Abstract
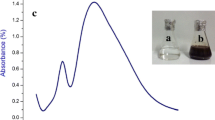
Vector-borne diseases pose a significant public health challenge in economically disadvantaged nations. Malaria, dengue fever, chikungunya, Zika, yellow fever, Japanese encephalitis, and lymphatic filariasis are spread by mosquitoes. Consequently, the most effective method of preventing these diseases is to eliminate the mosquito population. Historically, the majority of control programs have depended on chemical pesticides, including organochlorines, organophosphates, carbamates, and pyrethroids. Synthetic insecticides used to eradicate pests have the potential to contaminate groundwater, surface water, beneficial soil organisms, and non-target species. Nanotechnology is an innovative technology that has the potential to be used in insect control with great precision. The goal of this study was to test the in vitro anti-dengue potential and mosquitocidal activity of Chaetomorpha aerea and C. aerea–synthesized Mn-doped superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (CA-Mn-SPIONs). The synthesis of CA-Mn-SPIONs using C. aerea extract was verified by the observable alteration in the colour of the reaction mixture, transitioning from a pale green colour to a brown. The study of UV–Vis spectra revealed absorbance peaks at approximately 290 nm, which can be attributed to the surface Plasmon resonance of the CA-Mn-SPIONs. The SEM, TEM, EDX, FTIR, vibrating sample magnetometry, and XRD analyses provided evidence that confirmed the presence of CA-Mn-SPIONs. In the present study, results revealed that C. aerea aqueous extract LC50 values against Ae. aegypti ranged from 222.942 (first instar larvae) to 349.877 ppm in bioassays (pupae). CA-Mn-SPIONs had LC50 ranging from 20.199 (first instar larvae) to 26.918 ppm (pupae). After treatment with 40 ppm CA-Mn-SPIONs and 500 ppm C. aerea extract in ovicidal tests, egg hatchability was lowered by 100%. Oviposition deterrence experiments showed that in Ae. aegypti, oviposition rates were lowered by more than 66% by 100 ppm of green algal extract and by more than 71% by 10 ppm of CA-Mn-SPIONs (oviposition activity index values were 0.50 and 0.55, respectively). Moreover, in vitro anti-dengue activity of CA-Mn-SPIONs has good anti-viral property against dengue viral cell lines. In addition, GC–MS analysis showed that 21 intriguing chemicals were discovered. Two significant phytoconstituents in the methanol extract of C. aerea include butanoic acid and palmitic acid. These two substances were examined using an in silico methodology against the NS5 methyltransferase protein and demonstrated good glide scores and binding affinities. Finally, we looked into the morphological damage and fluorescent emission of third instar Ae. aegypti larvae treated with CA-Mn-SPIONs. Fluorescent emission is consistent with ROS formation of CA-Mn-SPIONs against Ae. aegypti larvae. The present study determines that the key variables for the successful development of new insecticidal agents are rooted in the eco-compatibility and the provision of alternative tool for the pesticide manufacturing sector.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Supporting data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Adawara SN, Shallangwa GA, Mamza PA, Ibrahim A (2021) In-silico approaches towards the profiling of some anti-dengue virus as potent inhibitors against dengue NS-5 receptor. Sci Afric 13:00907
Akhtar K, Javed Y, Muhammad F, Akhtar B, Shad NA, Sajid MM, Jamil Y, Sharif A, Abbas W (2021) Biotransformation and toxicity evaluation of functionalized manganese doped iron oxide nanoparticles. J Biomed Mater Res Part B Appl Biomater 109:1563–1577
Amutha S, Sridhar S (2018) Green synthesis of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticle using leaves of Glycosmis mauritiana and their antibacterial activity against human pathogens. J Inn Pharm Biol Sci 5:22–26
