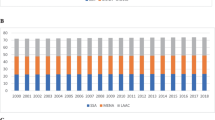
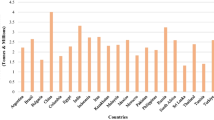
Abstract
Financial deepening is important in resource allocation for more productive enterprises, leading to sustainable green growth. Moreover, rapid development in the digital economy and export diversification significantly affect green growth. From this perspective, our study explores the impact of financial deepening, ICT development, and export diversification on green growth in China’s economies from 1996 to 2021. The study explores the linkage between financial deepening, ICT development, export diversification, and green growth by employing the nonlinear autoregressive distributed lag (NARDL) approach. The results obtained in the long run are as follows: positive shock in financial deepening brings positive change in green growth, whereas negative shock in financial deepening reduces green growth. In the long run, positive shock in ICT enhances green growth, but negative shock in ICT does not impact green growth. Moreover, positive shock in export diversification brings positive change in green growth, whereas negative shock in export diversification reports an insignificant impact on green growth. Based on findings, it is suggested that financial deepening, ICT development, and export diversification are conducive to sustainable green growth.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Aghion P, Howitt P, Brant-Collett M, & García-Peñalosa C (1998) Endogenous growth theory. MIT press.
Ahmed M, Hafeez M, Kaium MA, Ullah S, Ahmad H (2023) Do environmental technology and banking sector development matter for green growth? Evidence from top-polluted economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(6):14760–14769
Aragón-Correa JA, Hurtado-Torres N, Sharma S, García-Morales VJ (2008) Environmental strategy and performance in small firms: a resource-based perspective. J Environ Manage 86(1):88–103
Assi AF, Isiksal AZ, Tursoy T (2020) Highlighting the connection between financial development and consumption of energy in countries with the highest economic freedom. Energy Policy 147:111897
Bastida L, Cohen JJ, Kollmann A, Moya A, Reichl J (2019) Exploring the role of ICT on household behavioural energy efficiency to mitigate global warming. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 103:455–462
Cao J, Law SH, Samad ARBA, Mohamad WNBW, Wang J, Yang X (2022) Effect of financial development and technological innovation on green growth—analysis based on spatial Durbin model. J Clean Prod 365:132865
Chang SC (2015) Effects of financial developments and income on energy consumption. Int Rev Econ Financ 35:28–44
Chao T, Yunbao X, Chengbo D, Bo L, Ullah S (2023) Financial integration and renewable energy consumption in China: do education and digital economy development matter? Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(5):12944–12952
Chen R, Ramzan M, Hafeez M, Ullah S (2023) Green innovation-green growth nexus in BRICS: does financial globalization matter? J Innov Knowl 8(1):100286
Deshuai M, Hui L, Ullah S (2022) Pro-environmental behavior–Renewable energy transitions nexus: Exploring the role of higher education and information and communications technology diffusion. Front Psychol 13:1010627
Dwivedi YK, Hughes L, Kar AK, Baabdullah AM, Grover P, Abbas R, Wade M (2022) Climate change and COP26: are digital technologies and information management part of the problem or the solution? An editorial reflection and call to action. Int J Inform Manag 63:102456
Fu F, Ullah S (2023) Toward green growth in China: The role of green finance investment, technological capital, and renewable energy consumption. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 30(28):72664–72674
Hafeez M, Rehman SU, Faisal CN, Yang J, Ullah S, Kaium MA, Malik MY (2022) Financial efficiency and its impact on renewable energy demand and CO2 emissions: do eco-innovations matter for highly polluted Asian economies? Sustainability 14(17):10950
Haini H, Loon PW, Li PL (2023) Can export diversification promote export upgrading? Evidence from an oil-dependent economy. Resour Policy 80:103292
Hassan A, Yang J, Usman A, Bilal A, Ullah S (2023) Green growth as a determinant of ecological footprint: do ICT diffusion, environmental innovation, and natural resources matter? PLoS ONE 18(9):e0287715
Herzer D, Nowak-Lehnmann D, F. (2006) What does export diversification do for growth? Econ Anal Appl Econ 38(15):1825–1838
Iqbal N, Abbasi KR, Shinwari R, Guangcai W, Ahmad M, Tang K (2021) Does exports diversification and environmental innovation achieve carbon neutrality target of OECD economies? J Environ Manage 291:112648
Lee CC, **ng W, Wu W, Lee CC (2023) Export diversification and the green economy: the key role of economic risk. Technol Econ Dev Econ 29(2):717–740
Li X, Ozturk I, Majeed MT, Hafeez M, Ullah S (2022a) Considering the asymmetric effect of financial deepening on environmental quality in BRICS economies: policy options for the green economy. J Clean Prod 331:129909
Li X, Ozturk I, Ullah S, Andlib Z, Hafeez M (2022b) Can top-pollutant economies shift some burden through insurance sector development for sustainable development? Econ Anal Pol 74:326–336
