Abstract
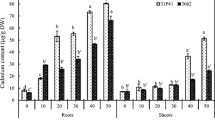
Phytoremediation is an effective way to reduce heavy metal content in agricultural soil. The effects of brackish water irrigation on phytoremediation efficiency of plants have not yet been completely understood. In this study, the effects of brackish water irrigation on cadmium (Cd) uptake by maize as the phytoremediator were investigated. In a pot experiment, maize seedlings were grown in soil with exogenously added Cd (0, 5, 10, or 15 mg kg−1) and irrigated with deionized water (T1), natural brackish water (T2), or water with NaCl with salinity equal to that of natural brackish water (T3). Salt stress and cation antagonism caused by brackish water affected maize plant growth and Cd uptake. Under 5, 10, and 15 mg kg−1 Cd, Cd accumulation in maize shoots was 5.55, 7.08, and 5.71 μg plant–1; 4.08, 3.04, and 5.38 μg plant–1; and 2.48, 3.44, and 5.33 μg plant–1 under the T1, T2, and T3 treatments, respectively. Cd accumulation in the shoots was significantly lower under the T2 and T3 treatments than under the T1 treatment at 5 and 10 mg kg−1 Cd; however, no significant differences were observed among all treatments at 15 mg kg−1 Cd. These findings indicated that phytoremediation efficiency decreased in response to both salt stress and cation antagonism caused by brackish water under low soil-Cd concentrations; however, this effect was negligible under high soil-Cd concentration. Therefore, brackish water irrigation can be considered for the phytoremediation of soils contaminated with high Cd levels to save freshwater resources.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Materials availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Ahmad A, Hadi F, Ahmad H, Jan AU, Ahmad S (2017) Salinity in soil increased cadmium uptake and accumulation potential of two terrestrial plants. Int J Biosci (IJB) 10(3):132–142
Bao S (2000) Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis, 3rd edn. Chinese Agriculture Press, Bei**g
Filipovic L, Romic M, Romic D, Filipovic V, Ondrasek G (2018) Organic matter and salinity modify cadmium soil (phyto)availability. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:824–831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.09.041
Ghallab A, Usman ARA (2007) Effect of sodium chloride-induced salinity on phyto-availability and speciation of cd in soil solution. Water Air Soil Pollut 185:43–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9424-y
Gupta P, Seth CS (2019) Nitrate supplementation attenuates As(V) toxicity in Solanum lycopersicum L. cv Pusa Rohini: insights into As(V) sub-cellular distribution, photosynthesis, nitrogen assimilation, and DNA damage. Plant Physiol Bioch 139:44–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.03.007
Gupta S, Seth CS (2021) Salicylic acid alleviates chromium (VI) toxicity by restricting its uptake, improving photosynthesis and augmenting antioxidant defense in Solanum lycopersicum L. Physiol Mol Biol Pla 27:2651–2664. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-021-01088-x
Hakeem KR, Alharby HF, Pirzadah TB (2022) Exogenously applied calcium regulates antioxidative system and reduces cadmium-uptake in fagopyrum esculentum. Plant Physiol Biochem 180:17–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.03.011
Hamid Y, Tang L, Hussain B et al (2020) Organic soil additives for the remediation of cadmium contaminated soils and their impact on the soil-plant system: a review. Sci Total Environ 707:136121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136121
Huang YZ, Wei K, Yang J, Dai F, Zhang GP (2007) Interaction of salinity and cadmium stresses on mineral nutrients, sodium, and cadmium accumulation in four barley genotypes. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 8:476–485. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2007.B0476
Ionov M, Yuldasheva N, Ulchenko N, Glushenkova AI, Heuer B (2013) Growth, development and yield of Crambe abyssinica under saline irrigation in the greenhouse. J Agron Crop Sci (1986) 199:331–339. https://doi.org/10.1111/jac.12027
Ji Y, Wan Y, Wang Q, Zhang Y, Li H (2017) Effects of root characteristics and transpiration on cadmium uptake by cucumber seedlings under varied iron levels. Acta Sci Circum 37:1939–1946
Jia Y, Li J, Zeng X et al (2022) The performance and mechanism of cadmium availability mitigation by biochars differ among soils with different pH: hints for the reasonable choice of passivators. J Environ Manag 312:114903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114903
Jiang XJ, Luo YM, Liu Q, Liu SL, Zhao QG (2004) Effects of cadmium on nutrient uptake and translocation by Indian mustard. Environ Geochem Health 26:319–324. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:EGAH.0000039596.15586.b3
**gyun F, **nxing N, Bo L, Fangmin LI, Li Y (2021) Efficiency of in-situ passivation remediation in cadmium-contaminated farmland soil and its mechanism: a review. J Agric Resour Environ 38(05):764–777. https://doi.org/10.13254/j.jare.2020.0521
Kadkhodaie A, Kelich S, Baghbani A (2012) Effects of salinity levels on heavy metals (Cd, Pb and Ni) absorption by sunflower and sudan grass plants. Bull Env Pharmacol Life Scien 1:47–53
Kumar D, Dhankher OP, Tripathi RD, Seth CS (2023) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles potentially regulate the mechanism(s) for photosynthetic attributes, genotoxicity, antioxidants defense machinery, and phytochelatins synthesis in relation to hexavalent chromium toxicity in Helianthus annuus L. J Hazard Mater 454:131418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131418
Li J, Xu Y (2022) Use of palygorskite to remediate cd polluted paddy soils under different water managements. Chin J Soil Sci 53:965–971
Liu JG, Liang JS, Li KQ et al (2003) Correlations between cadmium and mineral nutrients in absorption and accumulation in various genotypes of rice under cadmium stress. Chemosphere 52:1467–1473. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00484-3