Azizi A (2020) Green synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles and its application in preparation of Fe3O4/cellulose magnetic nanocomposite: a suitable proposal for drug delivery systems. Inorg Organo Poly Mater 30:3552–3561
Becker N, Petrić D, Zgomba M, Boase C, Madon MB, Dahl C, Kaiser A (2020) Mosquitoes: identification, ecology and control. fascinating life sciences. Springer International Publishing, Cham
Benelli G (2016a) Plant-mediated biosynthesis of nanoparticles as an emerging tool against mosquitoes of medical and veterinary importance: a review. Parasitol Res 115:23–34
Benelli G (2016b) Plant-mediated synthesis of nanoparticles: a newer and safer tool against mosquito-borne diseases? Asia Pac J Trop Biomed 6:353–354
Benmansour F, Eydoux C, Querat G, De Lamballerie X, Canard B, Alvarez K, Guillemot JC, Barral K (2016) Novel 2-phenyl-5-[(E)-2-(thiophen-2-yl)ethenyl]-1,3,4-oxadiazole and 3-phenyl-5-[(E)-2-(thiophen-2-yl)ethenyl]-1,2,4-oxadiazole derivatives as dengue virus inhibitors targeting NS5 polymerase. Eur J Med Chem 109:146–156
Bhatt S, Gething PW, Brady OJ, Messina JP, Farlow AW, Moyes CL, Drake JM, Brownstein JS, Hoen AG, Sankoh O, Myers MF (2013) The global distribution and burden of dengue. Nature 496:504–507
Buccolieri A, Serra A, Maruccio G, Monteduro AG, Padmanabhan SK, Licciulli A, Bonfrate V, Salvatore L, Manno D, Calcagnile L, Giancane G (2017) Synthesis and characterization of mixed iron-manganese oxide nanoparticles and their application for efficient nickel ion removal from aqueous samples. J Anal Meth Chem. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9476065
Casula MF, Conca E, Bakaimi I, Sathya A, Materia ME, Casu A, Falqui A, Sogne E, Pellegrino T, Kanaras AG (2016) Manganese doped-iron oxide nanoparticle clusters and their potential as agents for magnetic resonance imaging and hyperthermia. Phy Chem Chem Phy 18:16848–16855
Chandramohan B, Murugan K, Panneerselvam C, Madhiyazhagan P, Chandirasekar R, Dinesh D, Kumar PM, Kovendan K, Suresh U, Subramaniam J, Rajaganesh R (2016) Characterization and mosquitocidal potential of neem cake-synthesized silver nanoparticles: genotoxicity and impact on predation efficiency of mosquito natural enemies. Parasitol Res 115:1015–25
Chandani SR, Lokhande KB, Swamy KV, Nanda RK, Chitlange SS (2019) Data on docking of phytoconstituents of Actinidia deliciosa on dengue viral targets. Data Brief 25:103996
Chanthini KM, Senthil-Nathan S, Stanley-Raja V, Thanigaivel A, Karthi S, Sivanesh H, Sundar NS, Palanikani R, Soranam R (2019) Chaetomorpha antennina (Bory) Kützing derived seaweed liquid fertilizers as prospective bio-stimulant for Lycopersicon esculentum (Mill). Biocat Agri Biotechnol 20:101190
Chanthini KM, Senthil-Nathan S, Stanley-Raja V, Karthi S, Sivanesh H, Ramasubramanian R, Abdel-Megeed A, Maghraby DM, Ghaith A, Alwahibi MS, Elshikh MS (2021) Biologically active toxin from macroalgae Chaetomorpha antennina Bory, against the lepidopteran Spodoptera litura Fab. and evaluation of toxicity to earthworm, Eudrilus eugeniae Kinb. Chem Biol Technol Agri 8:1–5
Coria C, Almiron W, Valladares G, Carpinella C, Ludueña F, Defago M, Palacios S (2008) Larvicide and oviposition deterrent effects of fruit and leaf extracts from Melia azedarach L. on Aedes aegypti (L.) (Diptera: Culicidae). Biores Technol 99:3066–3070
Dadfar SM, Camozzi D, Darguzyte M, Roemhild K, Varvarà P, Metselaar J, Banala S, Straub M, Güvener N, Engelmann U, Slabu I (2020) Size-isolation of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles improves MRI, MPI and hyperthermia performance. J Nanobiotech 18:1–3
