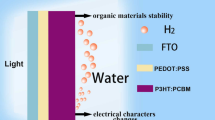
Abstract
Photoelectrochemical setups based on semiconductor photoelectrodes are known for their effectiveness in wastewater treatment, powered by solar energy, which is a renewable and sustainable source. These systems require semiconductor photocatalysts with excellent light-absorbing properties and high stability in aqueous environments. In this regard, silicon is highly investigated in solar cells thanks to its narrow bandgap, making it a potential solar harvester. Metal oxides stand as promising semiconductors, which are non-toxic and thermodynamically stable. In this work, two high-efficiency silicon-based cells have been investigated via Solar Cell Capacitance Simulator (SCAPS-1D) software. Thickness and do** concentration, of each layer, have been scrutinized for multiple buffer propositions to investigate the physical feasibility and optimal values allowing maximal light harvesting. It was found that the overall cell performance is influenced by extremely high do** concentrations for some layers. The effect of temperature was investigated as well at temperatures ranging from 300 to 350 K; it was discovered that the cell demonstrates great performance at the ambient temperature. A maximum solar efficiency of about 25.44% was calculated. Our findings build the path towards fabricating highly efficient Si-based solar cells for photoelectrochemical wastewater treatment.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used in this paper will be available on request.
References
Abd El Halim B, Mahfoud A, Mohammed Elamine D (2020) Numerical analysis of potential buffer layer for Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) solar cells. Optik (Stuttg) 204:164155. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJLEO.2019.164155
Anderson RL (1960) Germanium-gallium arsenide heterojunctions [letter to the editor]. IBM J Res Dev 4:283–287. https://doi.org/10.1147/RD.43.0283
Anggraini D, Kusuma Wardani P, Agustina M, et al (n.d.) Tio2/Co3O4 composite as photoanode of photoelectrochemical water splitting. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1351/1/012032
Aroonratsameruang P, Chakthranont P, Pattanasattayavong P (2021) The cause of limited photoelectrochemical water reduction performance of Co3O4 photocathodes. Mater Chem Phys 270:124834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.124834
Bae D, Seger B, Hansen O et al (2019) Durability testing of photoelectrochemical hydrogen production under day/night light cycled conditions. ChemElectroChem 6:106–109. https://doi.org/10.1002/celc.201800918
Bak T, Nowotny J, Rekas M, Sorrell CC (2002) Photo-electrochemical hydrogen generation from water using solar energy. Materials-related aspects Int J Hydrogen Energy 27:991–1022. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-3199(02)00022-8
Bally A (1999) Electronic properties of nano-crystalline titanium dioxide thin films. https://doi.org/10.5075/EPFL-THESIS-2094
Boumaour M, Sali S, Kermadi S et al (2019) High efficiency silicon solar cells with back ZnTe layer hosting IPV effect: a numerical case study 13:696–703. https://doi.org/10.1080/16583655.2019.1623476
Burgelman M, Nollet P, Degrave S (2000) Modelling polycrystalline semiconductor solar cells. Thin Solid Films 361:527–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6090(99)00825-1
Chen X, Wu Z Liu D, Gao Z (n.d.) Preparation of ZnO photocatalyst for the efficient and rapid photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-017-1904-4
Elango G, Roopan SM (2016) Efficacy of SnO2 nanoparticles toward photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 155:34–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JPHOTOBIOL.2015.12.010
Gerischer H (n.d.) The role of semiconductor structure and surface properties in photoelectrochemical processes. 17
Habisreutinger SN, Schmidt-Mende L, Stolarczyk JK (2013) Photocatalytic reduction of CO2 on TiO2 and other semiconductors. Angew Chemie - Int Ed 52:7372–7408. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201207199
Hussain B, Aslam A, Khan TM, et al (2019) Electron affinity and bandgap optimization of zinc oxide for improved performance of ZnO/Si heterojunction solar cell using PC1D simulations. Electron 2019, Vol 8, Page 238 8:238. https://doi.org/10.3390/ELECTRONICS8020238
Jiang C et al (2017) Photoelectrochemical devices for solar water splitting – materials and challenges. Chem Soc Rev 46:4645–4660. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CS00306K
King LA, Hellstern TR, Park J et al (2017) Highly stable molybdenum disulfide protected silicon photocathodes for photoelectrochemical water splitting. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:36792–36798. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b10749
Kraut EA (1989) The effect of a valence-band offset on potential and current distributions in HgCdTe heterostructures the effect of a valence-band offset on barrier formation in graded Hg1−x cd x Te heterojunctions. Cit J Vac Sci Technol A 7:6373. https://doi.org/10.1116/1.576195
