Abstract
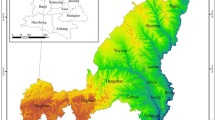
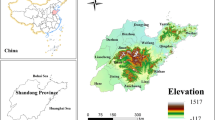
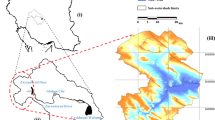
Investigating habitat quality under different climate scenarios holds significant importance for sustainable land resource management and ecological conservation. In this study, considering Nanchang as a case study, a coupled patch-generating land use simulation (PLUS) and system dynamics (SD) model was employed in the simulation and prediction of land usage under shared socioeconomic pathway (SSP) and representative concentration pathway (RCP) scenarios. To assess the habitat quality in Nanchang from 2000 to 2020 and in 2030 under three diverse climate scenarios, we used the Integrated Valuation of Ecosystem Services and Trade-offs (InVEST) model to analyze spatial and temporal changes. The findings indicate that the regions of forest land, cultivated land, and grassland in Nanchang City will dramatically decrease by 2030, the construction land will rapidly expand, and the fluctuations in the unutilized land and water area will be minimal. Additionally, the habitat quality declined from 2000 to 2020, and its spatial distributions changed. Zones having a high overall habitat quality were distributed in the mountains, hills, and lake areas, whereas those with relatively low quality were found in cultivated and urban areas. Under three climate scenarios, in 2030, the habitat quality index for Nanchang City will show a decreasing trend, mainly owing to areas with an index of 0.3–0.5 transitioning to <0.3. Considering each scenario, the degree of habitat degradation increased in the order SSP585>SSP245>SSP119. The findings of this study will inform high-quality development and biodiversity conservation in Nanchang City.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert CH, Rayfield B, Dumitru M, Gonzalez A (2017) Applying network theory to prioritize multispecies habitat networks that are robust to climate and land-use change. Conserv Biol 31(6):1383–1396
Bagstad KJ, Villa F, Batker D, Harrison-Cox J, Voigt B, Johnson GW (2014) From theoretical to actual ecosystem services: map** beneficiaries and spatial flows in ecosystem service assessments. Ecol Soc 19(2):64. https://doi.org/10.5751/ES-06523-190264
Bai L, **u C, Feng X, Liu D (2019) Influence of urbanization on regional habitat quality: a case study of Changchun City. Habitat Int 93:102042
Berta Aneseyee A, Noszczyk T, Soromessa T, Elias E (2020) The InVEST habitat quality model associated with land use/cover changes: a qualitative case study of the Winike Watershed in the Omo-Gibe Basin, Southwest Ethiopia. Remote Sens 12(7):1103
Brunner L, Pendergrass AG, Lehner F, Merrifield AL, Lorenz R, Knutti R (2020) Reduced global warming from CMIP6 projections when weighting models by performance and independence. Earth Syst Dynam 11(4):995–1012
Cai G, Lin Y, Zhang F, Zhang S, Wen L, Li B (2022) Response of ecosystem service value to landscape pattern changes under low-carbon scenario: a case study of Fujian Coastal Areas. Land 11(12):2333
Chen Y, Guo F, Wang J, Cai W, Wang C, Wang K (2020) Provincial and gridded population projection for China under shared socioeconomic pathways from 2010 to 2100. figshare. Collection. https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.c.4605713.v1
Chi Y, Shi H, Zheng W, Sun J, Fu Z (2018) Spatiotemporal characteristics and ecological effects of the human interference index of the Yellow River Delta in the last 30 years. Ecol Indic 89:880–892
Du F, Chen S, Pu J (2023) Land use change and spatial and temporal evolution of habitat quality in southeast Fujian from 2000 to 2020. Res Soil Water Conserv 6:345–356
Hu B, Kang F, Han H, Cheng X, Li Z (2021) Exploring drivers of ecosystem services variation from a geospatial perspective: insights from China’s Shanxi Province. Ecol Indic 131:108188
Huang J, Tang Z, Liu D, He J (2020) Ecological response to urban development in a changing socio-economic and climate context: policy implications for balancing regional development and habitat conservation. Land Use Policy 97:104772
Karimi A, Jones K (2020) Assessing national human footprint and implications for biodiversity conservation in Iran[J]. Ambio 49(9):1506–1518
Li Y, Li M, Li C, Liu Z (2020) Optimized Maxent model predictions of climate change impacts on the suitable distribution of Cunninghamia lanceolata in China. Forests 11(3):302
Li J, Chen X, Kurban A, Van de Voorde T, De Maeyer P, Zhang C (2021a) Coupled SSPs-RCPs scenarios to project the future dynamic variations of water-soil-carbon-biodiversity services in Central Asia. Ecol Indic 129:107936
Li M, Zhou Y, **ao P, Tian Y, Huang H, **ao L (2021b) Evolution of habitat quality and its topographic gradient effect in Northwest Hubei Province from 2000 to 2020 based on the invest model. Land 10(8):857
Li Y, Duo L, Zhang M, Wu Z, Guan Y (2021c) Assessment and estimation of the spatial and temporal evolution of landscape patterns and their impact on habitat quality in Nanchang, China. Land 10(10):1073
Liang X, Guan Q, Clarke KC, Liu S, Wang B, Yao Y (2021) Understanding the drivers of sustainable land expansion using a patch-generating land use simulation (PLUS) model: a case study in Wuhan, China. Comput Environ Urban Syst 85:101569