Danga SP, Nukenine EN, Batti AC, Younoussa L, Keziah EA, Esimone CO (2018) Mosquito oviposition-deterrent and ovicidal property of fractions and essential oils from Plectranthus glandulosus and Callistemon rigidus against Aedes aegypti, Anopheles gambiae and Culex quinquefasciatus. Inter J Biol Chem Sci 12:1423–1436
Dos Santos DR, Chaves LL, Pires VC, Rodrigues JS, de Assunção MA, Faierstein GB, Neto AG, de Souza RJ, Albuquerque EC, de Melo SA, Gaspar MC (2023) New weapons against the disease vector Aedes aegypti: from natural products to nanoparticles. Inter J Pharm 10:123221
Duan YT, Soni K, Patel D, Choksi H, Sangan CB, Saeed WS, Ameta KL, Ameta RK (2024) Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using Nicotiana plumbaginifolia and their biological evaluation. J Mol Liq 6:123985
Duong V, Lambrechts L, Paul RE, Ly S, Lay RS, Long KC, Huy R, Tarantola A, Scott TW, Sakuntabhai A, Buchy P (2015) Asymptomatic humans transmit dengue virus to mosquitoes. Pro Nation Acad Sci 112:14688–14693
Dutta B, Checker S, Barick KC, Salunke HG, Gota V, Hassan PA (2021) Malic acid grafted Fe3O4 nanoparticles for controlled drug delivery and efficient heating source for hyperthermia therapy. J Alloys Comp 883:160950
Finney DJ (1971) Probit analysis. Cambridge University, London, pp 68–78
Friesner RA, Banks JL, Murphy RB, Halgren TA, Klicic JJ, Mainz DT, Repasky MP, Knoll EH, Shelley M, Perry JK, Shaw DE (2004) Glide: a new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 1. Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J Med Chem 47:1739–1749
Gowthish K, Kannan R (2019) Pesticidal potentials of some red algal seaweeds from Tuticorin coast against the tobacco cutworm Spodoptera litura Fab. (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Int J Sci Technol Res 8:502–506
Halgren TA, Murphy RB, Friesner RA, Beard HS, Frye LL, Pollard WT, Banks JL (2004) Glide: a new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 2. Enrichment factors in database screening. J Med Chem 47:1750–1759
Hamed SM, Abd El-Rhman AA, Abdel-Raouf N, Ibraheem IB (2018) Role of marine macroalgae in plant protection & improvement for sustainable agriculture technology. Beni-Suef Uni J Bas Appl Sci 7:104–110
Haq SH, Al-Ruwaished G, Al-Mutlaq MA, Naji SA, Al-Mogren M, Al-Rashed S, Ain QT, Al-Amro AA, Al-Mussallam A (2019) Antioxidant, anticancer activity and phytochemical analysis of green algae, Chaetomorpha collected from the Arabian Gulf. Sci Rep 9:1–7
Haribabu V, Farook AS, Goswami N, Murugesan R, Girigoswami A (2016) Optimized Mn-doped iron oxide nanoparticles entrapped in dendrimer for dual contrasting role in MRI. J Biomed Mater Res Part B: Appl Biomater 104:817–824
Hou Y, Qi J, Hu J, **ang Y, **n L, Wei X (2020) Mesoporous Mn-Doped Fe nanoparticle-modified reduced graphene oxide for ethyl violet elimination: modeling and optimization using artificial intelligence. Proc 8:488
Jeyabalan D, Arul N, Thangamathi P (2003) Studies on effects of Pelargonium citrosa leaf extracts on malarial vector, Anopheles stephensi Liston. Biores Technol 89:185–189
Johnson A, Uwa P (2019) Eco-friendly synthesis of iron nanoparticles using Uvaria chamae: characterization and biological activity. Inorg Nano-Metal Chem 49:431–442
Justin C, Philip SA, Samrot AV (2017) Synthesis and characterization of superparamagnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) and utilization of SPIONs in X-ray imaging. Appl Nanosci 7:463–475
Kannan R, Shanmugam KR, Bhaduri S (2019) Status and role of NBFCs. Non-banking financial companies role in India’s development. Springer, Singapore, pp 1–7
Kocbek P, Teskač K, Kreft ME, Kristl J (2010) Toxicological aspects of long-term treatment of keratinocytes with ZnO and TiO2 nanoparticles. Small 6:1908–1917
Kohzadi S, Najmoddin N, Baharifar H, Shabani M (2022) Functionalized SPION immobilized on graphene-oxide: Anticancer and antiviral study. Diamond and Related Materials 127:109149