Long L, Zhang X, Luo J, Liu F (2022) Review of phytoremediation of cadmium contaminated soil. Appl Chem Ind 51:2143–2147
Ma K, Wang Z, Li H, Wang T, Chen R (2022) Effects of nitrogen application and brackish water irrigation on yield and quality of cotton. Agric Water Manag 264:107512
Mariyam S, Bhardwaj R, Khan NA, Sahi SV, Seth CS (2023) Review on nitric oxide at the forefront of rapid systemic signaling in mitigation of salinity stress in plants: crosstalk with calcium and hydrogen peroxide. Plant Sci 336:111835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2023.111835
Mensah E, Odai SN, Ofori E, Kyei-Baffour N (2008) Influence of transpiration on cadmium (Cd) and lead (Pb) uptake by cabbage, carrots and lettuce from irrigation water in Ghana. Asian J Agric Res 2:56–60
Naidu R, Bolan NS (2008) Contaminant chemistry in soils: key concepts and bioavailability. In: Hartemink AE, Mcbratney AB, Naidu R (eds) Developments in Soil Science. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 9–37
Qin S, Liu H, Nei Z et al (2020) Toxicity of cadmium and its competition with mineral nutrients for uptake by plants: a review. Pedosphere 30:168–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(20)60002-9
Rajendran S, Priya TAK, Khoo KS et al (2022) A critical review on various remediation approaches for heavy metal contaminants removal from contaminated soils. Chemosphere 287:132369
Sarwar N, Imran M, Shaheen MR et al (2017) Phytoremediation strategies for soils contaminated with heavy metals: modifications and future perspectives. Chemosphere 171:710–721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.12.116
Shah V, Daverey A (2020) Phytoremediation: a multidisciplinary approach to clean up heavy metal contaminated soil. Environ Technol Innov 18:100774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.100774
Shi R, Liang L, Liu W, Zeb A (2022) Kochia scoparia l., a newfound candidate halophyte, for phytoremediation of cadmium-contaminated saline soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 29:44759–44768. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18895-8
Siddique AB, Rahman MM, Islam MR, Naidu R (2022) Influences of soil pH, iron application and rice variety on cadmium distribution in rice plant tissues. Sci Total Environ 810:152296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152296
Takahashi H, Aoyama Y, Kikuchi N, Kawai S (2011) Evaluation for suppressive effects of additives on cadmium uptake of komatsuna grown in cadmium-contaminated soil. Kankyou Kagakkaishi 24:23–34. https://doi.org/10.11353/sesj.24.23
Tang X, Pang Y, Ji P, Gao P, Nguyen TH, Tong Y (2016) Cadmium uptake in above-ground parts of lettuce (Lactuca sativa l.). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 125:102–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.11.033
Tang X, Song Y, He X, Yi L (2019) Enhancing phytoremediation efficiency using regulated deficit irrigation. Pol J Environ Stud 28:2399–2405. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/91043
Usman ARA, Renella G (2015) Influence of NaCl-induced salinity and cd toxicity on respiration activity and Cd availability to barley plants in farmyard manure-amended soil. Appl Environ Soil Sci 2015:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/483836
Wang L, Chen H, Guo F, Zhang X, Fan Z, Wan S (2013) Effects of cadmium on peanut growth and mineral nutrient uptake. J Agro-Environ Sci 32:1106–1110
Wang S, Dai H, Cui S et al (2023) The effects of salinity and pH variation on hyperaccumulator Bidens pilosa l. accumulating cadmium with dynamic and real-time uptake of Cd2+ influx around its root apexes. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25213-3
Wei K, Zhang J, Wang Q, Guo Y, Mu W (2022) Irrigation with ionized brackish water affects cotton yield and water use efficiency. Ind Crops Prod 175:114244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.114244
Wielgusz K, Praczyk M, Irzykowska L, Świerk D (2022) Fertilization and soil pH affect seed and biomass yield, plant morphology, and cadmium uptake in hemp (Cannabis sativa l.). Ind Crops Prod 175:114245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.114245
**ao-Jun LU, Bo-Wen LI, Yang Z, Jia Y, Shu-Na LI (2010) Effects of microorganisms on the bioavailability of cadmium, lead and zinc in soil. J Agro-Environ Sci 29:1315–1319
Yanai JKUJ, Mabuchi N, Moritsuka N, Kosaki T (2004) Distribution and forms of cadmium in the rhizosphere of brassica juncea in Cd-contaminated soils and implications for phytoremediation. Soil Sci Plant Nutrition (tokyo) 50:423–430. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.2004.10408496
Zhao L, Gao K, Huang T, Gao Y, Ju T, Jiang Q, ** H, **ong L, Tang Z, Gao C (2023) The cadmium accumulation characteristics of maize inbred lines with high/low grain cadmium accumulation at different growth stages. Ecol Environ 32:766–775. https://doi.org/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2023.04.014
Funding
This research was funded by the Science and Technology Project of Hebei Education Department (grant No. BJ2021049), the foundation of Hebei University of Environmental Engineering (grant No.2023XJKT12), and the S&T Program of Qinhuangdao (202101A103). We thank Liwen Bianji, Edanz Group China (www.liwenbianji.cn/ac), for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, pot experiments, and sample collection were performed by XT, YH, and JZ. Data collection and analysis were performed by XT, YL, and YS. The first draft of the manuscript was written by XT and YH, and all authors provided insights on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Elena Maestri
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, Y., Zhang, J., Liang, Y. et al. Effect of brackish water irrigation on cadmium migration in a soil–maize system. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 12995–13002 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32041-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-32041-6