Liu K, Meng C, Tan J, Zhang G (2023) Do smart cities promote a green economy? Evidence from a quasi-experiment of 253 cities in China. Environ Impact Assess Rev 99:107009
Meng Y, Wu H, Wang Y, Duan Y (2022) International trade diversification, green innovation, and consumption-based carbon emissions: the role of renewable energy for sustainable development in BRICST countries. Renew Energy 198:1243–1253
Mo Y, Ullah S, Ozturk I (2023) Green investment and its influence on green growth in high polluted Asian economies: Do financial markets and institutions matter? Econ Res-Ekon Istraz 36(2):2140302
Nye JS Jr (2020) Power and interdependence with China. Wash Q 43(1):7–21
OECD. (2012). OECD Work on Green Growth. Retrieved April 23, 2023, http://www.oecd.org/greengrowth/oecdworkongreengrowth.htm
Ozturk I, Ullah S (2022) Does digital financial inclusion matter for economic growth and environmental sustainability in OBRI economies? An empirical analysis. Resour Conserv Recycl 185:106489
Park H, Kim JD (2020) Transition towards green banking: role of financial regulators and financial institutions. Asian J Sustain Soc Respons 5(1):1–25
Pesaran MH, Shin Y, Smith RJ (2001) Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. J Appl Economet 16(3):289–326
Qian Y, Liu J, Cheng Z, Forrest JYL (2021) Does the smart city policy promote the green growth of the urban economy? Evidence from China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:66709–66723
Saleem R, Nasreen S, Azam S (2022) Role of financial inclusion and export diversification in determining green growth: evidence from SAARC economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(40):60327–60340
Sarin V, Mahapatra SK, Sood N (2022) Export diversification and economic growth: a review and future research agenda. J Public Aff 22(3):e2524
Shahzad U, Ferraz D, Doğan B, do Nascimento Rebelatto, D. A. (2020) Export product diversification and CO2 emissions: contextual evidences from develo** and developed economies. J Clean Prod 276:124146
Sharma R, Sinha A, Kautish P (2021) Examining the nexus between export diversification and environmental pollution: evidence from BRICS nations. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:61732–61747
Shen Z, Wang S, Boussemart JP, Hao Y (2022) Digital transition and green growth in Chinese agriculture. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 181:121742
Shin Y, Yu B & Greenwood-Nimmo M (2014) Modelling asymmetric cointegration and dynamic multipliers in a nonlinear ARDL framework. Festschrift in honor of Peter Schmidt: Econ Methods Appl 281–314.
Swinton SM, Escobar G, Reardon T (2003) Poverty and environment in Latin America: concepts, evidence and policy implications. World Dev 31(11):1865–1872
Tang Y, Chen W, Chen S, Sohail MT (2023) Examining the potential role of ICT diffusion on green growth: does financial development matter in BRICS economies? Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(13):38582–38591
UNESCAP (2012) Green Growth and Green Economy. Retrieved April 23, 2023, from United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific: http://www.unescap.org/our-work/environment-development/green-growthgreeneconomy/about
Usman A, Ozturk I, Hassan A, Zafar SM, Ullah S (2021) The effect of ICT on energy consumption and economic growth in South Asian economies: an empirical analysis. Telematics Inform 58:101537
Wang Y & Ullah S (2023) Effects of digitalization on energy security risk: do financial development and environmental trade matter?. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–13.
Yan Z, Sun Z, Shi R, Zhao M (2023) Smart city and green development: empirical evidence from the perspective of green technological innovation. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 191:122507
Zarach ZH, Parteka A (2023) Export diversification and dependence on natural resources. Econ Model 126:106436
Zhang J, Lyu Y, Li Y, Geng Y (2022) Digital economy: an innovation driving factor for low-carbon development. Environ Impact Assess Rev 96:106821
Zhao X, Ma X, Shang Y, Yang Z, Shahzad U (2022) Green economic growth and its inherent driving factors in Chinese cities: Based on the Metafrontier-global-SBM super-efficiency DEA model. Gondwana Res 106:315–328
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Rui Hu: idea, software, methodology, and writing—original draft preparation. Baodan Liu: reviewing and editing, and methodology. Sidra Sohail: conceptualization, writing—original draft preparation, and reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
I am free to contact any of the people involved in the research to seek further clarification and information.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ilhan Ozturk
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, R., Liu, B. & Sohail, S. Green growth path dependence momentum under the prism of COP26: the role of financial deepening, ICT development, and export diversification. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 20073–20083 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32277-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32277-2