Koo KN, Ismail AF, Othman MH, Bidin N, Rahman MA (2019) Preparation and characterization of superparamagnetic magnetite (SPION) nanoparticles: a short review, Malays. J Fund Appl Sci 15:23–31
Lakshminarayanan S, Shereen MF, Niraimathi KL, Brindha P, Arumugam A (2021) One-pot green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles from Bauhinia tomentosa: characterization and application towards synthesis of 1, 3 diolein. Sci Rep 11:1–3
Madhiyazhagan P, Murugan K, Kumar AN, Nataraj T, Dinesh D, Panneerselvam C, Subramaniam J, Kumar PM, Suresh U, Roni M, Nicoletti M (2015) Sargassum muticum-synthesized silver nanoparticles: an effective control tool against mosquito vectors and bacterial pathogens. Parasitol Res 114:4305–4317
Majumder I, Paul S, Nag A, Kundu R (2020) Chloroform fraction of Chaetomorpha brachygona, a marine green alga from Indian Sundarbans inducing autophagy in cervical cancer cells in vitro. Sci Rep 10:1–2
Manilal A, Sujith S, Kiran GS, Selvin J, Shakir C, Gandhimathi R, Lipton AP (2009) Antimicrobial potential and seasonality of red algae collected from southwest coast of India tested against shrimp, human and phytopathogens. Ann Microbiol 59:207–219
Martins RM, Nedel F, Guimarães VB, Da Silva AF, Colepicolo P, De Pereira CM, Lund RG (2018) Macroalgae extracts from Antarctica have antimicrobial and anticancer potential. Front Microbial 9:412
Mostafa WA, Abdel-Raoof AM, Attala K, Elgazzar E (2021) Enhancement the larvicidal activity of nanostructure copper oxide against Culex pipiens mosquito by yttrium replacement based on crystallite size reduction and topographic surface nature. Mat Res Exp 8:115006
Murugan K, Aruna P, Panneerselvam C, Madhiyazhagan P, Paulpandi M, Subramaniam J, Rajaganesh R, Wei H, Alsalhi MS, Devanesan S, Nicoletti M (2016) Fighting arboviral diseases: low toxicity on mammalian cells, dengue growth inhibition (in vitro), and mosquitocidal activity of Centroceras clavulatum-synthesized silver nanoparticles. Parasitol Res 115:651–662
Murugan K, Dinesh D, Paulpandi M, Subramaniam J, Rakesh R, Amuthavalli P, Panneerselvam C, Suresh U, Vadivalagan C, Alsalhi MS, Devanesan S (2017) Mangrove helps: Sonneratia alba-synthesized silver nanoparticles magnify guppy fish predation against Aedes aegypti young instars and down-regulate the expression of envelope (E) gene in dengue virus (serotype DEN-2). J Clust Sci 28:437–461
Narayani SS, Saravanan S, Bharathiaraja S, Mahendran S (2016) Extraction, partially purification and study on antioxidant property of fucoxanthin from Sargassum cinereum. J Agardh J Chem Pharm Res 8:610–616
Otadi M, Panahi Shayegh Z, Monajjemi M (2021) Synthesis and characterization of Mn doped ZnO nanoparticles and degradation of pyridine in a batch reactor using: Taguchi experimental designing & molecular mechanic simulation. Biointerface Res Appl Chem 11:12471–12482
Otero-Lorenzo R, Fantechi E, Sangregorio C, Salgueiriño V (2016) Solvothermally driven Mn do** and clustering of iron oxide nanoparticles for heat delivery applications. Chem A Europ J 22:6666–6675
Oukerrou MA, Tilaoui M, Mouse HA, Bouchmaa N, Zyad A (2017) Differential cytotoxic activity of essential oil of Lippia citriodora from different regions in Morocco. Chem Biod 14(7):1600497
Paemanee A, Hitakarun A, Wintachai P, Roytrakul S, Smith DR (2019) A proteomic analysis of the anti-dengue virus activity of andrographolide. Biomed Pharma 109:322–332
Panneerselvam C, Murugan K, Roni M, Aziz AT, Suresh U, Rajaganesh R, Madhiyazhagan P, Subramaniam J, Dinesh D, Nicoletti M, Higuchi A (2016) Fern-synthesized nanoparticles in the fight against malaria: LC/MS analysis of Pteridium aquilinum leaf extract and biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles with high mosquitocidal and antiplasmodial activity. Parasitol Res 115:997–1013