Künneth C, Batra R, Rossetti GA et al (2019) Thermodynamics of phase stability and ferroelectricity from first principles. Ferroelectr Doped Hafnium Oxide Mater Prop Devices 245–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-102430-0.00006-1
Larsson F, Keller J, Edoff M, Törndahl T (2017) Evaluation of different intrinsic ZnO and transparent conducting oxide layer combinations in Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells. Thin Solid Films 633:235–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TSF.2016.09.015
Lee SY, Park SJ (2013) TiO2 photocatalyst for water treatment applications. J Ind Eng Chem 19:1761–1769. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JIEC.2013.07.012
Leung DYC, Xuan J (2015) Micro & nano-engineering of fuel cells. CRC Press
Li F, Liu Q, Hu J et al (2020) Recent progresses on SnO2 anode materials for sodium storage. J. Phys. D. Appl, Phys, p 53
Liao H, Deng Q, Shen Y et al (2020) Theoretical analysis of do** concentration, layer thickness and barrier height effects on BaSi2 based homojunction solar cells toward high efficiency. Sol Energy 201:857–865. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SOLENER.2020.03.056
Luo Z, Wang T, Gong J (2019) Single-crystal silicon-based electrodes for unbiased solar water splitting: current status and prospects. Chem Soc Rev 48:2158–2181. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8CS00638E
Mandadapu U, Vedanayakam SV, Thyagarajan K, Babu BJ (2018) Optimisation of high efficiency tin halide perovskite solar cells using SCAPS-1D. Int J Simul Process Model 13:221–227. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijspm.2018.093097
Mao J, Wang Y, Zheng Z, Deng D (2018) The rise of two-dimensional MoS2 for catalysis. Front Phys 13:138118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-018-0812-0
Patel M, Ban D-K, Nguyen TT, Kim J (2019) Earth-abundant semiconductors based electric power window. ECS Trans 92:15–20. https://doi.org/10.1149/09209.0015ecst
Pogrebnyak AD, Jamil NY, Muhammed AKM (2011) Simulation study of n-ZnO/p-Si heterojunction solar cell. Nanosystems Nanomaterials Nanotechnologies 9:819–830
Rashid H, Rahman KS, Hossain MI et al (2014) Prospects of molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) as an alternative absorber layer material in thin film solar cells from numerical modeling. Chalcogenide Lett 11:397–403
Remello SN, Hirano T, Kuttassery F et al (2015) Visible light induced oxygenation of alkenes with water sensitized by silicon-porphyrins with the second most earth-abundant element. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 313:176–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2015.07.016
Sah CT, Yamakawa KA, Lutwack R (1982) Effect of thickness on silicon solar cell efficiency. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 29:903–908. https://doi.org/10.1109/T-ED.1982.20797
Sakthivel S, Neppolian B, Shankar MV et al (2003) Solar photocatalytic degradation of azo dye: comparison of photocatalytic efficiency of ZnO and TiO2. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 77:65–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-0248(02)00255-6
Sayama K (2012) Mixed metal oxide photoelectrodes and photocatalysts. In: van de Krol R, Grätzel M (eds) Photoelectrochemical hydrogen production. Springer, US, Boston, MA, pp 157–172
Tammina SK, Mandal BK, Kadiyala NK (2018) Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye by nonconventional synthesized SnO2 nanoparticles. Environ Nanotechnology, Monit Manag 10:339–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENMM.2018.07.006
Tilley SD, Lany S, Krol R van de (2018) Advances in photoelectrochemical water splitting: theory, experiment and systems analysis. Royal Society of Chemistry
Zhang H, Cheng S, Yu J, et al (2016) Prospects of Zn(O,S) as an alternative buffer layer for Cu2ZnSnS4 thin-film solar cells from numerical simulation. Micro Nano Lett 11:386–390. https://doi.org/10.1049/MNL.2016.0130
Acknowledgements
This work is created under the FuelWater project by the Transformers program of IsDb submitted by the Green Energy Park. The authors would also like to express their appreciation to Dr. M. Burgelman from Ghent university for providing such a useful simulation software tool (SCAPS-1D) used in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hammam Zahdi: writing–review and editing, writing–original draft, methodology, investigation, formal analysis, data curation, conceptualization. Oussama Oulhakem: writing–review and editing, writing–original draft, validation, methodology, investigation, conceptualization. Safae Aazou: writing–review and editing, validation, supervision. Saida Laalioui: writing–review and editing, validation. Mohammed Belaïche: validation. Kawtar Belrhiti Alaoui: visualization, validation, supervision, resources, project administration, methodology, funding acquisition. Zouheir Sekkat: validation, resources, project administration, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zahdi, H., Oulhakem, O., Aazou, S. et al. Numerical simulation study of high-efficiency silicon-based cell destined for photoelectrochemical wastewater treatment. Environ Sci Pollut Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31805-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31805-w