium homeostasis: implications for neuronal death in Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroMolecular Med 1(1):55–67. https://doi.org/10.1385/nmm:1:1:55
Charrin S, Jouannet S, Boucheix C, Rubinstein E (2014) Tetraspanins at a glance. J Cell Sci 127(Pt 17):3641–3648. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.154906
Chen W, Xu B, **ao A, Liu L, Fang X, Liu R, Turlova E, Barszczyk A, Zhong X, Sun CL, Britto LR, Feng ZP, Sun HS (2015) TRPM7 inhibitor carvacrol protects brain from neonatal hypoxic-ischemic injury. Mol Brain 8:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-015-0102-5
Desai BN, Krapivinsky G, Navarro B, Krapivinsky L, Carter BC, Febvay S, Delling M, Penumaka A, Ramsey IS, Manasian Y, Clapham DE (2012) Cleavage of TRPM7 releases the kinase domain from the ion channel and regulates its participation in Fas-induced apoptosis. Dev Cell 22(6):1149–1162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2012.04.006
Fahlstrom A, Yu Q, Ulfhake B (2011) Behavioral changes in aging female C57BL/6 mice. Neurobiol Aging 32(10):1868–1880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2009.11.003
Feng J, Huang C, Wren JD, Wang DW, Yan J, Zhang J, Sun Y, Han X, Zhang XA (2015) Tetraspanin CD82: a suppressor of solid tumors and a modulator of membrane heterogeneity. Cancer Metastasis Rev 34(4):619–633. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-015-9585-x
Fleig A, Chubanov V (2014) TRPM7. Handb Exp Pharmacol 222:521–546. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-54215-2_21
Forner S, Baglietto-Vargas D, Martini AC, Trujillo-Estrada L, LaFerla FM (2017) Synaptic impairment in Alzheimer’s disease: a dysregulated symphony. Trends Neurosci 40(6):347–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2017.04.002
Graham WV, Bonito-Oliva A, Sakmar TP (2017) Update on Alzheimer’s disease therapy and prevention strategies. Annu Rev Med 68:413–430. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-med-042915-103753
Guix FX, Sannerud R, Berditchevski F, Arranz AM, Horre K, Snellinx A et al (2017) Tetraspanin 6: a pivotal protein of the multiple vesicular body determining exosome release and lysosomal degradation of amyloid precursor protein fragments. Mol Neurodegener 12(1):25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-017-0165-0
Huang Y, Leng TD, Inoue K, Yang T, Liu M, Horgen FD et al (2018) TRPM7 channels play a role in high glucose-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and neuronal cell apoptosis. J Biol Chem. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA117.001032
Jacobi E, von Engelhardt J (2018) AMPA receptor complex constituents: control of receptor assembly, membrane trafficking and subcellular localization. Mol Cell Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2018.05.008
Joos JP, Saadatmand AR, Schnabel C, Viktorinova I, Brand T, Kramer M et al (2018) Ectopic expression of S28A-mutated histone H3 modulates longevity, stress resistance and cardiac function in Drosophila. Sci Rep 8(1):2940. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-21372-3
Krapivinsky G, Krapivinsky L, Manasian Y, Clapham DE (2014) The TRPM7 chanzyme is cleaved to release a chromatin-modifying kinase. Cell 157(5):1061–1072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.03.046
Kyriazis GA, Wei Z, Vandermey M, Jo DG, **n O, Mattson MP, Chan SL (2008) Numb endocytic adapter proteins regulate the transport and processing of the amyloid precursor protein in an isoform-dependent manner: implications for Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. J Biol Chem 283(37):25492–25502. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M802072200
Lee SA, Suh Y, Lee S, Jeong J, Kim SJ, Kim SJ, Park SK (2017) Functional expression of dopamine D2 receptor is regulated by tetraspanin 7-mediated postendocytic trafficking. FASEB J 31(6):2301–2313. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201600755RR
Liu Y, Chen C, Liu Y, Li W, Wang Z, Sun Q et al (2018) TRPM7 is required for normal synapse density, learning, and memory at different developmental stages. Cell Rep 23(12):3480–3491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.05.069
Prigent C, Dimitrov S (2003) Phosphorylation of serine 10 in histone H3, what for? J Cell Sci 116(Pt 18):3677–3685. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.00735
Rangel-Barajas C, Coronel I, Floran B (2015) Dopamine receptors and neurodegeneration. Aging Dis 6(5):349–368. https://doi.org/10.14336/ad.2015.0330
Salas IH, Callaerts-Vegh Z, Arranz AM, Guix FX, D’Hooge R, Esteban JA, de Strooper B, Dotti CG (2017) Tetraspanin 6: a novel regulator of hippocampal synaptic transmission and long term plasticity. PLoS One 12(2):e0171968. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0171968
Shoji H, Miyakawa T (2019) Age-related behavioral changes from young to old age in male mice of a C57BL/6J strain maintained under a genetic stability program. 39(2):100–118. https://doi.org/10.1002/npr2.12052
Sun Y, Sukumaran P, Schaar A, Singh BB (2015) TRPM7 and its role in neurodegenerative diseases. Channels (Austin) 9(5):253–261. https://doi.org/10.1080/19336950.2015.1075675