Pattnaik A, Sahoo BR, Pattnaik AK (2020) Current status of Zika virus vaccines: successes and challenges. Vacc 8:266
Powers CN, Setzer W (2016) An in-silico investigation of phytochemicals as antiviral agents against dengue fever. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen 19:516–36
Pratheeba T, Taranath V, Gopal DS, Natarajan D (2019) Antidengue potential of leaf extracts of Pavetta tomentosa and Tarenna asiatica (Rubiaceae) against dengue virus and its vector Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae). Heliyon 5(11):02732
Raguvaran K, Kalpana M, Manimegalai T, Kalaivani S, Devapriya P, Siddharthan N, Balakrishnan R, Silambarasan TS, Maheswaran R (2022) Larvicidal, antioxidant and biotoxicity assessment of (2-(((2-ethyl-2 methylhexyl)oxy) carbonyl) benzoic acid isolated from Bacillus pumilus against Aedes aegypti, Anopheles stephensi and Culex quinquefasciatus. Arch Microb 204(10):650
Rahmani S, Hakimi S, Esmaeily A, Samadi FY, Mortazavian E, Nazari M, Mohammadi Z, Tehrani NR, Tehrani MR (2019) Novel chitosan based nanoparticles as gene delivery systems to cancerous and noncancerous cells. Inter J Pharm 560:306–314
Rahmani R, Gharanfoli M, Gholamin M, Darroudi M, Chamani J, Sadri K, Hashemzadeh A (2020) Plant-mediated synthesis of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) using Aloe vera and flaxseed extracts and evaluation of their cellular toxicities. Ceram Inter 46:3051–3058
Rajaganesh R, Murugan K, Panneerselvam C, Jayashanthini S, Roni M, Suresh U, Trivedi S, Rehman H, Higuchi A, Nicoletti M, Benelli G (2016) Fern-synthesized silver nanocrystals: towards a new class of mosquito oviposition deterrents? Res Veter Sci 109:40–51
Rajapandian R, Kadarkarai M (2023) Encapsulation of silver nano crystals using Salvinia molesta against the Anopheles stephensi and oxidative stress enzyme activity of larvivorous fish. J Nat Pest Res 3:100022
Rajkumar S, Jebanesan A (2005) Scientific Note Oviposition deterrent and skin repellent activities of Solanum trilobatum leaf extract against the malarial vector Anopheles stephensi. J Insect Sci 5(1):15
Rani JM, Kalaimathi K, Vijayakumar S, Varatharaju G, Karthikeyan K, Thiyagarajan G, Bhavani K, Manogar P, Prabhu S (2022) Anti-viral effectuality of plant polyphenols against mutated dengue protein NS2B47-NS3: a computational exploration. Gen Rep 27:101546
Reczyńska K, Marszałek M, Zarzycki A, Reczyński W, Kornaus K, Pamuła E, Chrzanowski W (2020) Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles modified with silica layers as potential agents for lung cancer treatment. Nanomater 10:1076
Rehman AU, Sharafat U, Gul S, Khan MA, Khan SB, Ismail M, Khan MI (2022a) Green synthesis of manganese-doped superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for the effective removal of Pb(ii) from aqueous solutions. Green Process Syn 11(1):287–305
Roni M, Murugan K, Panneerselvam C, Subramaniam J, Nicoletti M, Madhiyazhagan P, Dinesh D, Suresh U, Khater HF, Wei H, Canale A (2015) Characterization and biotoxicity of Hypnea musciformis-synthesized silver nanoparticles as potential eco-friendly control tool against Aedes aegypti and Plutella xylostella. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 121:31–38
Samrot AV, SaiPriya C, Selvarani J, Jane Cypriyana PJ, Lavanya Y, Soundarya P, Sherly Priyanka SP, Sangeetha P, Varghese RJ (2020) A study on influence of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) on green gram (Vigna radiata L.) and earthworm (Eudrilus eugeniae L.). Mater Res Exp 7:055002
Shaalan EA, Canyon D, Younes MW, Abdel-Wahab H, Mansour AH (2005) A review of botanical phytochemicals with mosquitocidal potential. Environ Inter 31:1149–1166
Singh H, Du J, Singh P, Mavlonov GT, Yi TH (2018) Development of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles via direct conjugation with ginsenosides and its in-vitro study. J Photochem Photobiol b: Biol 185:100–110