McGoff E, Irvine K (2009) A test of the association between lake habitat quality assessment and macroinvertebrate community structure. Aquat Conserv Mar Freshwat Ecosyst 19(5):520–533
Murakami D, Yoshida T, Yamagata Y (2021) Gridded GDP projections compatible with the five SSPs (shared socioeconomic pathways). Front Built Environ 7:760306
Nematollahi S, Fakheran S, Kienast F, Jafari A (2020) Application of InVEST habitat quality module in spatially vulnerability assessment of natural habitats (case study: Chaharmahal and Bakhtiari province, Iran). Environ Monit Assess 192(8):1–17
Pham HV, Sperotto A, Torresan S, Acuña V, Jorda-Capdevila D, Rianna G et al (2019) Coupling scenarios of climate and land-use change with assessments of potential ecosystem services at the river basin scale. Ecosyst Serv 40:101045
Rimal B, Zhang L, Keshtkar H, Haack BN, Rijal S, Zhang P (2018) Land use/land cover dynamics and modeling of urban land expansion by the integration of cellular automata and markov chain. ISPRS Int J Geo Inf 7(4):154
Sallustio L, De Toni A, Strollo A, Di Febbraro M, Gissi E, Casella L et al (2017) Assessing habitat quality in relation to the spatial distribution of protected areas in Italy. J Environ Manage 201:129–137
Su B, Huang J, Mondal SK, Zhai J, Wang Y, Wen S et al (2021) Insight from CMIP6 SSP-RCP scenarios for future drought characteristics in China. Atmos Res 250:105375
Sun Y, Cai J, Li T, Zhang L, Lei L, Song X (2023) Temporal and spatial pattern evolution and prediction analysis of habitat quality in Hangzhou based on InVEST and PLUS models. Journal of Guizhou Normal University (Natural Science Edition) 1–11
Tang F, Fu M, Wang L, Zhang P (2020) Land-use change in Changli County, China: predicting its spatio-temporal evolution in habitat quality. Ecol Indic 117:106719
Tian L, Tao Y, Fu W, Li T, Ren F, Li M (2022) Dynamic simulation of land use/cover change and assessment of forest ecosystem carbon storage under climate change scenarios in Guangdong Province, China. Remote Sensing 14(10):2330
Tonra CM, Marra PP, Holberton RL (2011) Migration phenology and winter habitat quality are related to circulating androgen in a long-distance migratory bird. J Avian Biol 42(5):397–404
Van der Lee GE, Van der Molen DT, Van den Boogaard HF, Van der Klis H (2006) Uncertainty analysis of a spatial habitat suitability model and implications for ecological management of water bodies. Landsc Ecol 21(7):1019–1032
Wang Y, Yu X, He K, Li Q, Zhang Y, Song S (2011) Dynamic simulation of land use change in Jihe watershed based on CA-Markov model. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering 27(12):330–336
Wang Y, Fu BT, Lyu YP, Yang K, Che Y (2016) Assessment of the social values of ecosystem services based on SolVES model: a case study of Wusong Paotaiwan Wetland Forest Park, Shanghai, China. Ying Yong Sheng tai xue bao= The. J Appl Ecol 27(6):1767–1774
Wang Z, Li X, Mao Y, Li L, Wang X, Lin Q (2022) Dynamic simulation of land use change and assessment of carbon storage based on climate change scenarios at the city level: a case study of Bortala. China Ecological Indicators 134:108499
Wu L, Sun C, Fan F (2021) Estimating the characteristic spatiotemporal variation in habitat quality using the invest model—a case study from Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area. Remote Sens (Basel) 13(5):1008
Wu J, Luo J, Zhang H, Qin S, Yu M (2022) Projections of land use change and habitat quality assessment by coupling climate change and development patterns. Sci Total Environ 847:157491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157491
Zhao B, Li S, Liu Z (2022) Multi-scenario simulation and prediction of regional habitat quality based on a system dynamic and patch-generating land-use simulation coupling model—a case study of Jilin Province. Sustainability 14(9):5303
Zhang H, Li S, Liu Y, Xu M (2022a) Assessment of the habitat quality of offshore area in Tongzhou Bay, China: using benthic habitat suitability and the InVEST model. Water 14(10):1574
Zhang S, Zhong Q, Cheng D, Xu C, Chang Y, Lin Y, Li B (2022b) Coupling coordination analysis and prediction of landscape ecological risks and ecosystem services in the Min River Basin. Land 11(2):222
Zhang S, Zhong Q, Cheng D, Xu C, Chang Y, Lin Y, Li B (2022c) Landscape ecological risk projection based on the PLUS model under the localized shared socioeconomic pathways in the Fujian Delta region. Ecol Indic 136:108642
Zhang X, Liao L, Xu Z, Zhang J, Chi M, Lan S, Gan Q (2022d) Interactive effects on habitat quality using InVEST and GeoDetector models in Wenzhou, China. Land 11(5):630
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 52168010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Chen Zhuan: data curation, conceptualization, writing—original draft preparation, methodology, software, formal analysis, writing—reviewing and editing. Chen Yasi: data curation, conceptualization, writing—original draft preparation, formal analysis. Liu Ziqiang: methodology, software, writing—reviewing and editing. Wei **: software, writing—reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Za., Chen, Y., Liu, Z. et al. Dynamic simulation of land use change and habitat quality assessment under climate change scenarios in Nanchang, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 31, 2569–2582 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31304-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31304-y