Sun M, Asghar SZ, Zhang H (2016) The polarity protein Par3 regulates APP trafficking and processing through the endocytic adaptor protein Numb. Neurobiol Dis 93:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2016.03.022
Tarantini S, Fulop GA, Kiss T, Farkas E, Zolei-Szenasi D, Galvan V et al (2017) Demonstration of impaired neurovascular coupling responses in TG2576 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease using functional laser speckle contrast imaging. Geroscience 39(4):465–473. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-017-9980-z
Tarantini S, Valcarcel-Ares NM, Yabluchanskiy A, Fulop GA, Hertelendy P, Gautam T, Farkas E, Perz A, Rabinovitch PS, Sonntag WE, Csiszar A, Ungvari Z (2018) Treatment with the mitochondrial-targeted antioxidant peptide SS-31 rescues neurovascular coupling responses and cerebrovascular endothelial function and improves cognition in aged mice. Aging Cell 17(2). https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12731
Ungvari Z, Tarantini S, Hertelendy P, Valcarcel-Ares MN, Fulop GA, Logan S et al (2017) Cerebromicrovascular dysfunction predicts cognitive decline and gait abnormalities in a mouse model of whole brain irradiation-induced accelerated brain senescence. Geroscience 39(1):33–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-017-9964-z
Valcarcel-Ares MN, Tucsek Z, Kiss T, Giles CB, Tarantini S, Yabluchanskiy A, Balasubramanian P, Gautam T, Galvan V, Ballabh P, Richardson A, Freeman WM, Wren JD, Deak F, Ungvari Z, Csiszar A (2019) Obesity in aging exacerbates neuroinflammation, dysregulating synaptic function-related genes and altering eicosanoid synthesis in the mouse hippocampus: potential role in impaired synaptic plasticity and cognitive decline. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 74(3):290–298. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/gly127
Visser D, Middelbeek J, van Leeuwen FN, Jalink K (2014) Function and regulation of the channel-kinase TRPM7 in health and disease. Eur J Cell Biol 93(10–12):455–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejcb.2014.07.001
Wang XC, Zhang YC, Chatterjie N, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Wang JZ (2008) Effect of melatonin and melatonylvalpromide on beta-amyloid and neurofilaments in N2a cells. Neurochem Res 33(6):1138–1144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9563-y
Wei Q, Zhang F, Richardson MM, Roy NH, Rodgers W, Liu Y, Zhao W, Fu C, Ding Y, Huang C, Chen Y, Sun Y, Ding L, Hu Y, Ma JX, Boulton ME, Pasula S, Wren JD, Tanaka S, Huang X, Thali M, Hämmerling GJ, Zhang XA (2014) CD82 restrains pathological angiogenesis by altering lipid raft clustering and CD44 trafficking in endothelial cells. Circulation 130(17):1493–1504. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.114.011096
**e Z, Dong Y, Maeda U, **a W, Tanzi RE (2012) RNAi-mediated knock-down of Dab and Numb attenuate Abeta levels via gamma-secretase mediated APP processing. Transl Neurodegener 1(1):8. https://doi.org/10.1186/2047-9158-1-8
Yap CC, Winckler B (2015) Adapting for endocytosis: roles for endocytic sorting adaptors in directing neural development. Front Cell Neurosci 9:119. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2015.00119
Zhao Y, Wang J, Jiang H, Yu Z, Li X, Shi J (2015) Following OGD/R, annexin 1 nuclear translocation and subsequent induction of apoptosis in neurons are assisted by myosin IIA in a TRPM7 kinase-dependent manner. Mol Neurobiol 51(2):729–742. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8781-y
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Jiapei Dai from Chinese Brain Bank Center for providing human brain tissues, Prof. Jianzhi Wang from Key Laboratory of Ministry of Education for Neurological Disorders at Tongji Medical College of HUST for N2a/APP cell line, and Ms. Kathy Kyler of the University of Oklahoma Health Science Center for English editing.
Funding
The current studies were supported by funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China Grant No. 31800868 (to Dr. Yin Zhao).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YZ, XL, AC, and XZ conceived and designed the project; YZ, TK, JD, LL, LZ, and XL performed the experiments; XZ, AC, ZU, and JS provided valuable advice, coordinated the studies, and/or conducted the data analysis; YZ, TK, and XZ wrote the manuscript with approval from all authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
All animal experiments were approved by the Ethics Committees for Animal Experimentation of Huazhong University of Science and Technology and the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center in strict accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals published by the U.S. National Institutes of Health. Efforts were made to minimize animal suffering and to reduce the number of animals used. This study was performed in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, HUST, China (2017-K-036).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Kiss, T., DelFavero, J. et al. CD82-TRPM7-Numb signaling mediates age-related cognitive impairment. GeroScience 42, 595–611 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-020-00166-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-020-00166-4