Srivastava GK, Alonso-Alonso ML, Fernandez-Bueno I, Garcia-Gutierrez MT, Rull F, Medina J, Coco RM, Pastor JC (2018) Comparison between direct contact and extract exposure methods for PFO cytotoxicity evaluation. Sci Rep 8:1–9
Sujitha V, Murugan K, Paulpandi M, Panneerselvam C, Suresh U, Roni M, Nicoletti M, Higuchi A, Madhiyazhagan P, Subramaniam J, Dinesh D (2015) Green-synthesized silver nanoparticles as a novel control tool against dengue virus (DEN-2) and its primary vector Aedes aegypti. Parasitol Res 114:3315–3325
Trujillo-Correa AI, Quintero-Gil DC, Diaz-Castillo F, Quiñones W, Robledo SM, Martinez-Gutierrez M (2019) In vitro and in silico anti-dengue activity of compounds obtained from Psidium guajava through bioprospecting. BMC Com Alter Med 19:1–6
Wadehra N, Gupta R, Prakash B, Sharma D, Chakraverty S (2017) Biocompatible ferrite nanoparticles for hyperthermia: effect of polydispersity, anisotropy energy and inter-particle interaction. Mater Res Exp 4:025037
Wahab NZ, Ibrahim N, Kamarudin MK, Lananan F, Juahir H, Ghazali A, Yusra AI (2018) Cytotoxicity and antiviral activity of Annona muricata aqueous leaves extract against dengue virus type 2. J Fund Appl Sci 10:580–589
Waris M, Nasir S, Abbas S, Azeem M, Ahmad B, Khan NA, Hussain B, Al-Ghanim KA, Al-Misned F, Mulahim N, Mahboob S (2020) Evaluation of larvicidal efficacy of Ricinus communis (Castor) and synthesized green silver nanoparticles against Aedes aegypti L. Saudi J Boil Sci 27:2403–2409
World Health Organization, Regional Office for the Western Pacific, Dengue situation updates (2021) WHO Regional Office for the Western Pacific. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/341149
Yu KX, Wong CL, Ahmad R, Jantan I (2015) Larvicidal activity, inhibition effect on development, histopathological alteration and morphological aberration induced by seaweed extracts in Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae). Asia Pac J Trop Med 8:1006–1012
Zhang M, Cao Y, Wang L, Ma Y, Tu X, Zhang Z (2015) Manganese doped iron oxide theranostic nanoparticles for combined T1 magnetic resonance imaging and photothermal therapy. ACS Appl Mater Inter 7:4650–4658
Zhang T, Wang ML, Zhang GR, Liu W, **ao XQ, Yang YS, Li JT, Xun ZM, Li DY, Chan PK (2019) Recombinant DENV 2 NS5: an effective antigen for diagnosis of DENV infection. J Virol Meth 265:35–41
Acknowledgements
For the verification of algae, we are grateful to the Central Salt and Marine Chemicals Research Institute (Council of Scientific and Industrial Research), Mandabam Camp, Ramanadhapuram District, Tamil Nadu, India. The mosquito larvae were provided by the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) in Mettupalayam, Tamil Nadu. We are grateful to Bharathiar University’s Common Instrumentation Centre in Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, for providing the essential infrastructural facilities for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RR — conceptualization; data curation; formal analysis; investigation; methodology; software; supervision; validation; visualization; original draft.
KM — investigation; supervision; validation; visualization; original draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
We confirm that if the paper is accepted, it could be published in this prestigious journal.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rajaganesh, R., Murugan, K. Anti-dengue potential and mosquitocidal effect of marine green algae–stabilized Mn-doped superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (Mn-SPIONs): an eco-friendly approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 19575–19594 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32413-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32413-y